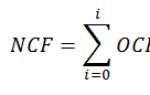Side cut of tires. What to do? Types of shallow foundations How to check at home, what's with a wheel
Let's agree that we will only talk about "tubeless" - wheels, in which there is no camera. This is the mainstream rubber these days, and for good reason.
I will list the main things: a lighter wheel, improved traction (due to lower pressure and air distribution), increased comfort, and what we are talking about is that it is much more difficult to pierce such a wheel. More precisely, catching a nail is just as easy, but here tubeless, you have every chance to get to the installation.
Damage types
1. Normal puncture.

It doesn't matter what you caught on the road - a nail, a piece of wire or a sharp stone (I've seen that). A puncture is a minor damage, which in most cases will allow you to get to the tire fitting. Also, a puncture does not damage the wheel.
2. Cut.

It can be either side or on a treadmill. Cutting a treadmill is rare because there is a massive rubber on the treadmill. But a side cut is easy: if you rub your wheel against something, or if you wave it into a hole with sharp edges, there is a cut. A shallow cut (when the cord is not damaged), as a rule, is not noticeable and the wheel does not deflate. A deep cut - the wheel deflates immediately, and almost always leads to an irreparable defect, but we will return to this later.
3. Lateral swelling: "lump, hernia, who calls it what."
It appears as a result of riding on a flat tire, or with a strong impact, not necessarily a side one. The bump occurs only on the lateral surface of the rubber. Failed into a hole at speed, or ran into something, that's a bump. Unfortunately, such a defect cannot be eliminated (just a little later - when I mention tire fitting), and leads to the tire being unusable.
4. Deformation of the disc.

Not exactly rubber damage, but also a problem related to the quality of the roads, and sometimes, the inexperience of the driver - the front wheels went into a turn, the rear ones drove along the curb. As a rule, after straightening the disc, the problem is solved, and the rubber does not suffer.
Wheel replacement and repair
If the trouble happened on the road, the first thing is to remove the car from the road.
1. Place a sign 30 meters away if you are outside the city and 15 in the city. If you can clearly see other cars on the road, this does not mean that they can see you well. You have to change a wheel, and it is very uncomfortable to do it on the road. Do not be afraid - a few meters on a flat tire will not damage the rubber, but you will work in comfort, and you will not interfere with movement.
2. Next - take out the spare tire, keys, jack - everything you need in advance. I have seen a picture: a car is standing on a jack, swinging, and a wretched man unloads bags from the trunk in order to get a spare tire - do not repeat such nonsense, yes - and kick out the passengers - let your legs stretch.
3. Before lifting the machine, be sure to rip off - slightly unscrew the wheel nuts or bolts.
4. Stop the car: handbrake, speed, if possible - pads under the opposite side of the car, ideally - diagonally. I mean: the rear left wheels are lowered, the pads are under the front right. No pads - anything at hand will do - an ordinary stone.
5. When you start lifting, make sure that the jack is level, and the car is not pulled towards you, or pushed away from you - it is better to lower it and move the base of the jack.
- When removing / installing, do not put your head under the wing, feet under the wheel.
- In no case do not hold the wheel from below - keep it on the sides, if anything - your hands will be whole.
- Do not completely tighten the wheel by weight: it must be tightened by weight so that the bolts / nuts sit in their seats (cones in the disc), and then, when lowering, tighten it completely.
Tire service
There is simple rules to remember. Side bump - the wheel is unusable. Whatever they say to you that it's okay, we will vulcanize - such a wheel can fit a spare tire, and then as a last resort. With such damage, there is a break in the cord - the threads that serve as the frame of the wheel - they will break further, or not - no one knows. But such a wheel can “shoot” (burst) - be careful. When a cut is made on a treadmill, if the cut is shallow, you can use it, if it is deep, the wheel is sent to a landfill.
Regarding: fungus or vulcanization. Definitely vulcanization. Fungus is a temporary measure - vulcanize the puncture as soon as possible. A poor-quality fungus, or tourniquet, can harden over time and lead to etching of the air. Various self-adhesive patches are also temporary - a temporary measure. And don't forget to balance the wheel after repair.
I forgot to mention: there are special sealants that are poured into the wheels. In principle, this is a good option, only if there is a small puncture from a thin object.
How to check at home what's with the wheel
Check the spool first by wetting the nipple of the wheel - if there are bubbles, it can be replaced - this can be done at home. Also, if there is a desire, and you have found the reason for the puncture, you can use the so-called harnesses, or inserts. They can be purchased, there is also an instruction there - you feel the strength in yourself - try it.
For any cuts, swelling, damage to the disc - a direct way to tire fitting.

If no reason is found
Unfortunately, it also happens - the wheel deflates, but the reason, not you, nor the tire service can find out. The following can help: first, let the wheel be pumped 1-1.5 atmospheres more during the installation, and lowered into the water. It is the whole wheel, and not to smear the outside with a brush. Any, the smallest defect will be clearly visible in the bubbles. And here's the second: everything new is well forgotten old. If you can't find the object sticking out in the wheel, use the old-fashioned method: disassemble the tire, ideally remove it completely from the wheel. Take a regular cloth and wipe it carefully inside the tire. Believe me - whatever sticks out there, the rag will surely catch on, and the rest is already a matter of technology.
These are some simple advice, what to do if the wheel is flat for the first time - neither a nail, nor a rod!
In many areas of construction, shallow foundations are most often used on natural foundation... A promising direction for their improvement can be attributed to the use of intermediate preparation of variable stiffness in strip foundations. Another direction is the use of the working side surface of both strip and single foundations. Such foundations of a shallow foundation in cohesive low-moisture soils of natural constitution include slotted, round, slotted, trench and single-plate. The technology of their device excludes backfilling of the lateral surface and thereby allows the use of lateral friction along their walls, which cannot be achieved when installing columnar or strip foundations.
The experience of using effective structures of shallow foundations on real objects is quite wide. The improved technologies introduced into construction practice were previously tested both on models and on construction sites specific sites in life size... The calculation method is the result of research, completed projects of foundations, put into operation.
For increase economic efficiency strip foundations structures, it is necessary to reduce the area of the supporting monolithic tape and reduce the consumption of metal during reinforcement work. This can be achieved by using preparation of variable stiffness (Fig. 1, a). The preparation is a continuous concrete layer 5-10 cm high, 20-40% wide of the pad (tape) width. On both sides of the intermediate preparation, a layer of loose sand of the same height is poured. A pillow or monolithic tape is arranged directly on the preparation after concrete curing.
This foundation structure transfers the initial load to the foundation soil through the base of the concrete preparation. As the load progresses, the foundation shrinks with simultaneous compaction of the loose soil, and at a certain load value, the entire lower plane of the belt sole comes into operation. There is an unloading of the cantilever parts of the pillow (tape). By increasing the calculated soil resistance, it becomes possible to reduce the width, that is, the area of the pillow (tape). A multi-storey experimental 144-quarter four-section residential building was erected on the foundation with intermediate preparation in the city of Kustanai, which is normally operated. A detailed study and determination of the methodology will ensure the widespread introduction of this foundation structure in construction practice.
Slotted foundations
Improved shallow foundations in cohesive low-moisture soils of natural constitution also include foundations with a working lateral surface. Excluding backfilling of side surfaces from the technology, we use lateral friction along the walls, which cannot be achieved when installing columnar or strip foundations in open pits. These foundations include slotted, round, slotted, trench and single-plate.
Sufficient research volume slot foundations showed their effectiveness and ease of manufacture. They are one or two narrow concrete (reinforced concrete) plates in the ground, connected by a grillage to transfer the load from the aboveground structures to the plates themselves. The technology of the device consists in cutting narrow cracks in the ground with a width of 100 - 300 mm, a depth of 1 to 3 m with a bar (chain or rotary slot-cutter), followed by filling concrete mix... The parameters of the slotted foundations are selected depending on the engineering and geological conditions, the values of the design loads, the type and design of the aboveground structure. The use of slot foundations instead of strip foundations on a natural base is advisable in the absence of basements.
The peculiarity of the work of slotted foundations is as follows. The load on the base with a single-slot foundation (Fig. 1, b) except for the bottom of the grillage, it is transmitted by the lateral planes and the end of the wall. In a two-slot foundation (Fig. 1, v) the soil mass enclosed between the plates is also included in the work, thereby the main load is transferred in the plane at the level of the lower ends of the walls. The optimal distance between the walls, corresponding to the maximum bearing capacity of the foundation, is 0.6 - 1.3 m. The soil core, plates and grillage enclosed between the walls can be considered as a concrete-ground foundation on a natural foundation, equal in height to the height of the working walls. The considered single-slot foundations are designed for one-, two-storey cottages, summer cottages, garages, two-slot - for residential and public buildings up to 7 floors, as evidenced by the practice of design and construction on such foundations.
Round foundations
Device technology round foundations up to 3 m deep, 0.6 - 1.2 m in diameter, is similar to the technology of bored piles. However, they cannot be attributed to piles, since they have a ratio of length (height) to diameter l / d ≤ 5 , which significantly exceeds the number 10, according to which the structure is classified as a pile. Round foundations are used for reinforced concrete columns (Fig. 1, G) and metal (Fig. 1, e) frames of light structures (fences, warehouses, workshops, garages, utility rooms). As an example, we can cite round foundations made for unheated prefabricated warehouses made of profiled galvanized steel sheets.
One of the types of round are foundations for supports engineering communications as reinforced concrete racks embedded inboreholes to their entire height. They compare favorably with driven piles-supports in that they can be straightened in plan and in height. This is achieved by the fact that wells are drilled with a larger diameter than the cross-section of the supports along the diagonal (Fig. 1, e). In case of re-drilling of wells, a sand-gravel mixture is filled in and compacted to the design level of the bottomhole, as a result of which a low-compressive cushion is formed. The cavities between the walls of the wells and the edges of the supports (columns-columns) are filled to the full height with concrete and compacted with a deep vibrator. Thus, a high accuracy of the laying of communications such as busbars, fuel lines, heating mains, cable routes, and compensatory pipeline sections is achieved.
Description of Figure 2: a- slotted foundation for a three-hinged frame; b - the same under reinforced concrete column; c - trenchI-beam foundation; d - trench foundation for a lighting mast; d - single-plate underreinforced concrete column.
Slotted foundations
Slotted foundations They are arranged with a bucket in short trenches (slots) with an oval-shaped sole up to 3 m long, 0.4 - 1.0 m wide, and up to 3 m deep. Excavators, including those with a narrowed bucket, are used to develop slots. Rod-type pressure grabs can also be used for the installation of buried structures and anti-seepage curtains by the "wall in the ground" method. When using a grab, the dimensions of the slot in the plan will correspond to its outer dimensions with the maximum opening of the jaws. Sludge from the bottom of the slot is removed with a scraper device, compacted with a flat part of the bucket or a closed grab by creating maximum pressure on the bottom of the slot. The slot is concreted with a spigot (without formwork) at the same time as the nest is made (Fig. 2, a) or a glass (fig. 2, b). Slotted foundations are most rational with significant inclined, moment and horizontal loads. Therefore, they are best used for agricultural buildings made of three-hinged frames, as well as for industrial building auxiliary purpose of the frame type with a metal or reinforced concrete frame.
Trench foundations
Trench foundations are concreted in trenches with a width of 0.3 - 1.2 m with vertical walls up to 3 m deep with various configurations in plan: cross, T-shaped, I-beams (Fig. 2, v). The verticality of the walls of figured structures is ensured by framing the foundation in terms of narrow slots with a bar working body, especially in frozen and solid soils. The technology of the device is similar to that of slotted foundations. For example (fig. 2, G), under the steel lighting masts with a height of 28 m in frozen soils, trench foundations with dimensions of 5x4 m in terms of complex configuration with a trench width of 0.6 m and a depth of 2.0 m were used.
Single-plate foundations
Improved design columnar foundations on a natural basis are single-plate foundations (fig. 2, e). Their essence consists in cutting a rectangular or square pit, with notches or cuts with a depth equal to the height of the slab. The bottom is cleaned manually, after which the pit (slab) is reinforced and concreted. Slab cuts and cuts serve to reduce material consumption and stress concentration in base soils. To ensure an arched effect in places of rectangular cutouts, their area should not exceed 15 - 20% of the slab area.
conclusions
The above foundations are still in normal operation, which allows us to conclude about their reliability. The proven method for calculating the bearing capacity of the working side surface of shallow foundations can be recommended for use with further improvement. Its essence is as follows:
The load perceived by the lateral surfaces of the described foundation structures can be determined by the formula:
T = m Ʃm f u i f i l i ,
where m - coefficient of work of the concrete surface of the foundation in the ground, taken equal to 0.9;
m f - the coefficient of the working conditions of the soil along the lateral surface of the foundation, taken for loam and sandy loam equal to 0.7; for clays - 0.6 when constructing foundations in the summer, 0.5 and, accordingly, 0.4 - in the winter;
u i - the perimeter of the cross-section of the foundation or slotted wall (trench) at a depth h hm;
l i - thickness i-th layer of soil in contact with the lateral surface of the foundation (walls, trenches), m;
f i - design resistance i-th soil layer along the lateral surface of the foundation, determined according to table. one.
table 1
Design soil resistance along the lateral surfacefoundation |
||||||
The depth of the soil layer from the leveling mark hi, m |
Design soil resistance along the lateral concrete surface of the foundation fi, kPa, with a soil flow rate IL, equal |
|||||
Shallow ... Spelling dictionary-reference
Small, superficial, external; thoughtless, primitive, flat, empty, frivolous, unfounded, shallow, thoughtless, lightweight, simplistic, fluent, frivolous, light, shallow, simplistic, carefree. Ant. deep, ... ... Synonym dictionary
shallow- shallow, short. f. shallow, shallow, shallow and shallow, shallow and shallow; cf. Art. do not use ... Dictionary of pronunciation and stress difficulties in modern Russian
shallow- - Topics oil and gas industry EN shallow horizon ... Technical translator's guide
Adj. 1. Not having great depth; small. Ott. Shallow, shallow. 2. transfer. Not penetrating into the inner essence of something, not affecting the most essential properties, features, ... ... Modern Dictionary Russian language Efremova
Shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, shallow, ... shallow
Internal deep thorough full ... Dictionary of antonyms
shallow- shallow; short shape ok, ok a, ok oh ... Russian spelling dictionary
shallow- cr.f. shallow / k, shallow /, shallow / k /, shallow / ki / ... Spelling dictionary of the Russian language
shallow- A / B and A / C pr see Appendix II shallow / shallow / shallow / and shallow / shallow / and shallow / ... Dictionary of Russian stresses
Books
- Stone Island. Guide, Kozina G. N .. To the north-west of Vologda is Lake Kubenskoe - a large, but shallow body of water, part of the Severo-Dvinskaya water system. There is a monastery on an island called Kamenny, along ...
Off-road riding is often described as an “unearthly” feeling, and this is not surprising. Is it possible to convey the sensations that arise in magical moments of half-flight-half-glide in words?
Every year, hundreds and thousands of virgin soil lovers travel and fly to Sheregesh and Krasnaya Polyana, climb the Aykuayvenchorr ridge in Kirovsk and go to the “far South” or “North” of Cheget after snowfalls. In the US, virgin snow skiing is somewhat of a national ski feature - there are popular spots like the Alta resort in Utah, and special schools that teach snow skiing. In our country, there are not so many specialists in this type of skiing, and only a few of them are ready to teach someone: virgin soil is not a common thing, and spending a rare day of luck on excavations and searching for a ski lost in the snow by a novice rider is not the most interesting pastime.
However, for several years now, a “freeride with guides” program has been operating in the resorts of the Caucasus, and it makes sense for all skiers who want to learn how to ski on the virgin lands to participate in this program, regardless of which region - Krasnaya Polyana, Dombay or Elbrus - you are planning to spend your vacation. The guides in any of the regions are experienced riders, participants and prize-winners of Russian competitions, who know very well the slopes of the mountains on which they work. All of them, as a rule, are instructors, and not only themselves know how and love to ride in difficult conditions (on wet heavy snow, on sastrugs or breaking through crust) and in virgin snow, but they can also correct the technique of other ski lovers. The tips given here, shared by the guides, will help those who are just going off-piste to quickly get used to the unusual, but very attractive, snowy conditions.
Tip 1: get down to the rhythm of the snow
Skating in the virgin soil is very difficult to divide into separate turns, because their implementation requires an impulse, which in deep snow can be the result of only a rhythmic and smooth, without sudden movements, descent. The depth and density of the snow, the steepness of the slope, the speed of the descent, the width of the skis, the depth of the sidecut and even the weight of the skier are the conditions that determine the rhythm of the turns.
Conditions Rhythm and turn pattern
Shallow snow
Light snow Fast rhythm of turns possible
Steep slope Small turning radius allowed
High speed A large number of movement options
Wide skis
Deep side cut

Conditions
Deep snow
Heavy snow Slow turning rhythm required
Gentle slope Large turning radius required
Low speed Narrow range of permissible movements
Narrow skis
Shallow side cut
We must clearly understand that in the virgin soil it is impossible to turn as fast as on the packed snow. In addition, different conditions of deep snow require different speed, intensity and duration of movements.
The key to mastering a smooth and flowing rhythmic descent is ... the feeling of snow. What it is? It is necessary to master the skis and snow enough to feel the resistance of the snow to the movements of the skis with your feet. The goal is to constantly keep the skis in a state of even, without jerking, sliding through the snow by changing the intensity and duration of the impact on the skis. Naturally, the feeling of snow does not come with the first or second descent. It is necessary to spend a lot of time on virgin snow, and preferably accompanied by an experienced instructor who will be able to suggest which elements should be given maximum attention. Of course, you need to experiment - but first you need to master a certain “basic” set of knowledge, learn to move in such a way that the descent is stable, and only then try to expand the boundaries of what is permitted under the given conditions.
Tip 2: stick - go!
A classic technique used for deep snow skiing since the 60s of the last century. The basis of this technique is a very early forward movement of the stick, accompanied by the extension of the new “outer” hand forward and, as a consequence, the twisting of the body inward of the next turn, used as an initiating movement. In other words, immediately after the stick is made with the lower downhill stick, the other stick and arm begin to move forward. Then, after the skis have crossed the line of fall of the slope - at the end of the turn - the skier holds the stick brought forward with the tip down the slope until the next thrust.
The early movement of the stick and arm forward creates a torsional moment of the movement of the body, which helps to facilitate the re-edge of the skis simultaneously with their unloading during the transition from turn to turn. In addition, this movement, since it is directed downhill - across the skis, helps you stay balanced above your feet.
Many are lost in deep snow, which makes it difficult for them to control their skis with their usual movements and make conjugate turns. Strange as it may seem, a stick, put forward and ready for a prick, directs thoughts in a more familiar direction. The result is a smoother (and self-predictable) movement for the skier.

Holding the stick downhill with the tip down the slope during the second half of the turn (after the skis have crossed the fall line) helps you stay in the middle stance, above your feet. In addition, directing the tip of the stick downhill after the skis have crossed the ramp line keeps the torso in the direction of the next turn. And this torso position helps to effectively work the legs to control the skis and in order to feel the resistance of the snow to the movement of the skis and use it.
The main condition, a kind of key to the successful use of this technique, is the inner arm, which is stably held forward and the shoulder, which seems to be interlocked with the forearm and follows it at the moment of the injection. Without this blocking of the muscles of the arm and shoulder and the resulting stopping of the rotational movement of the torso, the body of the skier will twist into a turn. The result of this twisting is usually ... finding the unfastened ski in the fluffy snow.
There are various variations of this technique. Long ago, when a rotational motion of the upper body was considered necessary to initiate a turn, skiers performed a movement with an arm and a stick around the body, across the direction of movement of the skis. Amateurs who deliberately use this technique can still occasionally be found on the slopes.
Another option for performing this movement is with the direction of the stick down the slope and holding the elbow of the hand performing the anticipatory movement quite close to the thigh. In this case, accentuated angulation of the hips is used in combination with a turn of the hips and the upper part of the body downhill to provide powerful rotation of the legs and corresponding counter-rotation of the torso.
The technique of the early movement of the stick forward in the modern version is characterized by the position of the hands. The skier's arms are raised slightly higher and slightly wider to the sides, compared to their position when skiing on a prepared slope. This hand position is much more efficient and allows for precise control of the skis, especially modern models - wide and short, which turn much easier than their predecessors.
Mastering this technique, which is quite easy to use, often gives excellent results - the descent becomes rhythmic and smooth. At the same time, it is possible and even necessary to start mastering this technique on a rolled slope, since it is quite effective not only in virgin soil, but also on steep slopes, and on hillocks (with appropriate amorization - swallowing the hillocks by intense bending). I must say that mastering this technique, like any other element, is much easier under the supervision of an instructor who owns it. Without external control, it is easy to “slide” from moving the stick forward to twisting the torso into a turn.
Examining a flat tire, the car owner often discovers on it side cut of the tire. The consequences of this defect, as a rule, are reduced to short-term repairs and the subsequent replacement of a set of tires. Side cut can be caused by protruding reinforcement, or by a sharp edge of a hole in the hard surface of the road. Side cut of the tire with a knife do from hooligan intentions, or, for example, wanting to avenge an insult.
And sometimes swelling appears on the side surface of the tire, the so-called. "hernia". Fortunately, both her and by contacting a specialized service, that is, to us 😉
However, here you need to think about whether it is worth patching the wheel or it is easier to buy a new one. To do this, combine several factors:
- The cost of new rubber.
- Tread wear.
- Is the cord damaged?
- Damage size.
- Repair price.
How to evaluate tire maintainability
This should be done by professionals, since poor-quality repair of side cuts, in particular repair of a tire cord, is fraught with emergencies on the road. To prevent this from happening, we are waiting for you in our auto-studio!
However, something can be assessed "by eye" - the size of the cut and its direction, whether it is through or superficial. Look at the situation more broadly - if the tread is noticeably worn out, it is better to buy new rubber. And if the wheels are still new, the side cut of the tire is small, and the disks have a non-standard size, you can safely repair it.
Is tire cord repair safe?
To guarantee the normal subsequent operation of tires, longitudinal cuts up to 3.5 cm long and transverse cuts up to 2.5 cm long are accepted for repair.The distance from the tread to the tread should be at least 4 cm. should cause concern.
If the cuts are larger, the repair will be a temporary solution, since the side surface will behave unstable, “play” on the road while the wheel is spinning. After some time, even the best quality patch will start to let air through, and in the end the rubber will have to be replaced.
If the cut is on a truck, you need to be even more careful. It makes sense to "treat" such tires if no more than 10 cord cables are damaged.
Side cut repair technology
Cut, he is side puncture of a tubeless tire, glued only with reinforced patches. A rubber patch without reinforcement is useless. The cut is sealed on both sides - from the inside and from the outside. After inspection, the Center's specialists will advise how many layers of the patch to put on the cut. Their opinion is worth listening to and making a choice in favor of safety.
If the owner has certain skills and the necessary equipment, shallow side cut of the tire can be removed in the garage.
The cut site on both sides is cleaned, degreased, and the edges are slightly grinded, in the form of a saucer. This cavity is filled with wet rubber, onto which a patch is applied.
Adhesion of the patch can be cold or hot ("vulcanization"). The cold method is faster and retains the wheel geometry.
Vulcanization slightly deforms the rubber in the place of gluing, but only with this method it is possible to apply a multi-layer patch with a large cut. Garage repairs will save money, but in artisanal conditions it is difficult to achieve the required quality.
An additional argument for contacting "Wheel Repair" will be the need for a complete check of the tire for leaks. If a cut occurs, small cracks may form next to the damage, they must be identified immediately. Therefore, the masters of the Center are asked to bring a tire for repair along with a disk. Another difficulty is related to balancing the assembled wheel after repair. The patch will upset the balance and it is normal to install an additional 60-80 g balancing weights.