Economic model of Sweden presentation. Swedish economic model
Slide 3
The mixed nature of the Swedish economy, combining market relations And government regulation, predominant private ownership in the sphere of production and socialization of consumption.
Slide 4
Full employment and income equalization Goal
Slide 5
"functional socialism"
Socialism, based not on the elimination of private property and a radical change in production management, but on the implementation by the state of the function of redistributing national income in accordance with the priority of social needs in order to achieve greater social equality.
Slide 6
A priority
Solving problems of social security of their subordinates, employees of enterprises and firms.
Slide 7
The essence of the Swedish management model
The state does not interfere in production activities enterprises
Slide 8
Active labor market policies should minimize social costs market economy
Slide 9
The emphasis is on infrastructural elements and collective funds.
Slide 10
Specifics of the relationship between labor and capital in the labor market
Slide 11
Management style
Considering the individual in a business environment comes first
Slide 12
Equality All people are valuable, regardless of their different abilities
Slide 13
Difference
The Swedish management style is less hierarchical than other cultures: informality in relationships, minor differences in the status of managers and employees, loose and informal planning of the organizational structure.
Slide 14
Control. Even in large Swedish companies, control appears informal and implicit.
Slide 15
Controversies
Swedish model has its own internal contradictions. Employees need to be given the space to make their own decisions, but the boundaries they must not cross must be clearly defined.
Slide 16
Usage
It is necessary to consider it specifically as a Swedish model, because it is associated with some important cultural characteristics of the Swedish nation. Further, as noted above, Swedes are very successful in adapting to conditions of uncertainty. They are not inclined to exaggerate their position in the service hierarchy. All this makes it possible for managers to assign broad responsibility to their subordinates in the business sphere.
Slide 17
Goals
1) Full employment and equality 2) A combination of general restrictive measures and active labor market policies 3) General welfare policies and trade union solidarity policies in the area 4) Full employment without inflation 5) active labor market policies.
View all slides
Ministry of Education of the Republic of BelarusBelarusian National Technical University
Faculty of Civil Engineering
Department of Construction Economics
Subject "Foreign economic activity"
"ECONOMIC ANALYSIS OF SWEDEN"
student, group 312329, correspondence department
Patsenko T.V.
Supervisor
Gurinovich A.D.
Minsk 2015 CONTENTS:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
general characteristics of the country;
characteristics of natural resources;
production (industry, agriculture);
analysis of macroeconomic indicators;
analysis of the country's balance of payments and foreign trade;
characteristics of economic and political relations with
Belarus;
7. conclusion with analysis that we can export and
import from this country. Sweden
flag
coat of arms
Political system
Sweden-
a constitutional monarchy. The Constitution of 1975 is in force.
The head of state is the king. The state is governed by a government led by
with a prime minister who is elected by the Riksdag parliament), based in
1435. Since 1971, it has been a unicameral parliament, consisting of 349 deputies elected by
universal direct and secret suffrage every 4 years. Party or coalition
who receive a majority of seats in the Riksdag elections form a government led by
with the Prime Minister, who holds executive power.
The current King of Sweden since 1973 is Carl XVI Gustaf.
Government system of the Kingdom of Sweden
determined
Constitution
And
others
fundamental laws such as
Law on the Form of Government,
Position
O
Riksdage,
Law
O
succession to the throne and the Law on Freedom of the Press.
King Carl XVI Gustaf Total area: 449,964 km2, third largest country in Western Europe. Europe
Population: 9,723,809 people
Capital: Stockholm (871,952 people)
Large cities: Gothenburg (524,767 people), Malmo (309,912 people), Uppsala (140,454 people)
Language: Swedish; recognized minority languages: Sami, Finnish,
Tornedali dialect of Finnish (Meänkieli), Yiddish, Gypsy (Romani Chib).
Religion: 82% belong to the state Evangelical Lutheran
churches.
Existing in Sweden economic system usually characterized
as a “mixed economy connecting the main forms of ownership:
private, public, cooperative.” About 85% of all Swedish
companies with more than 50 employees are privately owned
capital. The rest comes from the state and cooperatives.
Natural resources
The subsoil of Sweden is rich in metals and poor in mineral fuels.Limited by the location of sedimentary rocks determined
virtual absence of deposits of coal, oil and
natural gas. Swedish iron - ore deposits
are among the richest in the world, both in terms of concentration of ore reserves,
as well as the metal content in it. Among the colored deposits
metals, the most significant are located in Norrland
plateau. This is a deposit of complex sulphide ores in the area
Buliden - Kristineberg, containing: copper, zinc, lead, gold,
silver, gray pyrite, arsenic, lead deposit
(Laiswall) and copper (Aitik).
Sweden is the main exporter of iron ore and the largest in
Europe.
In terms of iron reserves - about 3 billion tons with an average content
metal more than 60% - Sweden ranks second in foreign
Europe (after France).
Industry
Sweden ranks 2nd in Europe in iron ore production. In the countryFerrous and non-ferrous metallurgy are quite well developed, as well as
electrometallurgy.
Swedish steel is of the highest quality.
Sweden produces cars, trucks, ships,
aircraft, computers and electrical appliances. The country is on the first
world leader in the production of ball and roller bearings.
The woodworking industry is well developed. Sweden ranks
a leading place in the world in the development of the pulp and paper industry.
There are also chemical, textile and food processing enterprises in the country.
industry.
Agriculture
Only 3% of the working population is employed inagriculture, but this industry is so
highly developed and mechanized that it
products
enough
Not
only
For
satisfying internal needs, but
and for export. Sweden is self-sufficient
food
on
80%.
Agriculture is dominated by large
enterprises that provide over
90% of the country's food needs.
Leading
industries
are
meat and dairy
cattle breeding
And
bacon
pig farming. They grow wheat, rye,
oats, barley, as well as vegetables and potatoes.
From the food industry
production of dairy and meat products is highlighted
products.
Macroeconomic indicators
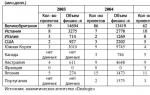
Foreign trade balance
Sweden's export volume, billion US dollarsSweden's import volume, billion US dollars
Major trading partners
NorwayGermany
Finland
Denmark
Great Britain
USA
Netherlands
Export %
10,7
10
7,1
6,7
6,5
6,2
5,3
Import %
8,9
17,5
5,5
8,1
6
2,7
7,8
Economic model
BelarusPreservation of a large public sector in all
main sectors of the economy.
Administrative regulation
monetary incomes of the population and prices for
essential goods.
Preservation of the socialist system
social protection of the population.
Maintaining employment through
system of government orders and a direct ban on
dismissals.
Non-application of bankruptcy proceedings to
unprofitable enterprises
state form of ownership.
Stimulating exports through
various systems of benefits for exporting enterprises.
Sweden
Mixed economy: private,
state and cooperative forms
property.
The most important role of the state
sectors - accumulation and
redistribution of significant
Money to social and
economic goals.
The primary role is played by social
policy.
Full employment and equality, which
depend on price stability
economic growth And
competitiveness.
Progressive taxation and
system of extensive government
services.
Economic ties with Belarus
Sweden is becoming an increasingly important trading partner forBelarus. Since 1999 growth rate of our exports
are constantly growing. It has also become more diversified
commodity structure. Large concerns and companies in Sweden
show a strong interest in the development of long-term
trade economic ties with Belarusian subjects
management.
Diplomatic relations between
Republic of Belarus and the Kingdom
Sweden established 14 January 1992
Sweden is interested in increasing trade and economic cooperation with Belarus.
Currently, indicators of economic cooperation are very positive.
Trade turnover in 2012 maintained its dynamics, the influx of direct Swedish
investments in the Belarusian economy.
Export and import
Belarusian exports for Jan.-Oct. 2014 - 43.21 milliondollars, in 2012 amounted to 74.8 million dollars. USA, in 2011 -
$91.5 million USA, not reaching record levels
2006 at 365.7 million dollars. USA. Main articles
Belarusian exports to Sweden in 2009-2011
were:
potassium
fertilizers;
peat;
tires;
raw
timber;
wire
from
alloy steel; linen fabrics
Imports from Sweden (mainly high-tech) for Jan.-Oct.
2014 – $104.45 million, in 2012 amounted to $209.5 million. USA (in
In 2011, this figure was $217.5 million. USA). The basis of it
consisted of: electric generating sets; tractors and fifth wheels
tractors; cars; communication equipment and parts for it;
flat rolled products; steam boilers; liquid pumps; polymers
ethylene; artificial and prepared waxes; petroleum products; acids,
industrial oils and alcohols; fittings for pipelines, etc.
Slide 1
 Slide 2
Slide 2
 Slide 3
Slide 3
 Slide 4
Slide 4
 Slide 5
Slide 5
 Slide 6
Slide 6
 Slide 7
Slide 7
 Slide 8
Slide 8
 Slide 9
Slide 9
 Slide 10
Slide 10
The presentation on the topic “The Swedish model of economic development” can be downloaded absolutely free on our website. Project subject: Economics. Colorful slides and illustrations will help you engage your classmates or audience. To view the content, use the player, or if you want to download the report, click on the corresponding text under the player. The presentation contains 10 slide(s).
Presentation slides

Slide 1
Swedish model of economic development
The term "Swedish model" appeared in the late 60s, when Sweden began to experience a combination of rapid economic growth and successful political reforms. The image of a successful and serene Sweden still contrasts with the growth of social and political conflicts in the surrounding world.

Slide 3
The Swedish model The main role in the model is given to social policy, social justice, income equalization, smoothing out inequalities, and building democratic socialism on the basis of welfare.
implementation of full employment policy; equalization of income of the population through taxes; high specific gravity public sector of the economy; redistribution budget funds in favor social programs; availability social guarantees all segments of the population (education, healthcare); increased influence of trade unions on all spheres of social economic life countries.

Slide 4
Strengths: full employment and income equalization; redistribution of funds for social and economic purposes centralized system collective agreements with the participation of powerful trade union organizations, solidarity between groups of workers, active policies in a highly developed labor market and a large government sector(sphere of redistribution)
Weaknesses: High politicization, predominance of private property in the sphere of production and non-interference of the state in it government spending, reaching record levels High taxes on wealth

Slide 5
Economy of Sweden
Main industries Resources (timber, iron ore) Hydropower Mechanical engineering Aircraft manufacturing Nuclear energy Armament Automotive telecommunications
In 2012, Sweden's GDP was $368.4 billion, inflation was 0.9% Employment level was 62.2% GNP per capita in Sweden was 373,500 thousand crowns (USD 55,200).
IN economic development Sweden can be distinguished into three stages: (from 1870 to 1914) Sweden turned from an agricultural to an industrial-agrarian country. (from 1920 to 1970) Sweden became industrialized developed country. (from 1970 to the present) Sweden is at the stage of a post-industrial country with high level life that stands out among other states at a fast pace growth.

Slide 7
National idea
The political system, management experience, neutrality in any blocs and associations - this is what we should learn from this country.
Sports Nation Ecologically Obsessed Animal Welfare Free dental services control of imports of alcohol and tobacco products Usual PROS of Sweden
If you have passed the probationary period and entered into an employment contract with the employer, it is almost impossible to fire you from your job, even if you have done something outrageous - the Swedish trade union is so strong.

Slide 8

Similar documents
The emergence of Sweden as one of the most socio-economically developed countries, historical background, cultural influence. The emergence of the term "Swedish model". Goals public policy, the main features of economic development.
abstract, added 11/02/2009
History of the world economy after the Second World War, economic consequences of the war. National programs for economic revival. The stage from the early 90s to the present. The crisis in world markets and its impact on financial system Russia.
abstract, added 02/19/2012
Development of the Japanese economy after the Second World War. The main trends and problems of the Japanese economy at the end of the twentieth century - beginning of XXI centuries. Dynamics of development of foreign trade relations between the Russian Federation and Japan today and development prospects.
course work, added 12/20/2012
Basic approaches to defining and classifying the creative economy. Dynamics of global trade in creative products by different economic groups. Justification of the feasibility of economic transition Russian Federation to the phase of creative development.
article, added 07/24/2018
Development of the world economy. The evolution of the world economy in the second half of the twentieth century. Stages of integration of the world economy. Factors, main features and directions of globalization of the world economy. Problems created by globalization. Centers of world economy.
abstract, added 09/07/2008
The history of the emergence and formation of Swedish economic model, its characteristics and specifics. Status and description of Sweden's foreign economic relations in modern conditions, their prospects and development. Rates of growth industrial production countries.
abstract, added 04/14/2015
Main features, models and prerequisites for the emergence of a mixed economy. The state of the West German economy after the Second World War. Creation of the German mixed economy model. Development of the German economy and its promotion to leading positions in Europe.
course work, added 03/24/2015
The role of industrialized countries in the world economy. Features of democratic corporatism and the social market model of a modern market economy. Economic development and integration processes in Western Europe after World War II.
test, added 11/17/2015
Analysis of the period of occupation in the post-war history of Japan. The place and role of the Emperor in the new Constitution; socio-economic reforms. The Korean War and Japan. The specific nature of economic recovery and features of the country’s political development.
course work, added 11/08/2011
Conditions and factors for the development of the Japanese economy after World War II. Features of the structure of private entrepreneurship. System of financing, management and crediting. Japan in international economic relations, strengthening the position of the yen.
The Swedish model of economic development The term “Swedish model” appeared in the late 60s, when Sweden began to experience a combination of rapid economic growth and successful political reforms. The image of a successful and serene Sweden still contrasts with the growth of social and political conflicts in the surrounding world.

Swedish model Swedish model The main role in the model is given to social policy, social justice, income equalization, smoothing out inequalities, and building democratic socialism on the basis of welfare. full employment policy implementation of full employment policy; equalization of income equalization of income of the population through taxes; high share of the public sector of the economy; redistribution of budget funds redistribution of budget funds in favor of social programs; availability of social guarantees availability of social guarantees to all segments of the population (education, healthcare); influence of trade unions increased influence of trade unions in all areas socio-economic life of the country.

Strengths: full employment and income equalization; redistribution of funds for social and economic purposes, a centralized system of collective agreements with the participation of powerful trade union organizations, solidarity between groups of workers, active policies in a highly developed labor market and a large public sector (sphere of redistribution) Weaknesses: Highly politicized, the predominance of private property in the sphere of production and non-interference in government spending at record levels High taxes on wealth

Economy of Sweden Main industries Resources (timber, iron ore) Hydropower Mechanical engineering Aircraft manufacturing Nuclear energy Armament Automotive telecommunications 1. In 2012, Sweden's GDP - $368.4 billion, 2. inflation - 0.9% 3. Employment level - 62.2% 4 .GNP per capita in Sweden thousand kroner (US dollars). Three stages can be distinguished in the economic development of Sweden: (from 1870 to 1914) (from 1870 to 1914) Sweden turned from an agricultural to an industrial-agrarian country. (from 1920 to 1970) (from 1920 to 1970) Sweden became an industrialized country. (from 1970 to the present) (from 1970 to the present) Sweden is at the stage of a post-industrial country with a high standard of living, which stands out among other countries due to its high growth rates.


National idea The political system, management experience, neutrality in any blocs and associations - this is what we should learn from this country. -Sports nation -Environmental obsession -Animal protection -Free dental services -Control of import of alcohol and tobacco products PROS Usual PROS of Sweden If you have passed the probationary period and entered into an employment contract with the employer, it is almost impossible to fire you from your job, even if you have done something wrong - It's amazing how strong the trade union in Sweden is. The country has a high rating in the environmental category, and 95% of the population is satisfied with the quality of drinking water.

Economic indicators Sweden and Ukraine for 2012. IndicatorsSWEDENUKRAINE GDP, billion dollars $368.4 billion, $173.9 billion GDP per capita, dollars $ $ 7300 Gold reserves, billion dollars $ 125.7 $ 36.4 Unemployment rate, % 0.9% 1.8%

Summary The Swedish experience is that strong and well-organized labor market policies are highly productive and in fact effective way use of taxpayers' money. Social politics and labor market regulation is precisely what attracts most attention in the Swedish model.