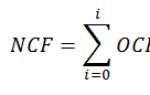Presentation of the 8th class, the main issues of the economy. Presentation on the topic: "The main issues of the economy
In this lesson, we will find out what are the main questions in economics, why it exists and how it tries to answer these main questions. We will also talk about economic efficiency and economic choice. We will try to show how the economy enters the life of every person.
Topic: Economics
Lesson: Basic Questions of Economics
In the last lesson, we talked about the fact that resources are very limited, and the economy, in fact, is called upon to decide how to use these resources to the maximum benefit for humanity. All participants economic processes one way or another, they are in a state of choice: they choose which of the resources to use now, and which to use later, which goods to produce, etc. Accordingly, the economy arises three main questions to which she must respond: "What to produce?", "How to produce?" and "For whom to produce?"... The answer to these three questions is the answer to the main task of economic processes. Let's talk about each of them separately.
Rice. 1. Basic questions of economics ()
So the first question is - "What goods to produce?" It is clear that a person is a being who, living in a social environment, largely serves himself. Primitive people, of course, served themselves on their own. So, the primitive hunter made the items he needed for hunting: a spear, a bow and other things he needed. And in our time, each of us can do some things for ourselves on our own, or can get these things in a different way. They can give you something, something can be inherited, and you can buy something on the market. Thus, you create your life the way you want it to be. You can become an absolutely satisfied person, all your needs and desires can be realized, but society, alas, cannot live like this because of our limited resources.
That is why all manufacturers (they can be the state, private firms, even private individuals) are in a situation of constant choice which of the products they need to produce. It depends on what exactly will be in demand in the near future. Over time, the demand for certain goods changes. A century or two ago, some things were absolutely necessary, but now the need for them has disappeared, among other things, they have become archaic. An example of such a thing is bast shoes.
In a situation of choice, manufacturers strive not only to gain momentary benefits, but also to lay the foundations for their future production. They strive to increase their profits in the future, anticipating the needs of society that may arise.
Of course, it is very profitable for all manufacturers to produce those services or goods that cannot be refused. After all, a person cannot refuse food or clothing. But the essence of the economy lies in the presence of competition, in the confrontation between different manufacturers, so that the consumer has the opportunity to choose whether to buy at a lower price or to buy at a higher price. By the way, it should be explained why things are generally cheaper or more expensive. This is because the manufacturer always decides how to produce the goods.
Rice. 3. The essence of the economy is competition between manufacturers ()
So we come to the second question - "How to produce goods and services?"... There are always a variety of ways and opportunities to produce the same product or service. The way it is made, the decisions that manufacturers make in the course of manufacturing the goods, depend on what the final product will be like. One way or another, any manufacturer makes sure that his solutions are the most effective. And under economic efficiency understand the product of a given volume of a finished product at the lowest cost of limited resources. Having understood this relationship, we can understand why this or that product has such a price. The manufacturer always seeks to reduce the cost of its production, but in no case wants to reduce its profits. This is the basis of any production, on this balance there is an economics of production.
However, there is also a third question, which we have outlined today - "For whom to produce goods and services?"... It is clear that we all have different desires, we have different possibilities. By producing any product, the manufacturer seeks to please the interests of the broad masses of the population. But it is simply impossible to do this with the help of any one service or product. That is why each of the manufacturers strives to either narrowly specialize or produce a wide range of goods and services for various social strata. It does not matter if it is a physical product or a service that has no physical expression, because it also has a value and brings profit to the manufacturer.
So, in order to obtain correct answers to the main questions of the economy, it is necessary to know the capabilities of the economic system, the state of the market, the factors of formation of demand and supply.
As you can see, three main economic issues put human society in a state of choice. One way or another, we have to choose where to produce, how to produce, what to produce, for whom to produce. This question is painful every time, because for some time the production of some things and services can be profitable, but then it ceases to be so. It should be understood that almost every day manufacturers are in limbo, because it is very difficult to determine the exact priorities of a person. There is a possibility that our outlook on life will change and the need for an item or service will disappear. You can give a lot of examples in the history of mankind, when some important and interesting things that a person used, eventually came to naught. This is life, this is the economy.
Consider why the quality of the goods produced is different. One and the same thing on the market can have completely different cost depending on its quality. Let's take pens as an example. This is a common everyday object that you are familiar with. But even it can cost completely differently. You can buy a simple and inexpensive ballpoint pen that you will use every day, or you can buy a very expensive gift pen for special occasions. But, nevertheless, it is still the same pen, writing instrument.
Rice. 4. Simple or gift, - the pen is just a writing instrument ()
So where does this price difference come from? It's about human interests and desires. The manufacturer initially focuses on a specific customer. People's tastes are varied: some have more craving for luxury and a desire to surround themselves with expensive items, while other people just need to have simple and multifunctional items at hand. From the point of view of the manufacturer, it is a person with a craving for luxury, unusual things who is the buyer who is willing to pay large amount for the same item. The most expensive items and services are focused on it. For example, a watch can be simple in design, or it can become a complex elite item that has a lot of additional functions and indicates the high social status of its owner. The need for them is very conditional, but the owner of such watches is proud that he has them.
Rice. 5. An expensive watch is more of a luxury than a necessity, but the owner is proud to own it ()
We all surround ourselves with the things and objects that we need. This is how we build our own life. This is how the economy enters the life of every person.
Bibliography
1. Kravchenko A.I. Social Science 8. - M .: Russian word.
2. Nikitin A.F. Social Science 8. - M .: Bustard.
3. Bogolyubov L.N., Gorodetskaya N.I., Ivanova L.F. / Ed. Bogolyubova L.N., Ivanova L.F. Social Science 8. - M .: Education.
3. Site for professional traders ().
Homework
1. Explain what is economic efficiency.
2. Describe three main economic issues.
3. * Imagine that you have been inherited the right to own a chain of confectionery factories. Answer the main economic issues: what exactly you will produce, how and for whom.
8 cl. social studies "MAIN ISSUES OF ECONOMY" Purpose: to bring students to an understanding of the main problem of economics, limited resources and infinity
human needs; to acquaint with the principles of work
market, economic system and its functions.
Continue the formation of skills to analyze, do
conclusions, work with the text, establish causal relationships.
English writer George Bernard Shaw
(1856-1950) - claimed:
“Economics is the ability to use
life in the best way "
Topic: MAIN QUESTIONS OF ECONOMY Any society, regardless of the level of welfare, should be able to determine what goods, how and for whom
Topic: MAIN QUESTIONS OF ECONOMYAny society, regardless of the level of welfare, must
be able to determine what goods, how and for whom to produce.
1. WHAT TO PRODUCE?
Organizations, enterprises, firms, taking into account the demand
consumer, limited resources, constantly
make decisions about what goods and services should
be produced using available in their
disposal of resources.
.
2. HOW TO PRODUCE?1. There is a choice:
-Economic resources
- Technologies
-Location of the enterprise
- Use of financial, technical costs
- Labor resources
.
1. The economic efficiency is considered, i.e.economic calculation is performed how to perform
volume of production at the lowest cost. For
the manufacturer uses the following methods:
- introduction and use of new technologies;
- economical and careful use of resources;
- attraction of highly qualified workers;
CONCLUSION: manufacturers should
solve:
what technologies, from
what resources and who should
be produced good as
should be organized
production.
.
3. FOR WHOM TO PRODUCE THE PRODUCT?The manufacturer takes into account
needs for goods and
services different groups
population with different
income and decides for whom
produce: for the rich
(luxury goods), for
mass consumer
(goods of everyday
demand), for the poor
(cheap products).
Through choice
the problem is being solved
distribution
economic benefits.
.
ECONOMIC SYSTEM AND ITS FUNCTIONSThere are several options for organizing
economic life, i.e. it is ECONOMIC
SYSTEM - a set of organizational methods
harmonization of the economic activities of people for
addressing issues: what, how and for whom to produce.
.
TYPES OF ECONOMIC SYSTEMS1. TRADITIONAL
Based on the use of manual labor, community
housekeeping, natural exchange. The main
economic issues are resolved in accordance with
traditions and customs (to do everything as before).
The leading industry belongs to agriculture.
Currently traditional economy survived
in Central Africa, South and Southeast Asia
.
2. TEAM (PLANNED)The state is the owner of all
economic and natural resources... State
controls and regulates production and
distribution of basic goods. The main
economic decisions are made by the state. What
how and for whom the state plans to produce from
a single center based on orders, laws,
planned assignments. Manufacturers turned into
executors of other people's orders. Such
the economic system was in the USSR and others
socialist countries. Main role
belongs to the manufacturing industry
(industry)
Currently, such an economy is present in
North Korea, Cuba
.
3. MARKET ECONOMYMarket - aggregate economic relations,
manifested in the field of exchange and transactions
The market economy is based on private
property, entrepreneurship, competition,
free pricing. Each manufacturer
independently takes economic solutions v
in accordance with their own interests and
needs: what to produce, how to produce, for
whom to produce. In a free market
economy, the rule is that demand creates
sentence.
D.Z. § 12, detailed synopsis
4. MIXED ECONOMYModern economy - plays an active role and
market and state. Various shapes are used
state regulation... Private
property and state interact.
For example in good developed countries USA, Japan.
CONCLUSION: the economic system promotes
solving the problem effective use
limited resources. The main task is to bring in
matching limitless needs and
limited opportunities for members of society through
solution of questions: what, how and for whom to produce?
D.Z. § 12, detailed synopsis
To use the preview of presentations, create yourself an account ( account) Google and log into it: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
The main issues of economics
ECONOMIC SYSTEM AND ITS FUNCTIONS. Traditional system economy. Command economy. Market system economy.
Review: 1. How does the economy depend on the volume and focus of our needs? 2. Where do people get the benefits of life? 3. Why can't the planet's natural resources be considered inexhaustible? 4. What is the complexity of the economic choice? 5. What is opportunity cost? 6. How do you determine the opportunity cost of choice?
The limited economic resources on the planet give rise to the need for man to solve the problem of their rational use and distribution.
Any society, regardless of the level of welfare, must be able to determine what goods, how and for whom to produce. These three questions of the organization of the economy are decisive for the development of society.
Economic system and its functions
Society answers these questions in a variety of ways. The way society answers these questions is its economic system. An economic system is a way of organizing the economic activity of people. Basis of the housekeeper Basis of the housekeeper Basis of the housekeeper Basis of the housekeeper
According to tradition Traditional economic system HOW? WHO? With such an economic system, experience, traditions, customs determine practical use natural resources. The traditional system of the economy is based on the widespread use of manual labor, backward technology, communal farming, and natural exchange. Such an economic system is capable of satisfying only the minimum, vital needs of people. WHAT?
AS? WHAT? WHO? Command economy According to directive plans This system is based on state ownership and centralized management methods. The state owns and disposes of the most important natural and capital resources. These resources are allocated using plans that dictate what, how, and how much to produce. For all business entities, these plans are binding. Was in the USSR
"+" And "-" command economy More sustainable More confidence in the future Less inequality in society Practically no problem of employment No economic incentives to work Inefficiency Dictate of producers over consumers Low living standards of the population
market Using a market mechanism HOW? WHO? The market system is characterized by the domination of private property, the extensive development of exchange relations carried out with the help of money. In this economic system, the decision of the questions of what to produce and for whom is the result of the interaction of buyers and sellers in the market. In the economic sense, the market is a set of economic relations that manifest themselves in the field of exchange, as well as the conditions due to which buyers and sellers find each other and can make transactions. Price is the organizer and coordinator in the market economy. WHAT?
In a market economy, the consumer makes a purchase decision, guided by the desire to get more benefit from the consumption of the product. A manufacturer, deciding to produce this or that product, expects to make a profit. Therefore, the question "what to produce?" in a market economy there is one answer: only those goods that can bring profit will be produced, and those goods whose production entails losses will not be produced.
"+" And "-" market economy High entrepreneurial spirit and efficiency Distribution of income by work More rights and opportunities for consumers Does not require a large management apparatus Increases inequality Unstable Does not care about creating necessary, but non-profitable goods for society Indifference to the damage caused by business to nature
The purchase by consumers of the manufactured product depends on the value of their cash income and prices for goods and services. The more the consumer's income, the more of the product he will be able to purchase. The lower the price of a product, the more it is consumed, and vice versa. It is the prices that are freely formed in the process of buying and selling that give the answer to the questions: what, how and for whom to produce?
The modern economies of most countries are mixed. It is based on the market, but at the same time various forms of government regulation, private property and state property interact. Mixed economy- a modern economy in which both the market and the state play an active role.
1. How to solve the contradiction between limited resources and the growing needs of people? 2. What is cost effectiveness? 3. What is the difference in the ways of coordinating economic choices in different economic systems? 4. What are the features of the functioning of the main economic systems?
Homework: par. No. 12, table to paragraph.
"MAIN ISSUES OF THE ECONOMY" Grade 8 "Social Studies" ed. Bogolyubova L.N.

8 cl. social science "MAIN ISSUES OF THE ECONOMY" Target: to bring students to an understanding of the main problem of the economy, limited resources and the limitlessness of human needs; to acquaint with the principles of the market, the economic system and its functions. Continue the formation of skills to analyze, draw conclusions, work with text, establish cause-and-effect relationships. English writer George Bernard Shaw (1856-1950) - claimed: “Economics is the ability to use life in the best way "

Topic: MAIN QUESTIONS OF ECONOMY Any society, regardless of the level of welfare, must be able to determine what goods, how and for whom to produce.
1. WHAT TO PRODUCE?
Organizations, enterprises, firms, taking into account consumer demand, limited resources, constantly make decisions about what goods and services should be produced using the resources at their disposal.

2. HOW TO PRODUCE?
1. There is a choice:
- Economic resources
- Technologies
- Location of the enterprise
- Use of financial, technical costs
- Labor resources

1. The economic efficiency is considered, i.e. an economic calculation is performed on how to fulfill the volume of production at the lowest cost. For the manufacturer uses the following methods:
- introduction and use of new technologies;
- economical and careful use of resources;
- attraction of highly qualified workers;
CONCLUSION: Manufacturers must decide:
with the help of what technologies, from what resources and by whom the goods should be produced, how the production should be organized.

3. FOR WHOM TO PRODUCE THE PRODUCT?
The manufacturer takes into account the needs for goods and services of various groups of the population with different income and decides for whom to produce: for the rich (luxury goods), for the mass consumer (consumer goods), for the poor (cheap goods). The problem of distribution of economic benefits is solved through the choice.

ECONOMIC SYSTEM AND ITS FUNCTIONS
There are several options for organizing economic life, i.e. it is an ECONOMIC SYSTEM - a set of organizational ways of coordinating the economic activities of people to address issues: what, how and for whom to produce.

TYPES OF ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
1. TRADITIONAL
Based on the use of manual labor, community farming, exchange in kind. The main economic issues are resolved in accordance with traditions and customs (to do everything as before). The leading industry belongs to agriculture.
Currently, the traditional economy is preserved in Central Africa, South and Southeast Asia

2. TEAM (PLANNED)
The state is the owner of all economic and natural resources. The state controls and regulates the production and distribution of basic goods. The main economic decisions are made by the state. What, how and for whom, the state plans to produce from a single center on the basis of orders, laws, and planning targets. Producers turned into executors of other people's orders. Such an economic system existed in the USSR and other socialist countries. The leading role belongs to the manufacturing industry (industry)
Currently, such an economy is present in North Korea, Cuba.

3. MARKET ECONOMY
Market - a set of economic relations manifested in the field of exchange and transactions
The market economy is based on private property, entrepreneurship, competition, free pricing. Each manufacturer independently makes economic decisions in accordance with their own interests and needs: what to produce, how to produce, for whom to produce. In a free market economy, the rule is that demand creates supply.

4. MIXED ECONOMY
Modern economy - both the market and the state play an active role. Various forms of government regulation are used. Private property and state property interact. For example, in the well-developed countries of the USA, Japan.
D.Z. § 12, p. 99 questions, task 1, repeat § 11.
CONCLUSION: the economic system contributes to solving the problem of efficient use of limited resources. The main task is to bring into line the unlimited needs and limited opportunities of members of society by solving the questions: what, how and for whom to produce?

Used material: 1. "Social Studies" 8 cl. textbook ed. Bogolyubova L.N. Ed. Education, 2011 2. Internet resource narod.ru
MAIN QUESTIONS OF ECONOMY. PRESENTATION ON SOCIETY. 8TH GRADE. A BASIC LEVEL OF.
WHAT WE SHOULD FIND OUT. DO I NEED TO REGULATE PRODUCTION? WHAT TO PRODUCE ?. HOW TO PRODUCE? FOR WHOM TO PRODUCE THE PRODUCT? ECONOMIC SYSTEM AND ITS FUNCTIONS TYPES OF ECONOMIC SYSTEMS TYPES OF ECONOMIC SYSTEMS. JOBS AT HOME ..

CONCEPTS AND TERMS. COSTS, PROFIT, ECONOMIC EFFICIENCY, TECHNOLOGIES, ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: TRADITIONAL, CENTRALIZED (COMMAND), MARKET, MIXED, ECONOMIC SYSTEM FUNCTIONS, STATE WORK STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM WE KNOW .. THAT RESOURCES ON THE PLANET ………………. LIMITED FREE AND ECONOMIC GOODS ARE LIMITED ………. WHAT SHOULD HUMAN BE DO? HOW TO RATIONAL USE THE AVAILABLE RESOURCES ..

LET'S REPEAT THE NEED FOR WHAT IS NECESSARY. NEEDS. PRIMARY NEEDS WATER, FOOD AIR, REST .. ACQUIRED NEEDS COMMUNICATION .. HIGHER NEED FOR SELF-REALIZATION.

LET'S REPEAT AUXILIARY TOOL RESOURCES. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN RESOURCES AND NEEDS. LIMITED RESOURCES AND INCREASING DEMANDS NATURAL BENEFITS OF WATER, AIR .. ASSESSMENT OF LOST BENEFITS, PAYMENT FOR THE DECISION TAKEN. ALTERNATIVE COST. WATER. WIND ENERGY. RAIN, SEWING CLOTHES, ICE CREAM, EXERCISE IN THEATER CIRCLE, APARTMENT REPAIR, BUS RUNNING, STREET LIGHTING. FREE GOODS ECONOMIC GOODS THE ECONOMY IS …………………………. GET THE BEST OF LIFE …………………………. SKILL IN THE IMAGE

DO I NEED TO REGULATE PRODUCTION? THE ENERGIZATION OF RESOURCES DEMANDS A HUMAN SOLUTION OF THE PROBLEM OF THEIR RATIONAL USE AND DISTRIBUTION OF HOUSEHOLDS. FIRMS OF THE STATE PROBLEM OF CHOICE THREE QUESTIONS: WHAT PRODUCTS TO PRODUCE.? HOW TO PRODUCE.? FOR WHOM TO PRODUCE?

WHAT TO PRODUCE ?. HOW TO PRODUCE? FOR WHOM TO PRODUCE THE PRODUCT? WHAT TO PRODUCE? SOCIETY AS A WHOLE CANNOT INCREASE THE PRODUCTION OF GOODS AND SERVICES. BEFORE IT IS A CHOICE: WHAT SHOULD GET IMMEDIATELY AND WHAT TO REFUSE. FIRMS, ENTREPRENEURS ARE CONSTANTLY MAKING DECISIONS WHICH PRODUCTS SHOULD BE PRODUCED BASED ON THE AVAILABLE RESOURCES THE ESSENCE OF THE PROBLEM: RESOURCES ARE LIMITED AND THE ECONOMY CANNOT SUPPLY AND UNDERSTAND. THEREFORE, SOME GOODS AND SERVICES SHOULD REFUSE .. HOW TO PRODUCE ... THE SOLUTION OF THIS ISSUE IS CONNECTED WITH THE CHOICE OF ECONOMIC RESOURCES, TECHNOLOGIES, LOCATION OF ENTERPRISES. FROM ALL THE OPTIONS IT IS NECESSARY TO CHOOSE THE MOST EFFECTIVE. (ONE IS COSTS, THE OTHER DEMANDS LABOR RESOURCES, THE THIRD - NEW TECHNOLOGIES.) FIRST PLAN: ECONOMIC EFFICIENCY: RECEIVING THE VOLUME OF PRODUCTS WITH THE LOWEST COSTS. WHAT SHOULD BE DONE: 1. IMPLEMENTATION OF TECHNOLOGY, 2. ECONOMY, 3. QUALIFICATION OF EMPLOYEES, 4. DIVISION OF LABOR. SOCIETY AS A WHOLE SOLVES THE QUESTION: BY WHOM, FROM WHAT RESOURCES GOOD SHOULD BE PRODUCED. WHAT SHOULD BE PRODUCTION FOR WHOM THE PRODUCT IS PRODUCED .. WHO CAN PURCHASE THE GOODS AND HOW IS THE DISTRIBUTION. SOCIETY IS NOT IN A STATE TO PROVIDE EVERYONE AND THEREFORE ORIENTS THE MANUFACTURER TO A SPECIFIC CONSUMER OF WELLS. TAKE INTO ACCOUNT THE NEEDS OF DIFFERENT GROUPS WITH DIFFERENT INCOME: TO WHOM THE GOLDEN WATCHES ... AND TO WHOM THE EASY ...


TYPES OF ECONOMIC SYSTEMS. o Land and capital are in common ownership o Continuity, adherence to tradition is valued o Subsistence economy dominates Underdeveloped exchange Lack of technical progress Weak production potential Limited production material wealth TRADITIONAL ECONOMY MARKET ECONOMY + Allocates resources to the production of necessary goods + Encourages rational and efficient activities + Quickly responds to the needs of society + Uses the achievements of scientific and technological revolution Does not contribute to the conservation of resources Does not stimulate large projects that do not provide quick benefits Does not provide basic research in science Development is unstable with recessions and inflation. Unemployment and increased economic differentiation of society are possible. TEAM ECONOMY. + Development without economic crises +Low prices+ Lack of unemployment + Guaranteed earnings Weak motivation for activity Formation of the psychology of dependence Deficiency of goods Poor quality of products Waste attitude to resources ALL ECONOMIC RESOURCES IN THE HANDS OF THE STATE, STATE PROPERTY, PLANNING, DISTRIBUTION AND CONSUMPTION. MIXED ECONOMY. MIXED ECONOMY - AN ACTIVE ROLE OF THE STATE AND THE MARKET ECONOMY. stabilization of the economy protection of property rights regulation money circulation support for basic science redistribution of income regulation of relations between employers and employees control over foreign economic activity AND SO, HOW DO WE ANSWER THE PROBLEM STATED AT THE BEGINNING OF THE LESSON .. WHAT SHOULD A HUMAN BE DO IN CONDITIONS OF LIMITED RESOURCES? PAGE 99 ..

IN CLASS AND AT HOME. 1. TEXT OF THE EDUCATIONAL MANUAL. C 92 - TABLE P.100. TASK. 3. WRITTEN. 3. CHOOSE A QUESTION ON WITH AND ANSWER IN THE BLOG OR ON THE FORUM Diary - Personal site Smirnova Evgenia BorisDnevnik - Personal site Smirnova Evgenia Boris