A balanced budget suggests. Balanced budget
Rice. 1.2 Deficit and surplus of the state budget
This or that budget balance is not always evidence of a change in the macroeconomic situation; it may be a consequence of the fiscal policy pursued by the government aimed at solving certain macroeconomic problems.
In order to isolate the impact on the budgetary balances of targeted government measures, the "full employment budget" is used - the state of the budget in the conditions of the functioning of the economy at the natural rate of unemployment.
Budget deficits and surpluses are related to output, making it possible to distinguish between structural and cyclical deficits.
The deficit included in the structure of income and expenditure in the formation of the budget is called structural . It is calculated as the difference between current government spending and revenues that could go to the budget under the condition of full employment at existing system taxation.
However, the real deficit may be larger than the structural one. The main reason for this in countries with market economy is a decline in production. It leads, on the one hand, to a reduction in the income of entrepreneurs and the population, which reduces tax revenues to the budget, and, on the other hand, to an increase in unemployment payments and other social programs, which increases state spending. The difference between real and structural deficit is called the cyclical budget deficit. Cyclical budget deficit is a government budget deficit caused by an automatic reduction in tax revenues and an increase in government transfers against the backdrop of a downturn in business activity.
If the actually observed budget deficit is less than the structural one, the difference between the structural and real deficit is called cyclical surplus . In the case when, during the formation of the budget, an excess of income over expenses is laid down, they speak of a surplus of budget revenues.
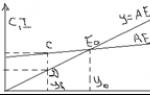
2 Balanced budget and its multiplier
2.1 Balanced budget
Balanced budget A budget that balances expenditures and revenues.
Budget balance is a mandatory requirement for the preparation and approval of the budget. A balanced budget is designed to ensure the normal functioning of authorities at all levels. The imbalance of even a small part of the budgets leads to a delay in the financing of state and municipal orders, to failures in the system of estimated and budgetary financing, giving rise to non-payments in the national economy of the country.
The best option to ensure a balanced budget is to develop a deficit-free budget, in which the volume of expenditures, including the costs of servicing and repaying the state (municipal) debt, does not exceed the amount of income. If, however, it is not possible to avoid a budget deficit, even after exhausting the usual sources of financing, then in order to balance the budget, one has to resort to various forms of borrowing, which requires minimizing the size of the budget deficit at all stages of the budget process.
The balance of the budget is achieved by different methods: some of them are used in the formation of the budget, others - in its execution. The methods of balancing the budget, widely used in the practice of budget planning, include:
Limitation budget spending taking into account the economic opportunities of society and the volume of centralized revenues;
Improving the mechanism for distributing revenues between budgets different levels, adequate distribution of spending authority between them;
Identification and mobilization of reserves for the growth of budget revenues;
Building an effective system of budgetary regulation and financial assistance in the field of interbudgetary relations;
Planning the directions of budget expenditures that positively affect the growth of income and at the same time ensure the solution of the social and economic problems facing society at minimal cost and with maximum effect;
Reducing the scale of the public sector of the economy based on the reasonable privatization of state property; austerity of expenses by excluding unnecessary costs from their composition, not due to extreme necessity;
Use of the most effective forms of budgetary borrowings that can ensure real cash flows from financial markets.
In the course of budget execution, balance is achieved through:
Introduction of a procedure for authorizing budget expenditures;
Strict observance of the established limits of budgetary obligations, oriented towards real incoming income;
Determining the optimal timing of spending; use of the mechanism of reduction and blocking of budget expenditures;
Improving the system of budget financing based on the gradual cessation of subsidies to enterprises and the introduction of full property liability of economic entities for the fulfillment of their obligations to the state and partners;
Mobilization of additional reserves for the growth of budget revenues; successive financial control for targeted, economical and efficient spending budget funds;
Providing financial assistance, in its various forms, by other budgets; use of budgetary reserves, etc.
Balanced budgets means a situation where all budget expenditures are covered by its revenues. Only this situation is normal.
Depending on the features economic development States can distinguish 3 states of the budget:
deficit (income< расходов);
balance (income = expenses);
surplus (income > expenses).
A balanced budget is designed to ensure the normal functioning of authorities at all levels. The imbalance of even a small part of the budgets leads to a delay in the financing of state and municipal orders, to failures in the system of estimated and budgetary financing, giving rise to non-payments in the national economy of the country. That is why a balanced budget is especially important for Russia, where financial position during the reform period was characterized by an acute shortage of budgetary resources due to the crisis state of the economy.
The best option to ensure a balanced budget is to develop a deficit-free budget, in which the volume of expenditures, including the costs of servicing and repaying the state (municipal) debt, does not exceed the amount of income. If, however, it is not possible to avoid a budget deficit, even having completely exhausted the usual sources of financing, then in order to balance the budget, one has to resort to various forms of borrowing, which requires minimizing the size of the Budget Deficit at all stages of the budget process.
The balance of the budget is achieved by different methods - some of them are used in the formation of the budget, others - in its execution.
To the methods of balancing the budget, widely used in practice budget planning, relate:
limiting budget expenditures, taking into account economic opportunities society and the volume of centralized revenues;
improving the mechanism for distributing revenues between budgets of different levels, adequate to the distribution of spending authority between them;
identification and mobilization of reserves for the growth of budget revenues;
building an effective system of budgetary regulation and provision of financial assistance in the sphere of interbudgetary relations;
planning the directions of budget expenditures that have a positive effect on income growth and at the same time ensure the solution of social and economic problems facing society at minimal cost and with maximum effect;
reduction of the scale of the state sector of the economy on the basis of reasonable privatization of state property;
austerity of expenses by excluding unnecessary costs from their composition, not due to extreme necessity;
use of the most effective forms of budgetary borrowings that can ensure real cash flows from financial markets.
In the course of budget execution, balance is achieved through:
introduction of a procedure for authorizing budget expenditures;
strict adherence to established limits budget commitments, focused on real incoming income;
determining the optimal timing of expenditures;
use of the mechanism of reduction and blocking of budget expenditures; improving the system of budget financing based on the gradual cessation of subsidizing enterprises and the introduction of full property liability of economic entities for the fulfillment of their obligations to the state and partners;
mobilization of additional reserves for the growth of budget revenues;
consistent financial control over targeted, economical and efficient spending of budgetary funds; provision of financial assistance, in its various forms, by other budgets; use of budgetary reserves, etc.
At the stage of budget execution, additional factors affecting the balance of the budget are, on the one hand, the methods of operational regulation of budget flows, which make it possible to maneuver budget funds with the greatest efficiency, and on the other hand, the mechanism for reducing budget expenditures and budget reserves, using which the executive authority implements financing of sudden, unforeseen expenses.
At present, the balance of the budget must be ensured at every level of management of the efforts and professional skills of the employees of the relevant authority. Under these conditions, the stability of the budget and the responsibility of the financial body for its provision are of great importance.
Deficit and surplus, ways to overcome the deficit.
In economic theory, there are several signs of the classification of the budget deficit:
Depending on the cause:
emergency, which is based on extraordinary circumstances (wars, natural disasters, etc.);
crisis, caused by a decline in the development of the economy;
interbudgetary deficit is typical for territorial budgets and arises as a result of a decrease in revenues or an increase in expenditures as a result of decisions made by authorities.
Depending on the economic content and directions of influence:
active, through the management of which it is possible to stimulate or discourage the socio-economic development of the state as a whole or individual territories;
passive, i.e. a deficit that no one manages. typical for developing countries.
According to the nature of occurrence:
random (cash), which occurs due to cash gaps in receipt and expenditure of funds;
real, which is associated with a real lag of income from expenses.
Depending on the relationship with the size of public debt:
primary, calculated as the difference between income and expenses, excluding interest payments on debt;
secondary, calculated taking into account debt service costs.
According to the budget code, the size of the deficit federal budget approved federal law on the federal budget for the next fiscal year and the planning period, cannot exceed the size of the oil and gas deficit of the federal budget.
Subject's budget deficit Russian Federation should not exceed 15 percent of the approved total annual budget revenues of the subject of the Russian Federation, excluding the approved amount of gratuitous receipts.
The deficit of the local budget should not exceed 10 percent of the approved total annual volume of local budget revenues, excluding the approved volume of gratuitous receipts and (or) receipts of tax revenues for additional deductions.
Sources of financing the budget deficit in accordance with the budget code:
Internal sources (allowed for use by all authorities):
loans received from credit institutions in the currency of the Russian Federation;
state and municipal loans carried out by issuing valuable papers in the currency of the Russian Federation;
budget loans received from budgets of other levels;
proceeds from the sale of property owned by the state or municipality.
External sources (allowed to be used only by the authorities of the Russian Federation and in exceptional cases by the authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation):
loans foreign states, banks, international financial institutions provided in foreign currency;
government loans carried out in foreign currency by issuing securities.
State loan - a loan in which the borrower is the state, attracting resources in the market to cover government spending on terms of payment and repayment.
Subjects: creditor - legal and individuals; the borrower is the state. An object: government spending. The source of interest payment is budget revenues. Role - covering the budget deficit without using money issue.
Borrowers and lenders in the public sector credit relations can change places, which is essential feature. Acting as a creditor, the state, through central bank makes loans:
specific industries or regions experiencing a special need for financial resources, if the possibilities of budget financing have already been exhausted, and loans from commercial banks cannot be attracted due to market factors;
commercial banks in the process of auction or direct sale of credit resources in the interbank credit market.
The state acts as a borrower in the process of placing government loans or in carrying out operations in the government short-term securities market, attracting funds to cover budget deficits, without using money emission. The main form of raising funds is the issuance of government bonds and other types of securities.
The essence of the state loan is manifested through the functions it performs:
budget system russia
Table 1. Functions of the state loan
|
Function name |
|
|
fiscal |
State credit is a means of mobilization financial resources states. With the help of this function, the state more evenly distributes tax burden in time. severity tax burden depends on the terms of borrowing funds and interest on the loan paid by the borrower. The higher the amount of debt, the greater part of the funds is directed to its service. |
|
Regulatory |
The state directly or indirectly affects the state monetary circulation, level interest rates, the production process, employment of the population, and also contributes to the redistribution of funds between the territories of the state. |
|
Control |
Associated with control over the funds raised by the state and with the timeliness of payment of interest |
Along with these functions, according to some authors state credit the function of stimulating (or restraining) economic growth is also inherent.
BALANCED BUDGET
BALANCED BUDGET
(balanced budget) Equality between the revenue and expenditure parts of the state budget. If the budget is balanced, the state does not need to borrow additional funds and thus increase the government debt. With constant economic fluctuations, it is impossible, and not necessary, to draw up a fully balanced budget every year. However, some economists are sure that the budget should be, on average, balanced in phases. business cycle(trade cycle). Other economists believe that there is no point in making a balanced budget, and argue that in any case the very definition of a budget deficit (budget déficit) opens up such a wide scope for discussion that any argument becomes meaningless. For example, should the budget be cyclically adjusted? at nominal or real rate percent should provide for interest payments by the state on the existing public debt? Should the budget include interest payments on public enterprise debt and returns on assets national fund insurance? The Maastricht Treaty does not contain a requirement to maintain balanced budgets, but establishes a limit for the budgets of EU member states in the form of a maximum allowable budget deficit of 3% of GNP.
Economy. Dictionary. - M.: "INFRA-M", Publishing house "Ves Mir". J. Black. General editorial staff: Doctor of Economics Osadchaya I.M.. 2000 .
BALANCED BUDGET
a budget that balances expenditures and revenues.
Raizberg B.A., Lozovsky L.Sh., Starodubtseva E.B.. Modern economic dictionary. - 2nd ed., corrected. Moscow: INFRA-M. 479 p.. 1999 .
Economic dictionary. 2000 .
See what "BALANCED BUDGET" is in other dictionaries:
Equality of government spending with total receipts minus government borrowing. English: Balanced budget See also: Balance of the state budget Financial vocabulary Finam ... Financial vocabulary
A budget in which expenses match income...
balanced budget A budget that balances expenditures and revenues... Dictionary of economic terms
Balanced budget- (BALANCED BUDGET) is achieved when government spending on goods and services (g) equals tax revenue less transfer payments (t); … Modern Money and Banking: A Glossary
Equality of government spending on goods and services to net tax revenues within the business cycle. At the same time, the budget deficit that occurs during periods of downturn in business activity is offset by a budget surplus during periods ... ... Financial vocabulary
Civilization is a stage in the development of society where nothing can be done without funding. Budgeting is the art of distributing frustrations evenly. Maurice Stans, Director of the US Budget Office The ideal politician votes for everything... ... Consolidated encyclopedia of aphorisms
- (see BALANCED BUDGET) ... Encyclopedic Dictionary of Economics and Law
Equality of government spending on goods and services to the volume of tax revenues in the long run. Fiscal deficits that occur during periods of downturn in business activity are offset by budgetary surpluses during periods of prosperity. Business vocabulary... Glossary of business terms
cyclically balanced budget- Equality of government spending on goods and services with net tax revenues within the economic cycle: the budget deficit that occurs during periods of downturn in business activity is offset by a budget surplus during periods ... ...
balanced neutron budget- - [A.S. Goldberg. English Russian Energy Dictionary. 2006] Topics energy in general EN balanced neutron budget … Technical Translator's Handbook
Books
- Kudrin system. The Story of a Key Economist in Putin's Russia, Pismenny Evgenia. What is this book about The book of Evgenia Pismenny is the history of Russian power and Russian economy, told on behalf of those people who created it: ministers, deputies, economists and ...
The concept of a balanced and unbalanced budget
In our country there is a three-level system of budgets. The upper level is the federal budget, the second is the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, the third is the budgets municipalities (local budgets). First of all, it is worth deciding what a budget is.
The ideal situation is when the budgets of all levels are balanced, i.e. budget revenues are equal to its expenditures. But this happens extremely rarely, more often there is a budget deficit, i.e. the excess of expenditures over budget revenues as a result of the influence of various kinds of economic, political and other factors. A surplus is the opposite situation, it is an extremely rare phenomenon for a modern economy. The presence of a small deficit has a certain stimulating effect on the economy, spurring its individual directions towards development and more efficient operation, while a surplus, on the contrary, is not a sign of effective use budget revenues.
Remark 1
World experience shows that a level of budget deficit that does not exceed 3% of GDP is considered safe. In the 1990s, the budget deficit in Russia reached quite large values, especially in 1997 (95.4 billion rubles), and the authorities were forced to sequester (reduce) the expenditure side of the budget.
Causes of deficiency
As already mentioned, the deficit is the excess of the expenditure side of the budget over the revenue. There are a number of reasons why a deficit budget may develop:
- Decline in industrial production
- Economic crises
- Emergence of emergencies, natural disasters
- Inefficient work financial system
- High level of corruption
- High level of shadow economy with inefficient tax policy
Despite many reasons. Many of which are constantly present in the economy, there is a limiting level of deficit for the budget of each level, it is determined by law in the Budget Code of the Russian Federation.
The presence of a budget deficit is important to distinguish from the situation of cash gaps - a situation in which income and expenses are separated over time, which leads to a lack of funding in a specific period of time. In addition, the budget deficit is of a planned nature, since it is laid down in the budget initially when it is drawn up.
Sources of financing the budget deficit
The rule of balancing the budget is one of the fundamental for the normal development of the state economy. In scientific circles, it is believed that the problem is not the existence of a deficit, but the ways to cover it.
Definition 2
Under the financing of the budget deficit understand the attraction of resources obtained through the implementation of government loans, and their direction to cover the negative budget balance.
The sources of financing the budget deficit are determined when the budget for the next financial year is adopted. These sources can be divided into 2 groups: external and internal.
External include:
- State loan in foreign currency through the issue of securities on behalf of the Russian Federation.
- Loans received from foreign countries, banks, international organizations in foreign currency
Domestic sources of financing the budget deficit:
- Loans granted credit institutions in national currency
- State loan through the issuance of securities
- Budget loans provided by budgets of other levels of the budget system
In the practice of the Russian economy, there are still some ways to cover the budget deficit, for example, raising income from the sale of part of state reserves, privatization, and income from state entrepreneurial activities.
THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND SCIENCE
FEDERAL AGENCY FOR EDUCATION
STATE EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION
HIGHER PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION
"TYUMEN STATE UNIVERSITY"
INSTITUTE OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
SPECIALTY "Finance and credit
Subject: budget law
On the topic of: Budget balance
Completed:
Student __5 course
9____ semester
Tyumen, 2009
Introduction
Modern economic theory pays great attention to the problem of deficit and balance of the budget. The reason for this is the rapid growth of states with huge budget deficits.
On the present stage development of the world economy, there is not a single state that is not familiar with these phenomena. The world has common economic laws and principles for all, which makes it possible to predict the future economic situation countries at various stages of development.
In this regard, one of the important tasks economic policy state is to find the optimal solution to the problems of the deficit budget and its balance.
The implementation of economic reforms in the Russian Federation has changed the basis for the functioning of the country's budget system and the relationship between bodies state power different levels, which required the development of a methodology for the formation of a new budget mechanism.
The reduction of irrational government spending has led to positive changes in the structure of budget expenditures, a deficit-free federal budget, and the rejection of its emission financing.
In this paper, we will consider the issues of budget deficit and surplus, as well as the problem of budget balance.
The concept and essence of the budget
The budget is the most important financial category, an integral part of state and municipal finance. The essence of the budget is determined not only by the essence of the priority category of finance in relation to it, but also by the essence of the state and the socio-political system. With all socio-economic formations, the budget satisfies the needs of the state in cash.
The budget functions within the framework of a relatively separate financial system of the state. Such isolation is due to the fact that any state is called upon to protect the national interests of citizens. The budget sets the initial parameters for the balance of social and economic policy, represents the ratio of the goals of the development of society and the means to achieve them. The specific forms of this balance are the relationships between accumulation and consumption, between economic efficiency and social justice, between different models of economic development.
On the one side, distinguishing feature budget is that it is focused directly on the interests of citizens. But no less important feature of the budget is that it is related to the sphere of redistribution and consumption of the social product. As is known, the method of distribution is determined by the mode of production, however, redistributive relations, having relative autonomy, can either slow down or contribute to the production process, be a factor in increasing labor productivity.
On the other hand, the specifics of the budget is to focus on the economic growth and increase in material wealth. This expands the freedom of choice in the sphere of redistribution and opens up more opportunities for the implementation of the state's economic policy.
The budget reflects the cyclical nature of the development of society and its dialectics, when the old is not absolutely denied, but everything positive in it is perceived and assimilated at a new stage of development, which is the key point in considering the role and significance of the budget. The budget must be considered as a historical and economic category, inextricably linked with the functioning of the state.
The state budget is the most important financial document country. It is a set of financial estimates of all departments, public services, government programs, etc. It defines the needs to be met at the expense of the state treasury, as well as the sources and amounts of expected revenues to the state treasury.
The activity of the state in the formation, consideration, approval, execution of the budget, as well as the preparation and approval of a report on its execution (the wording applies to budgets of all levels included in the budget system of the Russian Federation) is called budget process.
The budget system of the Russian Federation includes the budgets of the following levels: Federal budget; budgets of subjects of the Russian Federation ( regional budgets); municipal budgets (local budgets)
If the planned budget revenues exceed the budget expenditures, then this is called a budget surplus (or budget surplus). If planned budget expenditures exceed budget revenues, then this is called a budget deficit (or budget deficit). When, during the execution of the budget, the level of the budget deficit exceeds the indicator established during the approval of the budget, or there is a significant decrease in the expected budget revenues, the representative body of power (based on the proposals of the executive body) decides to introduce statutory cost reduction mechanism. Such "cutting" of budgeted expenditures is called sequestration.
Let us consider in more detail the issues of budget deficit and surplus.
Budget surplus
Budget surplus - the excess of budget revenues over its expenditures. Since the centralization of financial resources in the hands of the authorities always reduces the financial capabilities of economic entities, preventing them from better equipping production, switching to new technologies faster and thereby achieving more efficient economic results, in connection with this, excessive mobilization of revenues to the budget only harms.
It is precisely because of this negative impact of the budget surplus on the economy that the legislation of many countries contains a legal norm prohibiting the formation and adoption of a budget with an excess of income over expenditure.
In Russia Budget Code The Russian Federation stipulates that any budget (federal, regional, local) must be drawn up and approved without a budget surplus. If, however, during the preparation or consideration of the draft budget, an excess of revenues over expenditures is predicted, then before the budget is approved, it is necessary to take measures to eliminate the budget surplus in the following sequence: reduce the attraction of income from the sale of state (municipal) property, reduce revenues to the federal budget from the sale state reserves and reserves; provide for the allocation of budgetary funds for additional repayment of debt obligations; increase budget expenditures, including by transferring part of revenues to budgets of other levels.
If it is impractical to list the measure, it should be reduced tax income budget by amending and supplementing tax law RF.
If a budget surplus is discovered in the process of budget execution, then here its presence cannot be unequivocally assessed positively.
The budget surplus resulting from a more economical and efficient use of budgetary funds with 100% financing of budgeted expenditures is a positive phenomenon.
However, if higher budget revenues were received only as a result of a favorable economic situation, were the result of savings, a boom or underfunding of expenditures, and the like, then there is no reason to positively assess the budget surplus. But whatever the reason for the formation of a budget surplus, it is necessary to take measures to preserve budgetary funds that are not intended for spending within the approved budget. As a rule, funds received from a budget surplus are used to replenish reserves, to additionally pay off debt obligations, and to cover expenses provided for in the budget for the next financial year.
The federal budget surplus for 2009 will amount to 1 trillion 913 billion rubles.
According to the Ministry of Finance: federal budget revenues in 2009, in accordance with the updated plan, will reach 10 trillion 908 billion rubles or 21.2% of GDP, and expenditures - 8 trillion 995 billion rubles or 17.5% of GDP.
In 2010, revenues in accordance with the updated plan will amount to 11 trillion 733 billion rubles or 19.8% of GDP, expenses - 10 trillion 320 billion rubles or 17.4% of GDP. The surplus will amount to 1 trillion 413 billion rubles or 2.4% of GDP.
Incomes in 2011 are estimated at 12 trillion 839 billion rubles or 19% of GDP, expenses - 11 trillion 318 billion rubles or 16.7% of GDP. The federal budget surplus in 2011 was 1 trillion 521 billion rubles, or 2.2% of GDP.
In 2009, it is planned to allocate 1 trillion 281.4 billion rubles for national issues, or 14.4% more than in 2008, for national defense - 1 trillion 266.8 billion rubles, which is 23.1% more than in 2008, on the national security and law enforcement - 1 trillion 085.3 billion rubles (an increase of 30.6%), for the national economy - 1 trillion 026.7 billion rubles (+ 28%), for housing and communal services - 107.2 billion rubles (an increase of 65, 3%), on guard environment- 13.8 billion rubles (+38.3%), for education - 432.2 billion rubles (+24.9%), for culture and cinematography and the media - 113.9 billion rubles (an increase of 20.9%) , for healthcare, physical culture and sports - 357 billion rubles (+19.2%), for social policy- 324.9 billion rubles (a decrease of 6.8%), 2 trillion 986.3 billion rubles (+15.3%) will be allocated for interbudgetary transfers.
The federal budget for 2009-2011 is calculated in accordance with inflation of 7.5-8.5% in 2009, 5.5-7% in 2010 and 5-6.8% in 2011.
In accordance with the updated forecast of the socio-economic development of the Russian Federation, in 2009 GDP will reach 51 trillion 475.3 billion rubles, an increase of 6.7%, in 2010 - 59 trillion 146 billion rubles (an increase of 6.6%) and in 2011 - 67 trillion 610 billion rubles (+6.2%).
Urals oil prices are expected to average $95 per barrel in 2009, $90 per barrel in 2010 and $88 per barrel in 2011 4 rubles per dollar, in 2010 - 26.6 rubles per dollar, in 2011 - 28 rubles per dollar.
The volume of the reserve fund by 2011 will reach 6 trillion 761 billion rubles, and the fund national welfare- 6 trillion 457.8 billion rubles.
In 2009 reserve fund will amount to 5 trillion 147.5 billion rubles, and the National Welfare Fund - 3 trillion 717.2 billion rubles or 7.2% of GDP. In 2010, these funds will reach 5 trillion 569 billion rubles and 2 trillion 700.8 billion rubles, respectively.
Budget deficit
Tutoring
Need help learning a topic?
Our experts will advise or provide tutoring services on topics of interest to you.
Submit an application indicating the topic right now to find out about the possibility of obtaining a consultation.