Terms of payment of dividends. Personal income tax dividend tax, accrual, postings, kbk
1. Quarterly in the organization (USN 6%), dividends are accrued to the founder-director of the LLC. How to compose correctly? I make DT 84 CT 75.2 (profit allocated to the payment of dividends), DT 75 CT 70 (dividends accrued to the employee) DT 70 CT 68 (personal income tax accrued). Questions: 1. What are the sub-accounts for these accounts? 2. Account 84 does not close (be sure to specify a subaccount). Express check shows negative balance on account 84. Be sure to specify sub-accounts. In addition to the question. Dividends are both accrued and paid.
Answer
In this situation, when calculating interim dividends, this operation is reflected in the debit of account 84. At the same time, the chart of accounts does not provide for the creation of sub-accounts for this account. That is, accrued dividends are accounted for in the debit of account 84. Thus, before the reformation of the balance sheet (when the financial result is written off to account 84), the organization has a loss. It should not be closed, therefore, in this situation, such a reflection is allowed.
Please note that. Account for assets under the new rules. Read the details in the magazine
The rationale for this position is given below in the materials of the Glavbukh System (as amended for commercial organizations)
Additional articles about the calculation of dividends
1. Recommendation: How reflect v accounting and at taxationaccrual and payment of surprises
accounting
To reflect the calculations for the payment of dividends in accounting, use:
- separate sub-account 75-2 “Settlements with the founders for the payment of income”;
- account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”.
Use a separate subaccount to account 75 for settlements with founding organizations and with founding citizens who are not on the staff of the organization (that is, with those with whom an employment contract has not been concluded). When accruing dividends to the founders - employees of the organization, use account 70. These are the requirements of the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts and).
In accounting, the accrual of dividends both at the end of the year and at the end of the reporting period (quarter, six months, nine months) reflect one of the following entries:
Debit 84 Credit 75-2
- dividends are accrued to an organization or to a person who is not an employee of the organization;
Debit 84 Credit 70
- dividends were accrued to a person who is an employee of the organization. *
Make these entries on the day when the total ().
An example of the reflection in accounting of dividends accrued to people
At the end of 2013, CJSC Alfa received a net profit of 266,000 rubles. On March 5, 2014, the general meeting of shareholders decided to allocate this amount for the payment of dividends.
The authorized capital of the company is divided into 100 ordinary shares. Of these, 60 shares belong to the director of Alfa A.V. Lvov, and 40 shares - to an Iraqi citizen R. Smith (not an employee of Alfa).
Debit 84 Credit 70
Debit 84 Credit 75-2
- 106,400 rubles. (266,000 rubles: 100 shares × 40 shares) - dividends were accrued to Smith.
Withholding tax on dividends in accounting reflect one of the following entries:
- personal income tax withheld from the income of a person who is not an employee of the organization;
- withheld personal income tax from the income of a person who is an employee of the organization; *
Debit 75-2 Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for tax at a profit"
- Income tax withheld from the income of the organization.
An example of the reflection in accounting of personal income tax from dividends accrued to people
At the end of 2013, CJSC Alfa received a net profit of 266,000 rubles. Income from equity participation in other organizations, "Alpha" did not receive.
On March 5, 2014, the general meeting of shareholders decided to allocate all profits (266,000 rubles) to the payment of dividends. The authorized capital of the company is divided into 100 ordinary shares. Of these, 60 shares belong to the director of the organization A.V. Lvov, 40 shares - to an Iraqi citizen R. Smith (not a Russian and an employee of Alfa).
Dividends were paid to the founders on March 26, 2014. Lvov received dividends in the organization's cash desk, and Smith received them in his bank account.
Alfa's accountant made such entries in the accounting.
Debit 84 Credit 70
- 159,600 rubles. (266,000 rubles: 100 shares × 60 shares) - dividends were accrued to Lvov;
Debit 84 Credit 75-2
- 106,400 rubles. (266,000 rubles: 100 shares × 40 shares) - dividends accrued to Smith.*
Debit 70 Credit 68 subaccount "Calculations for personal income tax"
- 14 364 rubles. (159,600 rubles × 9%) - personal income tax was withheld from the income of Lviv;
Debit 75-2 Credit 68 sub-account "Calculations for personal income tax"
- 15 960 rubles. (106,400 rubles × 15%) - personal income tax withheld from Smith's income (Russia and Iraq do not have an agreement on the avoidance of double taxation on personal income tax);*
Debit 70 Credit 50
- 145,236 rubles. (159,600 rubles - 14,364 rubles) - dividends were paid to Lvov;
Debit 75-2 Credit 51
- 90 440 rubles. (106,400 rubles - 15,960 rubles) - dividends were transferred to Smith.*
Latest news on USN:
2. Article: What can you spend money on this year? accounts84 "Undestributed profits"
Dividends
Dividends in JSCs and income from participation in LLCs are always paid at the expense of retained earnings companies ( , ). That is, dividends reduce the balance of retained earnings by.
What is often wrong. Reflect annual or interim dividends on the account, not . And in tax accounting, dividends are included in expenses.*
How to reflect in accounting. Accrual and payment of dividends are events that occurred after the reporting date. This means that they must be taken into account according to special rules. When accruing and paying dividends for 2013, postings must be made in 2014. That is, when the accrual and issuance of money actually occur ().
Carefully!
Do not forget to withhold personal income tax from dividends at a rate of 9 percent (15% for non-residents). Otherwise, you may be fined tax code RF.
Accrued dividends reflect on the debit and credit of the sub-account "Calculations for the payment of income". Such wiring is directly provided for in the accounting.
Example 1: At the end of the year, the accounting department accrued and paid income to the owners of the company
In March 2014, the owners of Vega LLC held a general meeting based on the results previous year. Ivanov I.M. and Petrov A.I. (owners of the company) decided to allocate a part of retained earnings, reflected in , to the payment of income from participation. The total amount of net profit for distribution amounted to 580,000 rubles. Ivanov and Petrov prescribed in the decision general meeting of participants dated March 5, 2014 to calculate the income from participation in proportion to the shares of the founders. Ivanov's share is 70 percent, while Petrov's is 30 percent.
The accountant of Vega LLC calculated the amount of income for each participant. Ivanov's income amounted to 406,000 rubles. (580,000 rubles × 70%). And Petrov's income is 174,000 rubles. (580,000 rubles × 30%).
The accountant made entries on the accrual and payment of income based on the accounting statement. A sample reference can be found below.
And here are the wiring:
Debit 84
- 406,000 rubles. - Ivanov's income was accrued;
Debit 84Loan 75 sub-account "Calculations for the payment of income"
— 174,000 rubles. - Petrov's income was accrued.
— 36,540 rubles. (406,000 rubles × 9%) - personal income tax withheld from Ivanov's income;
Debit 75 subaccount "Calculations for the payment of income" Credit 68 subaccount "Calculations for personal income tax"
— 15 660 rubles. (174,000 rubles × 9%) - personal income tax was withheld from Petrov's income;
— 369,460 rubles. (406,000 - 36,540) — dividends were paid to Ivanov;
Debit 75 subaccount "Calculations for the payment of income" Credit 51
— 158 340 rubles. (174,000 - 15,660) — dividends were paid to Petrov.*
By the way, interim dividends (distribution of LLC profits) must be reflected in the same postings. Moreover, interim dividends accrued for the 1st quarter, half a year or 9 months will affect retained earnings in 2014.*
3. ORDER OF THE MINISTRY OF FINANCE OF RUSSIA dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n
On approval of the Chart of Accounts for financial accounting economic activity organizations and instructions for its use (as amended on November 8, 2010)
Account 84 "Retained earnings
(uncovered loss)"
Account 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" is intended to summarize information on the presence and movement of amounts of retained earnings or uncovered loss organizations.*
The amount of net profit of the reporting year is debited by the closing turnovers of December to the credit of account 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" in correspondence with "Profits and losses". The amount of the net loss of the reporting year is debited by the closing turnovers of December to the debit of account 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" in correspondence with "Profits and losses".
Direction of part of the profit of the reporting year to the payment of income to the founders (participants) of the organization following the approval of the annual financial statements reflected in the debit of account 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" and the credit "Settlements with the founders" and "Settlements with personnel for wages". A similar entry is made in the payment of intermediate income.
The write-off from the balance sheet of the loss of the reporting year is reflected in the credit of account 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" in correspondence with the accounts: "Authorized capital" - when the amount of the authorized capital is brought to the value net assets organizations; "Reserve capital" - when funds are directed to pay off the loss reserve capital; "Settlements with the founders" - when paying off the loss of a simple partnership at the expense of targeted contributions from its participants, etc. *
Analytical accounting on account 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" is organized in such a way as to ensure the formation of information on the areas of use of funds. At the same time, in analytical accounting, retained earnings used as financial support production development of the organization and other similar activities for the acquisition (creation) of new property and not yet used, can be divided.
|
Account 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" | |||
Director
Dividends are any income received by a shareholder or participant from an organization in the distribution of profit remaining after tax on shares owned by this participant, in proportion to the participants' shares in the authorized capital of the paid organization (1 clause 43 of Article TC).
Important: Dividends are part of the net profit left after paying all taxes. If we are talking about the general taxation regime, then this is the net profit that remains after paying income tax. If we are talking about the simplified tax system, then this is the profit remaining after paying taxes on the simplified tax system. If this is UTII, then this is the net profit that remains after paying a single tax on imputed income.
How is profit calculated?
Net profit is the profit left after paying all taxes. All expenses are deducted from all income of the enterprise, the financial result is obtained and profit remains, it is the basis for calculating the tax. The amount of tax that must be transferred is determined, and the tax itself is deducted from the profit based on the results of activities. There remains a cleared amount that is at the disposal of the company, and the company has the right to dispose of the net profit at its discretion.
Where is the net profit indicator recorded in the financial statements?
- In section 3 of the balance sheet “Capital reserves”, profit appears on the line “retained earnings” or “uncovered loss”. V balance sheet displays all profits as of a certain accounting date. This line takes into account the amount of net profit not only for the last reporting period, but also for past years, if it remained and was not distributed at one time.
- If you need to find out the amount of net profit for the reporting period, then refer to the income statement. Here, the net profit indicator for the reporting period (for example, for the reporting year) is shown on the line “Net profit or loss”.
If the company does not have a net profit, then there can be no talk of paying dividends until the loss received by the company is covered by the profit received in subsequent periods.
What if errors were made in calculating profit?
For accounting and tax legislation, the company, represented by the accounting department and the chief accountant, must make changes and correct the financial statements so that the net profit indicator is true.
- If, as a result of errors and violations, the net profit indicator was underestimated, then, after making changes to the balance sheet and reporting, additional net profit should appear, which is also distributed among the founders according to their decision.
- If, as a result of errors and violations, the amount of net profit was overestimated and dividends were already paid on the basis of incorrect information, then after correcting the errors, the net profit indicator will be slightly underestimated. As a result, a situation will arise when the founders initially distributed to themselves a little more net profit. There is nothing to worry about, because after a certain period, the net profit will be smaller, and the participants will distribute the profit in a smaller amount.
If errors were made in accounting and then corrected, then the founders, participants will still receive the due amounts of dividends. But the process can take time.
Net assets
This is the difference between the company's assets and its debts (liabilities). The difference between assets and liabilities is recorded in the final line 3 of the balance sheet of the enterprise. Conditions:
- In accordance with the law on LLC, the amount of net assets must necessarily exceed the amount of the authorized capital. If the amount of net assets is less than the amount of the authorized capital, then the company is obliged to reduce it to the amount of net assets after the time has elapsed. This entails difficulties and risks for the company, because many small businesses have the minimum amount of authorized capital allowed by law: 10 thousand rubles for an LLC. If a situation arises in which the amount of net assets is less than this threshold amount, then, on the one hand, the company is obliged to reduce the amount of the authorized capital, and on the other hand, the amount of the authorized capital cannot be less than 10 thousand rubles.
- If the company allows such a situation for a long time, then it falls under sanctions up to liquidation. As for the payment of dividends, in accordance with Article 29 of the Law on LLC and Article 43 of the Law on JSC, a decision on the payment of dividends cannot be made if at that moment the value of the net assets of the company is less than its authorized capital. Therefore, it is important to follow the size of net assets.
- The payment of dividends is not allowed until authorized capital not paid in full.
The dividend payment procedure is regulated by corporate legislation and the company's charter. The classic option is the annual payment of dividends based on the results fiscal year when financial statements are prepared last year. In accordance with the law on LLC, the company must hold a regular annual meeting of participants, shareholders at the end of the year, at which the financial statements, the amount of net profit are approved, and then the company's owners decide on the distribution of net profit.
How will the net profit be distributed? This issue is within the competence of the general meeting of participants. The state does not interfere in the distribution processes, it controls the procedure in terms of taxation, because at the time of the decision to pay dividends, a tax base for personal income tax arises.
Important:
- The results of the general meeting of shareholders or participants must be documented: they pay attention to this when holding audits. Often decisions on the distribution of dividends and net profit are made orally and on this basis the money is paid. Subsequently, this can lead to serious problems: if one of the owners, participants or shareholders considers that he has been deprived, he has the right to go to court to restore his violated rights. If there is no document drawn up on paper, then it will be difficult for any of the parties to the conflict to refer to it.
- In the absence of the minutes of the general meeting, the accounting department does not have the right to reflect business transactions, make postings on accrual and payment of dividends. In accordance with the law on accounting 402-FZ, which has been in force since January 1, 2013, and in accordance with the previous law on accounting records, the facts of economic activity are recorded in accounting only on the basis of primary documents. In this case primary document is the decision of the general meeting on the payment of dividends, drawn up on paper.
Regularity of dividend payments
Article 29 of the LLC Law and Article 42 of the JSC Law provide that a company has the right to pay dividends quarterly, once every six months and annually.
If members of the company, owners or shareholders want to distribute dividends more often than once a year, then they need to reread the articles of association and find the section that says in what order and how often dividends can be paid. Often the texts of statutes are formed on the basis of general principles and available blanks: when creating a company, few people think about how often they would like to distribute dividends. Therefore, if the charter states that dividends are distributed annually, then before deciding to change the frequency, it is necessary to amend the charter.
The dividend payment period is no more than 60 days from the date of the decision on payment. After its expiration, a shareholder who has not received dividends may regard this fact as a violation of their rights. He can go to court or otherwise influence the company, so it is also important to follow the terms of payment.
Often, enterprises, drawing up the minutes of the general meeting, where decisions are made on the distribution of net profit and on payment, immediately fix the payment schedule:
- to make it clear how the amounts will be paid;
- in the case of small businesses, the number of owners is small. Usually they are all physically present at the general meeting, where decisions are made on the distribution of net profit, payment of dividends and sign the minutes. If the text contains a schedule of dividend payments, and if part of them is paid later than in 60 days, then having the signatures of the owners, it will subsequently be difficult for any of the shareholders to make claims regarding the timing of payment.
Forms of payment of dividends from the point of view of the director
- The classic option - payment in monetary form, cash or non-cash. If this moment is important for owners, shareholders and participants, then it will not be superfluous to indicate in the minutes of the general meeting in what form and how dividends will be paid.
For owners who are used to receiving cash dividends from the cash register, there are subtleties and limitations. Our legislation, documents of the Central Bank, which regulate cash transactions, it is not allowed to pay dividends at the expense of cash receipts received at the cash desk of the enterprise. Withdrawal can be carried out only at the expense of funds that were specially received from the bank or at the expense of other amounts that were returned to the company's cash desk in various ways.
– Payment not in cash, but in the form of property owned by the company (in the form of fixed assets, materials, finished products, accounts receivable, securities, claims). That is, any assets that are on the balance sheet of the enterprise and are recorded in the financial statements approved by the participants.
This issue is quite troublesome and more expensive in terms of taxation. Because, according to the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service, the payment of dividends by any property other than money is recognized as a sale. From the point of view of Article 39 of the Tax Code, a change in ownership of goods, works, services is recognized as a sale. Therefore, if dividends are paid, for example, by fixed assets, then the original owner was an enterprise, and an individual becomes the new owner. The status of this property changes, there is a sale and, as a result, the taxable base. If we are talking about the general taxation regime, then there is VAT and income tax. If we are talking about a simplified taxation system, then additional income appears here.
If we are talking about UTII, then the situation is more subtle. Depending on the type of activity carried out by an enterprise transferred to UTII, most likely, a property transfer operation will not fall under this type. That is, under a transaction for the alienation of property and the transfer of fixed assets, the enterprise will not be on UTII, but on a general taxation regime or on a simplified one, if there is permission to use the simplified tax system.
Thus, before making a decision to pay dividends in kind, be sure to clarify this issue with your accountants, auditors or lawyers so that you understand what such a dividend payment will cost the company.
Distribution of net profit of previous years and payment of dividends from it
There are no restrictions and problems for the company, because all net profit can be distributed in accordance with the decisions of the owners. It is advisable to note this moment in the minutes of the general meeting, at which a decision is made on the distribution and payment of dividends. It is better to state directly: “according to the results of a certain reporting period, for 2014, such and such net profit was received. As of the reporting date, December 31, 2014, the enterprise also has retained earnings of previous years in such and such an amount. A decision is made to distribute all net profit, which is reflected in the balance sheet: that which was received during the reporting period, for 2014, and that which remained at the disposal of the enterprise from previous years. The figures are indicated directly and reflect what proportion of net profit is directed to the payment of dividends.
Accountant
The first thing to do Chief Accountant- reflect the company's debt to pay dividends to its shareholders, participants or owners. Posting D84, K75.2 reflects the accrual of dividends based on the decision of the general meeting. Without a paper version of the minutes of the general meeting, on which the decision on the distribution of dividends is fixed, this entry cannot be made.
After the appearance of the posting in the balance sheet of the enterprise, accounts payable in liabilities to the participants on the payment of dividends. The turnover on the debit of account 84 reduces the net retained earnings, which is recorded in section 3 "Balance". The source of dividend payment is net profit, economic sense and legal nature this operation is fully consistent with reality and does not contradict the law.
Forms of payment of dividends from the point of view of an accountant
— Consider the classic option when dividends are paid in cash. D75.2 is credited from 68 personal income tax account, because in this case, the enterprise that is the source of the payment of dividends is recognized as a tax agent in accordance with Article 226 of the Tax Code. The tax agent is obliged to withhold and transfer to the budget the withheld amount of personal income tax.
In accordance with article 224 of the Tax Code, the tax rate on income received by an individual in the form of dividends from January 1, 2014 is set at 13%. From total amount, due to receive dividends, 13% must be given to the state in the form of tax - this operation is reflected in the first entry.
The remaining amount, 87%, is paid to the shareholder, participant, owner of the enterprise in cash non-cash or through the cashier. Therefore, the posting is formed with correspondence: D75.2, K50 or 51.
After the first two postings are generated, the payables for the payment of dividends on account 75.2 are completely closed. After paying the tax and transferring it to the budget (third posting - D68.NDFL, K51), the company fulfilled all obligations to the owners of the company and to the state in terms of withholding and transferring the amount of income tax.
— Another option for paying dividends is a payment at the expense of the property of the enterprise.. If the general meeting decided to pay dividends by transferring fixed assets or materials to shareholders, then the disposal of these assets should be reflected through 91 accounts. We reflect these operations as follows:
1) D75.2, K91.1. Correspondence is made here for the cost of fixed assets, materials, including VAT. VAT is taken into account in cases where property is paid at enterprises that apply the general taxation regime and at enterprises that pay single tax on imputed income.
2) D91.2, K68 VAT in the amount of VAT is reflected if the general taxation regime and UTII are applied.
3) D91.2, K01 or 10 accounts. This reflects the book value of materials or residual value fixed assets.
Why 91 accounts? These are other income and expenses of the enterprise, because the disposal of fixed assets, materials, that is, assets not intended for further sale, is carried out through 91 accounts, and not through the 90s.
If dividends are paid by the transfer of goods or finished products, then the disposal of these assets should be reflected in the sales accounts. Therefore, in this case, the 90th accounts will be involved. The last three correspondences reflect this situation.
- D75.2, K90.1 reflects the cost of goods and finished products, including VAT.
- The second correspondence is the amount of VAT, D90.3, K68 VAT.
VAT arises if the general taxation regime is applied. It may occur when paying dividends at an enterprise that uses UTII, depending on what is being transferred. If goods intended for retail, then VAT does not arise, because such a transfer falls under the definition of retail sale, will be included in retail turnover and will fall into the type of activity that the enterprise uses on UTII.
- Write-off book value goods or finished products: D90.2, K41 or 43 accounts.
When dividends are paid in non-monetary form, the company (the source of the payment) still has the obligation to withhold tax, because it is a tax agent. On the other hand, the company does not have the physical ability to do so. If the payment is made in natural form then there is no money. It is impossible to recover these amounts in another way, especially if the founder, shareholder or owner is not an employee of the company.
The source of payments - the enterprise (the tax agent) does not have the ability to withhold income tax from such dividends, therefore the company is obliged to send a notice within a month of the impossibility of withholding income tax in tax office at the place of registration of the individual to whom dividends are paid, and at the place of its own registration. In this situation, there will be no claims against the enterprise. Having received such information, the tax authorities will independently contact the individual and demand payment of the amount of tax due.
If a company pays dividends in cash (in cash or non-cash form), then she has an obligation to calculate the tax, withhold it, transfer it to the budget, and at the end of the year, by April 1, submit information on the amounts paid in favor of individuals in the form of 2 personal income tax, where you must also indicate the amount of dividends paid. The personal income tax rate is 13%, no additional taxes need to be paid on these amounts.
Contributions to off-budget funds, in particular in Pension Fund and in the FSS, they are not withheld from dividends paid. Why? In accordance with 212-FZ, the basis for calculating contributions, in particular to a pension fund, are:
— payments within the framework of labor relations,
- payments under GPC agreements providing for the performance of work or the provision of services (contract and paid services agreement).
The chief accountant must be able to clearly identify payments to employees of the company. If money is paid on the basis of an employment contract and a person receives it for the performance of labor duties, then these are payments within the framework of labor relations. They are subject to contributions to off-budget funds.
Dividends cannot be classified as such payments, because they are paid to individuals, regardless of how well or poorly they worked. A dividend payment is a distribution of the net profit that remains after paying all taxes. Even those owners of the company, shareholders and participants who are employees and often managers of the company, receive dividends not for the results of their work, but for the result of the entire company, because:
1) profit remained at the disposal of the company
2) net profit is the result of the activities of not only the head
This means that the payment of dividends is not a payment within the framework of an employment relationship. That is why dividends are not subject to contributions to off-budget funds. The FSS mentioned this several times in letters.
How much taxes do you need to pay before you get a net profit?
Here you can compare different modes taxation. Under the general taxation regime, the income tax rate is 20% of the profit received by the company as a whole from financial and economic activities. Compare this, for example, with the rate provided for the simplified tax system with the object of taxation income minus expenses in the territory of the Sverdlovsk region. General rate for all is 7%. The price of dividends in the first and second cases is different, because in order to distribute dividends under the general tax regime, you need to pay 20% to the state, and being on a simplified tax system - only 7%.
If we talk about UTII, it is difficult to say how much interest you need to pay in order to distribute dividends, because the amount of UTII tax does not depend on revenue, income, expenses, but depends on financial result. Knowing the size of this tax, seeing the result of financial and economic activity, it is also possible to calculate the tax burden. It will not exceed the amounts provided for the general taxation regime.
Thus, if a company is on special tax regimes(USN, UTII), the tax burden when paying dividends, it is significantly lower than for situations where the company is under the general taxation regime.
Periodicity of dividend payment
Russian corporate legislation provides for several options for paying dividends: quarterly, semiannually, and at the end of the year. If the leaders of your company are interested in the option in which dividends will be paid quarterly, then the chief accountant must definitely warn them about the risks that arise in connection with this.
1) The charter should provide for the quarterly distribution of profits and the payment of dividends. Each fact of the distribution of net profit and the direction for the payment of dividends must be recorded and recorded on paper, there must be a fixed decision of the general meeting.
2) Recall that dividends are the distribution of net profit remaining after paying all taxes. With a quarterly payment, this situation may arise. According to the results of the first quarter, the company had a net profit distributed through dividends. According to the results of the first half of the year, the company still has profit, and it is also distributed through dividends. Following the results of 9 months, the company again had a net profit, the company is working with a plus and feels quite confident, therefore, according to the results of this period, dividends are distributed in the same way.
But if at the end of the reporting period a loss is recorded at the enterprise, then the payments that were made during the year, following the results of the first quarter, six months and 9 months, will be reclassified tax authorities in payments from net income. They will need to pay not only personal income tax at a rate of 13%, but also a fee sy contributions to off-budget funds at an aggregate rate of 30%, because at the end of the year there was a loss, and the amounts paid cannot be qualified as dividends.
The accounting department should voice this idea to shareholders so that they understand that if they want to pay themselves dividends more often than once a year, then they need to ensure that the company ends up with a profit every year. Otherwise, there will be an additional tax burden on the company and directly on the shareholders.
Since these payments will be reclassified from dividends to payments from net profit, personal income tax can be paid at a rate of 13%. At the same time, the already paid 9% of the dividends most likely will not be able to be offset against the payment of 13%, because. they are different CBCs. A problem arises: who should be responsible for the return of the paid 9% from dividends? On the one hand, the taxpayer is an individual who receives dividends. If the shareholder of the company is an employee of our company, then this work can be shifted to the accounting department, although this is quite troublesome. But if the shareholder and participant of the company is an individual who is not in an employment relationship with our company, then the company has no opportunity, grounds and rights to engage in the 9% return procedure. As a result, a person is left alone with the tax authorities. He will have to interact with them himself, to return income tax.
If the shareholder who received dividends from us, which were later reclassified into payments from net profit, is not an employee of the company, then we cannot withhold 13% from him, and the enterprise, as a source of payment, is obliged, under Article 226 of the Tax Code, to submit a notice of the impossibility to withhold income tax to the tax office, and the KO will communicate directly with this individual.
3) Since the net profit that the enterprise has left is the property of this company and the property of shareholders, the shareholders, participants, owners of the enterprise can dispose of this money in any way they like. In particular, a decision may be made on the disproportionate distribution of net profit. For example, an LLC has two owners, each of whom owns 50%. In this situation, no one can forbid these participants to distribute the net profit not 50/50 in accordance with their shares. They can decide on a non-proportional distribution, for example, in the ratio of 90 and 10. The amount exceeding its share will no longer be recognized as a dividend, because the dividend is recognized as part of the net profit to be distributed in accordance with the share that belongs to the shareholder, owner or participant.
As a result, out of 90 rubles received, 50 rubles will be recognized as dividends, personal income tax at a rate of 13% must be paid on them, and contributions to extra-budgetary funds will not need to be paid: an amount of 40 rubles is recognized as a payment from net profit. Personal income tax is withheld from it at a rate of 13%, and contributions to extra-budgetary funds are paid at an aggregate rate of 30%: there is a letter from the Federal Tax Service on this subject. Here we are talking about the payment of dividends not to an individual, but to a legal entity, therefore the income tax rate of 20% appears, the company burdens the recipient of dividends general regime taxation. Thus, if a shareholder or owner receives a net profit in a larger amount than he is entitled to in accordance with his share, then this will no longer be recognized as a dividend.
According to the results of the financial year, the enterprise, in accordance with the current legislation, may decide to pay dividends to the founders from the net profit received. We have already introduced our readers to the procedure for accruing dividends and the problems associated with their taxation. How to accrue and pay dividends in "1C: Accounting 8" is told by the specialists of the Sarychev Implementation Center.
The basis for reflecting the accrual of dividends in accounting will be the minutes of the meeting of the founders and the accounting statement-calculation of the amounts accrued to each of the owners.
The founders of the enterprise can be both legal entities and individuals, including employees of the organization. Accounting for dividends in "1C: Accounting 8" will depend on the qualifications of the recipient of income and on whether the organization paid interim dividends at the end of each quarter.
The organization as a tax agent is obliged to withhold taxes from the amounts paid: on profit from dividends accrued to legal entities, and personal income tax from dividends accrued to individuals. At the same time, the tax rate of 9% is applied if both parties are residents of the Russian Federation, and the rate of 15% and 30% - if any of the parties is not a Russian organization or the recipient of income is an individual non-resident of the Russian Federation.
It should be remembered that the withholding agent for the payment of taxes on dividends is only Russian organization. If the taxpayer receives dividends from a source outside the Russian Federation, then he is obliged to independently calculate and pay the corresponding amount of tax.
Dividends are not subject to UST in accordance with clause 1 of Article 236 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, contributions to the FSS of the Russian Federation and contributions to compulsory pension insurance (clause 2 of Article 10 of the Federal Law of December 15, 2001 No. pension insurance In Russian federation").
Calculation of dividends to employees of the organization
In 1C:Accounting 8, it is advisable to start accruing dividends to employees of an organization based on the results of a financial year or quarter by introducing a new type of accrual "Dividends" in the "Plan of the type of settlements" of the "Operations" menu (see Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Filling in the directory "Accruals of the organization"
In the "Name" field, the name of the accrual "Dividends to employees of the organization" is indicated. In the field "personal income tax" from the directory " personal income tax"the type of income is selected with the code 1010" Dividends, taking into account Art. 214 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation". In the field "UST" - it is indicated that this type of accrual "is not an object of taxation, in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 236 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation". In the field "FSS" - "Not taxed."
Then, in the reference book "Methods of reflecting wages in regulated accounting" (Field of the document "Reflection in accounting") - using the button - the accounting entries for the accrual of dividends for employees of a particular organization are indicated. Accounting: Debit 84/01 Credit 70. Accounts tax accounting remain empty, since dividends paid out of net profit are not recognized as expenses of the organization for income tax.
The direct accrual of dividends to employees in the program will be carried out using the document "Personal income tax and unified social tax: income and taxes" (menu "Salary" -> "Accounting for personal income tax and unified social tax" -> "Input of income and taxes personal income tax and unified social tax") (see Fig. 2).
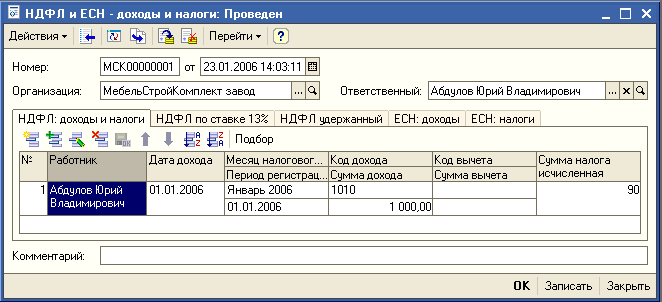
Rice. 2. Accrual of dividends to the founder, who is a resident of the Russian Federation ( personal income tax rate - 9%).
Data on the amount of accrued dividends and taxes withheld from them, entered in this document, will be reflected in tax cards 1-NDFL and 2-NDFL.
The document is filled out for each of the organizations on the date of accrual of dividends.
Using the button, the recipient of income is selected from the list of employees, in the field "Date of income" the day of accrual of dividends is indicated - usually it coincides with the date of the minutes of the meeting of the founders. "Month tax period" and "Registration period" will be filled in automatically based on the entered "Income date". In the "Income code" field, select code 1010 - dividends.
The amount of dividends due is indicated in the "Amount of income" field. The program will automatically calculate the "calculated tax amount" at a rate of 9% or 30% based on the citizenship data specified in the "Individuals" directory for the employee we have chosen (resident / non-resident of the Russian Federation).
The "Individual income tax withheld" tab is filled in when the dates of the accrued and withheld tax coincide, and in the "Scientific policy of the organization for personnel" (menu " Accounting policy") is not definitely simultaneous calculus and withholding personal income tax. If the data on the "Individual income tax withheld" tab is not filled out, then the date of withholding personal income tax (and reflecting this data in the 1-personal income tax card) will be the day the dividends are paid to the employee through the cash desk or bank.
Posting a document using the button will enter data on dividends, as well as accrued and withheld tax in Section 4 "Calculation tax base and tax on income of an individual from equity participation in the activities of the organization "card 1-NDFL (menu" Salary "->" Accounting for personal income tax and unified social tax "-> " tax card 1-NDFL")
In order for the amounts of dividends and personal income tax accrued to the employee to be reflected in the accounting accounts, it is necessary to create the document "Reflection of wages in regulatory accounting" in the "Salary" menu (see Fig. 3).

Rice. 3. Filling in postings for accrual of dividends.
In this document, using the button, only the amount of calculated personal income tax is automatically filled in on the basis of the document "personal income tax and unified social tax: income and taxes" for the same period.
The dividend amount itself is entered manually, by selecting the D84 / 01-K70 postings from the corresponding directory using the posting button. Tax accounting accounts remain empty (see Fig. 3).
Dividends to non-employee founders
Dividend amounts for legal entities or individuals who are not employees of the organization, as well as withheld taxes, are calculated using the document "Operation (accounting and tax accounting)" of the "Positions" menu (see Fig. 4).

Rice. 4. Accrual of dividends to the founders: Electrotovary LLC - in the amount of 10,000 rubles. and Lyubimov O.M. - in the amount of 2,000 rubles.
The required accounting entries are entered manually:
Debit 84.01 Credit 75.02 - for the amount of accrued dividends; Debit 75.02 Credit 68.04.02 - for the amount of income tax withheld by the tax agent; Debit 75.02 Credit 68.01 - on personal income tax amounts from dividends.
In order for the accrued tax on income from payments to individuals who are not employees of the organization to be reflected in the 2-NDFL certificate, it is necessary to reflect the amount of dividends also in the document "Adjustment of entries in the accumulation register" (see Fig. 5).

Rice. 5. Reflection in the document "Adjustment of Accumulation Register Entries" of information on accrued dividends.
Using the "Settings" button, the form of the document is configured to adjust the "Personal Income Tax Information" register. The further filling principle coincides with the filling out of the document "PIT and UST: income and taxes" discussed above.

Reporting on paid dividends
All operations for the distribution of profits of the organization are reflected in the reporting of the period in which these operations actually occurred, that is, in which the meeting of the founders took place, which decided to pay dividends. At the same time, the opening figure of retained earnings is not adjusted. The fact of accrual of dividends is sufficient to be reflected only in explanatory note. That is, for example, the payment of dividends in January 2006 for 2005 will be reflected in annual accounts for 2006 and in the explanatory note to the financial statements for 2005.
The accrual of dividends is reflected in the Statement of changes in capital (menu "Reports" -> "Regulated reports" -> "Accounting statements" -> "Form No. 3") in line 103 "Dividends" as a value that explains the decrease in retained earnings in the organization's balance sheet between the opening and closing dates of the period in which the decision to pay dividends was made. When the button is pressed, the data on dividends reflected in the documents "Operation (accounting and tax accounting)" and "Salary reflection in regulatory accounting" are automatically entered into the report.
In addition, the amount of dividends paid to the founders - individuals must be reflected in the Certificate of income of individuals in the form 2-NDFL (menu "Salary" -> "Accounting for personal income tax and unified social tax" -> "Tax card 2-NDFL").
This report is filled in automatically using the "Fill" button for the entire list of employees. After posting the document, if necessary, you can print the Help (the "Print" button) and upload it to a floppy disk for transfer to the tax office (the "Get file to disk" button).
Dividends paid to legal entities will be reflected on Sheet 3 of the corporate income tax return.
Automatic filling of information on Sheet 3 is not provided, so the amount of dividends must be entered manually.
Interim dividends: to pay or not to pay?
The current legislation allows paying dividends based on the decision of the general meeting of founders more than once a year - based on the results of the first quarter, six months and 9 months. However, there is a possibility that by paying dividends during the year, at the end of the year, the company may incur a loss. This means that the amounts paid to the owners as dividends cannot be qualified, since according to paragraph 1 of Article 28 of the Federal Law of February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ "On Limited Liability Companies" and paragraph 2 of Article 42 of the Federal Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208- Federal Law "On joint-stock companies" Dividends are paid only from the net profit of the organization. In addition, the issue of accounting for interim dividends is ambiguously resolved.
In accounting practice, two options for solving the problem are used.
Financially stable enterprises, confident in making a profit at the end of the year, can keep records of dividends during the year on account 84.01, referring to the Instructions for the Application of the Chart of Accounts, where the commentary to account 84 expressly states: "a similar entry is made in the payment of intermediate income".
The reflection of transactions in "1C: Accounting 8" will be similar to the accrual of dividends at the end of the year.
If the company cannot predict the amount of net profit, then it is advisable to take into account interim dividends during the year on a separate sub-account of account 99. And if there is profit at the end of the financial year, transfer the entire amount of accrued dividends with the final entry:
Debit 84 Credit 99
With this option, until the end current year the organization on account 84 does not reflect net, but retained earnings, that is, one that is not subject to distribution. The net profit of the company is determined according to the financial statements of the company and is reflected in the financial statements before the end of the financial year by comparing the credit and debit turnovers on account 99. Therefore, supporters of this point of view, the accrual of interim dividends during the year, make the posting:
Debit 99 Credit 75
In the second case, in "1C: Accounting 8" in the Profit and Loss Statement, accrued interim dividends will have to be reflected with a minus sign (in parentheses) after the line " current tax on profit" using manual adjustment.
Taxes on both quarterly and annual dividends are paid on the same dates.
When paying dividends to an individual, the deadline for paying income tax is established by paragraph 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Tax agents are required to transfer the amount of withheld tax no later than the day of actual receipt of cash from the bank for the payment of dividends or the day of transfer of income from bank accounts. In case of issuance of dividends in kind - no later than the day following the day of actual withholding of the tax amount.
When paying dividends to a legal entity, the deadline for paying income tax to the budget is set at 10 days from the date of income payment. This is evidenced by paragraph 4 of Article 287 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Today, the legislation covers in sufficient detail the issue of accruing dividends, as well as receiving income from this type of activity.
But at the same time, one should not forget about the many nuances associated with this activity. First of all, about the need to appropriately make deductions in favor of the state from income of this kind.
An enterprise paying dividends is, in fact, a tax agent. Therefore, it is required to properly reflect all transactions by postings.
Basic moments
Today, many enterprises and companies are joint-stock companies. They issue shares securities), in the presence of which a particular individual / legal entity has the right to receive some income.
Moreover, the date of receipt and the amount depends on many different factors - the type of shares, the date of the beginning of their possession and many others.
There are specialized documents that determine the date of receipt of income. It is important to remember that the accrual of dividends to employees of the organization is reflected in the accounting entry.
This rule is very important to observe in all cases. Otherwise, there is a high probability of various kinds of difficulties with the tax service.
Before answering the question which accounting entry means the distribution of dividends to shareholders, you should familiarize yourself with some fundamental points. These include the following:
- what it is?
- who can be the owner?
- the legislative framework.
Thus, it will be possible to avoid difficulties and problems in reporting.
What it is?
Income from shares is dividends - they mean certain percentages of the company's income for any reporting period (quarter, other).
Dividend deductions are reflected in the accounting department with special entries.
Moreover, in this particular case, the term "wiring" means a record in documents or a special database on a computer about the current and future state of an object.
Wiring always includes two main components (required):
- debit account;
- credit account.
Also, the wiring must indicate the characteristic component of a particular action. It can be, for example, quantity or quality.
If dividends are used as an accounting object, then a more detailed analytical identifier is used when accounting for them. The purpose of income, counterparty is always indicated.
Keeping records of dividend payments has many features and difficulties. You should familiarize yourself with them in advance in order to avoid mistakes.
If, during the inspection, employees tax service find any errors, this may lead to the appointment of a holding.
Auditors quite often find many errors in accounting even for conscientious taxpayers. Therefore, you should not attract the attention of the Federal Tax Service once again.
Who can be the owner
If all the shares of a company are owned by a single founder, then it is he who will be the recipient of this income. In all other cases, it is required to focus on a special federal law.
According to this regulatory document, dividends can be received by persons who own shares on the date of the special calendar. There are some important rules.
These include the date the recipients were determined:
Individuals/legal entities may be directly owners of shares that allow receiving any dividends.


But regardless of the legal status of the owner, the company that pays dividends will still be a tax agent. This point is covered in the regulatory framework on this matter.
The legislative framework
All persons having any relation to the payment of dividends should familiarize themselves with the legislation in force in this regard in advance.
Scroll legal documents regulating this moment, is relatively small. However, it is worth reading all of them carefully.
Shareholders, accountants and other officials should review the following NAPs:
- Federal Law No. 208-FZ Chapter V:
All of the above federal laws are not independent legal acts.
They only carry out the addition, edit its articles.
That is why, when performing a variety of actions, one should focus on this document.
It is also worth considering when conducting postings. This document explains in sufficient detail what exactly is considered an expense.
Accounting entries for the payment of dividends
Dividends can be paid to a variety of individuals. Moreover, some of them may be not just owners of the company's shares, but at the same time its employees, founders.
So, being employees, it will be necessary in without fail transfer income by special posting.
There are many nuances associated with accounting. Today, payments can be made to the following persons:
- founders of the enterprise;
- shareholders;
- who are not employees of the organization;
- calculation examples.
For all three categories indicated above, the postings are different. Accountant or other official bookkeeper should definitely keep this in mind.
If any fundamental rules are violated, there is a high probability of problems with the Federal Tax Service.
For the founders of the enterprise
Usually, accruals are made to the founders of the enterprise on preferred cumulative shares.
It is important to remember that a decision on net profit must be made without fail only at a meeting of founders - if there are several of them.
If the founder is alone and at the same time he needs to receive dividends, then he can independently issue the corresponding order. And based on it, get your income.
In this case, this procedure will need to be reflected in the accounting department with the following entries:
The above-mentioned postings simply reflect the accrual of the income itself. But at the same time, dividends received by individuals represent, in fact, ordinary income.
It is necessarily taxed at a rate of 13% - on personal income. Transfers to the state budget are also required to be properly reflected in the entries.
They look like this:
It must be remembered that dividends can be paid to the founder not only in cash, but also in kind. This moment must be taken into account.
Since such income is necessarily taxed at a rate of 13% and is also reflected in the financial statements. The reporting procedure is carried out in a similar way.
Shareholders
When accruing dividends to ordinary shareholders who have acquired shares of an enterprise through an exchange, it is important to correctly reflect this procedure in accounting. It has features, nuances.











Therefore, it is best for the responsible persons implementing the procedure in question to familiarize themselves in advance with the reports already drawn up using an example.
In this way, the assumption of the most common mistakes. Some of them may result in a fine.
If in this case dividends are paid to shareholders in cash and in kind, then an example of postings will look like this:
| Dr. | Kt | Name of operation, account |
| 75 | 50 | “Settlements with the founder” - the procedure for paying dividends is indicated |
| 75 | 90 | Reflects income from the sale of finished products |
| 90 | 43 | The cost of ready-to-sell products is written off in full - which is transferred to the account of dividends |
| 90 | 68 | The procedure for calculating VAT is indicated |
| 75 | 68 | The self-withholding of personal income tax in the amount of 13% is indicated |
| 70 | 68 | Personal income tax is withheld from the profit received by the founder himself |
| 75 | 68 | This transaction withholds tax on the profit of the founder, who at the time of receipt of income is not his employee/employee |
| 70 | 68 | This operation carries out the withholding of personal income tax from the income of the shareholder, who is also the founder |
| 76 | 68 | Income tax is deducted from the income of the founder himself |
Non-employees of the organization
But most often it is required to carry out postings on the operations of accruing profit in the form of dividends to persons who are employees of the organization.
In this case, it will be necessary to open a subaccount No. 75-2. It is opened in addition to account No. 75. At the same time, it is also strictly mandatory to use account No. 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”.
This procedure has its own nuances, therefore it is best to deal with all of them in advance using an example:
It is important to remember the significant differences in postings for employees of the enterprise and those who are not. Both accounts and credit / debit differ.
The presence of inconsistencies can cause problems with the Federal Tax Service.
Video: dividends
Errors in this segment of taxation can serve as a signal to the Federal Tax Service about an attempt to avoid paying taxes.
Such schemes are quite common today. This is especially common with.
Accrual example
Posting numbers in general are almost always standard. Therefore, you can always carry out accounting according to the model.
It's simple enough. Especially if any specialized software- 1C: Accounting or other similar.
Dividend example:
Accounting support for operations related to the distribution of a part of the organization's net profit between the founders is carried out in the following sequence:
- formation of information on the amount of undistributed net profit;
- adoption of a decision by the general meeting of owners (shareholders) on the amounts and terms of payments;
- accrual of dividends separately for each participant;
- taxation of amounts;
- payment of dividends;
- transfer of taxes;
- writing off unclaimed amounts.
Dividends are part of the net income legal entity(joint stock companies or LLC), which is the income of the founders (shareholders). They are distributed among the participants in proportion to the shares they own in the company.
The frequency of payments and the amount of retained earnings payable to owners are determined at the general meeting of shareholders (founders of the LLC) and are specified in the organization's charter. The order of payments can be changed: adjustments are registered in the Charter of the company and registered with the Federal Tax Service. Based on the results of the meeting, a protocol is drawn up, on the basis of which the distribution of income begins. Payments can be made quarterly, at the end of six months or at the end of the year.
Note from the author! Legislated maximum term for the distribution of net profit between owners - no more than 60 days from the date of the decision at the general meeting (the date of the minutes); no more than 10 days for payments to nominee shareholders and trustees and no more than 25 days for other shareholders in the JSC.
Accounting records of undistributed net profit are kept on an accrual basis. . It is active-passive: a debit balance is the presence of an uncovered loss based on the results of the company's activities, a credit balance is a part of net profit subject to subsequent distribution (after payment of all necessary taxes and contributions).
Basic transactions for accrual and payment of dividends
Accounting for dividend payments depends on the status of the founder:
- Company founders - individuals a, who are employees of the company: mutual settlements on accrued amounts are displayed in the accounting of the company in correspondence with the account. , to which additional accounting can be opened for distributing employee payments.
Dt84 Kt70 - accrual of dividends from the company's net profit.
Dt70 Kt50.51 - cash payment or non-cash transfer of funds to the founders.
Note! Monitoring of the amounts collected on the account. 70 is carried out separately for each employee of the organization for an in-depth assessment of mutual settlements with personnel.
- The founders of the company are individuals who are not employees of the organization, and legal entities: accounting for mutual settlements with owners is carried out on the account. , to which a separate active-passive sub-account is opened.
Dt84 Kt75.02 - accrual of dividends on the basis of a general meeting of shareholders or founders of an LLC.
Dt75.02 Kt50.51 - payment of accrued amounts.
Taxation of payments
Since dividends represent the income of the founders (individuals and legal entities), these payments are subject to income tax in accordance with applicable law:
- Founders - individuals: personal income tax 13% for citizens of the Russian Federation and 15% from the amounts due foreign citizens.
- Founders - legal entities: the amounts are subject to income tax in the amount of 13% for companies created in Russia and 15% from dividends of foreign companies.
Note! If the organization is the recipient of part of its own dividends, the taxable base may be reduced when calculating income tax by reducing the total amount allocated for distribution among the participants of the company. The taxable base in this case will be calculated as follows: the amount to be issued minus the amount of dividends received.
Based on the protocol for the distribution of net profit between the participants of the legal entity, it is necessary to immediately calculate taxes, since they are transferred no later than the working day following the payment.
Accounting for taxes is carried out on the account. for the respective sub-accounts:
- Dt70 Kt68 - accrual of personal income tax on payments to founders - employees of the company.
- Dt75 Kt68 - tax assessment for the rest of the founders.
- Dt68 Kt51 - transfer of taxes to the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
Unclaimed amounts
There are situations when a member of the company did not receive the amount of dividends due to him on time. He has the right to demand payment within 3 subsequent years (the period can be extended up to 5 years, if this is determined by the Charter of the company) from the date of signing the protocol in joint-stock companies or the end of the 60-day period after the decision is made in limited liability companies.
If the participant has not claimed these amounts within 3-5 years, then they are transferred to the company's net profit:
Dt70.75 Kt84.
Practical example
According to the results of 2018, Compass LLC determined the amount of retained net profit: 100 thousand rubles. At the annual meeting of the founders of the company, the following decision was made: to distribute between 3 founders 60 thousand rubles, 20 thousand rubles each, since they have the same shares in the company. Transfer the rest of the funds to the reserve fund.
Note! One of the founders is the general director of the company, and an employment contract has been concluded with him.
accounting entries by operations:
- Dt99 Kt84.
100 thousand rubles - the undistributed part of net profit is displayed.
- Dt84 Kt75.02.
20 thousand rubles - dividends were accrued to pay 1 founder.
20 thousand rubles - dividends were accrued to pay 2 to the founder.
- Dt75.02 Kt68.
5,200 rubles - personal income tax has been charged, which will be withheld.
- Dt84 Kt70.
20 thousand rubles - payment was accrued to the founder - the general director of the company.
- Dt70 Kt68.
2,600 rubles - personal income tax has been charged, which will be withheld.
- Dt84 Kt82.
40 thousand rubles - replenishment reserve fund from the firm's net income.
- Dt75.02 Kt51.
34 800 rubles - cash were given to the founders.
- Dt70 Kt51.
17,400 rubles - dividends CEO were transferred to his current bank account.
- Dt68 Kt51.
7,800 rubles - the tax was paid to the IFTS.
Accounting for dividends for a recipient - a legal entity
Dt76 Kt91 - accrual of payments due to be received (posting date - date of the decision on the distribution of net profit).
Should be borne in mind! The amount of dividends due must be reflected net of income tax, which will be withheld by the organization - tax agent.
Dt51 Kt76 - actual receipt of funds.




