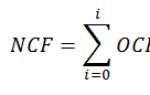An example of an indirect tax. tax code
Many people do not even suspect that they pay daily to the state treasury. a large number of fees. This happens at every step: when buying food for dinner, purchasing fashionable imported new clothes, when paying for the services of a beautician or hairdresser. And invisible indirect taxes are "guilty" of this. Today, their role in the development of the economy Russian Federation it is difficult to overestimate. They not only replenish the budget, but also regulate different areas market.
All taxes are divided into two large groups - direct and indirect. What is the principle of this separation? The classification is based on the following signs:
- the time at which the tax is calculated and paid;
- the relationship between the subject and the object of taxation.
Direct taxes are paid by the same person (natural or legal) who owns the object of taxation. For instance, self employed(here he is the subject of taxation) for the month he received a certain profit from sales (object). Now he must pay the amount established by law from this profit. Direct taxes are also levied on real estate.
Indirect taxes are also levied on the taxpayer, but with one essential feature: they are actually paid by another person. For example, a factory (entity) produces office supplies (entity) and sells them. The manufacturer pays VAT on the sale of office supplies, but this amount is already included in the price the buyer pays. Thus, de facto, the indirect tax is not paid by the subject of taxation itself, but by another person.
Types of indirect taxes:
- universal, which are included in the cost of any product or service (the most common example is VAT or value added tax);
- individual, included in the price of goods or services of a special type (this includes excise taxes, taxes on the purchase of jewelry, on the purchase and sale of real estate);
- fiscal monopolies - payments for obtaining documents issued only by the state, that is, the state acts as a monopoly in this area (for example, fees for obtaining licenses and permits);
- customs duties that are paid by importers and exporters of products (in fact, they are included in the cost of goods).
What are indirect taxes for?
Indirect taxes perform the following main functions:
- fiscal - that is, providing the state with monetary funds;
- regulatory - they either encourage any sector of the economy, or they slow down its development.
VAT and top-up state budget

VAT (value added tax) is the youngest type. The French economist M. Loret is called his "father". V tax system In the French Republic, VAT appeared only at the end of the 50s of the last century. Now it operates in 137 states. There is no value added tax in the US, but there is a sales tax.
Thanks to VAT, the state budget receives additional funds. This value is created at all stages of the production of goods. The percentage that the buyer pays depends on the type of product.
In theory, value added is the difference between the value of the product sold and the value material values who used to make this product. However, in real practice, it is very difficult to calculate the added value from the total.
Economists highlight the following main features of VAT. First, it targets final consumption. Unlike excise taxes and duties, it performs only a fiscal function (that is, provides the state budget with additional funds). Also, VAT differs from excise taxes and duties in that it is levied on all groups of goods and services.
Since 2004, the VAT rate in the Russian Federation has been 18%. Some groups of goods (for example, intended for children) are taxed at a reduced rate, while others are not taxed.
Excise taxes - economy regulators
Like VAT, excise taxes are included in the price of the item and paid by the buyer. Usually they are set for products of high value and for those goods that are produced by the state as a monopolist.
Among the goods on the sale of which excise taxes are established are alcoholic beverages, cigarettes and other tobacco products, cars, jewelry, firearms and gas weapons, diesel fuel, etc. Excise taxes are levied on gambling and lotteries.
The imposition of excise taxes on some goods affects their production and final consumption. These products are becoming more expensive, so people are cutting down on the consumption of excisable goods. Manufacturers, under the influence of a significant reduction in demand, are forced to reduce the volume of batches. Finance naturally flows into other areas of the economy.
The amount of excise duty is calculated using the established rates. They are specified in article 193 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The taxpayer is obliged to report on excise taxes on a monthly basis. Fees are paid based on sales results.
Customs duties
Customs duties are levied by the customs authorities of the state on export, transit and import goods upon import and export. Payment of such tax - required condition external economic activity.

This type of levy replenishes the state budget and protects the domestic market from oversaturation with foreign goods.
There are several types of customs duties: import (or import); export (or export), which in the Russian Federation apply only to raw materials; transit (on this moment zero transit duties are established in Russia). WTO recommends completely eliminating transit duties.
Customs duty rates can be calculated in different ways. Ad valorem duties are determined as a percentage of the customs value (for example, 6% of the established price of the goods).
This method is convenient for more expensive items. Specific fees are characterized by the collection of a specific sum of money for an established unit of production. This method is convenient for bulk cargo. The mixed method consists in combining the two previous ones. You need to pay the largest of the amounts received.
In the Russian Federation, import duty rates depend on the country from which the goods come. The preference is given to the countries of the "third world" and the states of the CIS.
Exploring the advantages and disadvantages of indirect taxation
Benefits of indirect taxes:
- Indirect taxes enter the budget regularly and quickly.
- They have a high profitability for the state budget, because almost all groups of goods and services are taxed with them.
- They are convenient for the consumer of goods and services, because they are already included in the cost of the final product.
- To regulate the collection of this type of taxes, it is not necessary to additionally expand the staff of the tax service.
- Convenience: payment takes place at the time of purchase of goods, there is no need to go additionally to any state authority, fill out the documentation.
- There is no compulsory character.
Disadvantages of Indirect Taxes:
- A number of economists argue that the very existence of indirect taxes contradicts the first law of A. Smith - justice, because they in no way take into account the income of the paying person.
- The rights of producers of goods and services are also violated. To establish the rate, government departments interfere in the production process, sometimes violate the accepted technology.
- Due to the volatility of consumption of certain goods, it is often difficult to predict profit from indirect taxes.
- Profits are limited. The entrepreneur does not always have the opportunity to increase the value of the goods in accordance with the current tax rate.
How is it done? This article will help you learn all the nuances of paying taxes for entrepreneurs.
LLCs can use the simplified taxation system. you will find guidelines to help you use this system.
Is it necessary to pay tax on the property of organizations. You will find out about this.
Direct and Indirect Taxation: Paths to an Ideal Economic System
For the efficient operation of the tax system, it is necessary to determine the ideal ratio of direct and indirect taxes. It is their share distribution that allows you to find out what methods the state budget is formed by - fiscal or regulatory.
There are several taxation schemes in the world today:
- Anglo-Saxon - preference is given to direct taxes that are collected from individuals(Great Britain, Australia, Canada, etc.);
- Eurocontinental - a large share of indirect fees, deductions in most cases go to social benefits;
- Latin American - the prevalence of indirect taxes, which is explained by high level inflation;
- mixed model - a combination of features of different schemes is chosen in order to reduce the dependence of the budget on a particular type of taxes.

At this stage of development, the Russian Federation combines the features of the Euro-continental and Latin American schemes.
The model operating in the country is associated with the level of economic development. Direct taxes can function successfully only in a country with high socio-economic development. The taxpayer must have a good stable level of income and real estate. Indirect taxes are levied automatically and do not depend on the standard of living.
Conclusion
Indirect taxes in modern world exist in the form of a premium to the price of a product or service. De facto, the purchaser of the product pays. The manufacturer deducts the amount received from sales to the state budget. The most common types of indirect taxes are VAT, excise taxes and customs duties.
VAT (or value added tax) is imposed on almost all groups of goods and services. Its main function is fiscal. Excise taxes are not only a means of replenishing the state budget, but also a regulator of the economy.
Customs duties are imposed on imports, exports and transit. Often interest rate depends on interstate relations.
Indirect taxes have a number of pros and cons. Proceeding from different points of view, their “invisibility”, convenience and mechanism of budget revenues are interpreted.
Despite this, in most parts of the world, indirect taxes prevail over direct taxes. This trend depends both on the socio-economic level of the country (in developing countries, direct taxation will not be effective), and on the political regime.
In contact with
A special tax is called, which is levied on certain types of goods and operations with these goods. This tax is included in the price and the burden of payment falls on the shoulders of the final consumer of this product. Excise tax is levied only on highly profitable products, the main purpose of such a tax is to obtain a sufficient amount of Money and limiting the consumption of products that harm people and the environment.
What type of taxes are excise taxes?
Taxes and fees are an important part of the taxation system of any state. The following factors are taken into account when classifying taxes:
- the nature of the tax withdrawal (direct and indirect taxes);
- withdrawal rate (federal, regional, local, municipal);
- subject of taxation (physical and);
- (goods, services,);
- intended purpose (general, special).
Indirect or direct
Excise tax, by the nature of the exemption, is classified as an indirect tax. Indirect tax is withdrawn in the form of a surcharge to the value of goods or depends on the added value of goods, turnover and sales of goods and services. The excise tax is similar in nature, but its distinctive feature is that this tax applies only to surplus products: tobacco products, oil products, cosmetics, alcoholic beverages.
- Indirect tax is paid by the end user products sold... Its size is influenced by the elasticity of demand. The higher the demand, the higher the payout. The lower the offer, the lower the amount of tax to be paid by the buyer.
- Indirect taxes are quantity dependent sold goods, therefore, in comparison with other payments to the treasury, they present fewer problems when collecting. Their size is less than the amount of direct taxes.
- Indirect tax is unconditional, because it does not depend on the income and profits received, on the results of economic activity and is withdrawn according to the amount of products produced.
- Indirect taxes are related to the consumption and distribution of goods, therefore they are classified as taxes on expenses, while direct taxes are considered taxes on income.
Direct and indirect tax
Federal or regional
Depending on who the taxes are sent to and who collects them, the taxes paid are divided into municipal, local or federal.
- Federal taxes are levied according to standard rules throughout the territory of the Russian Federation and, in general, are sent to the federal budget. These taxes are determined and established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Local and municipal taxes are established by local authorities, the leadership of the subjects of the federation.
Excise tax is used to form the state budget different levels... Distribution shares between federal budget and the local treasury are pre-established and unchanged. The excise tax is distributed as follows:
- Excise taxes on tobacco products, ethyl alcohol and some other goods are fully transferred to the federal budget.
- Taxes on motor oil, and some other products are listed in certain ratios between federal and regional budgets.
- , less than 9% - completely to the regional budget.
Object and subject of taxation
A complete list of goods subject to excise tax is given in article 181 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The most important objects of excise taxation are:
- alcohol and alcohol-containing products with an alcohol content of at least 9%;
- tobacco and tobacco products;
- gasoline and diesel fuel;
- petroleum products;
- cars and motorcycles.
The subjects of excise tax are;
- enterprises and organizations producing excisable goods;
- individuals who are consumers of excisable products.
Types of excise taxes and formulas for their calculation

Tax or levy
Taxes and fees refer to mandatory payments to the state budget. It is rather difficult to separate them from each other. But there are still differences:
| Tax | Collection | |
|---|---|---|
| Withdrawal method | periodically | lump sum |
| The nature of the seizure | payment | contribution |
| Purpose of payment | replenishment of the state budget | replenishment of the budget of a particular industry or government agency |
| What does the payment give to the payer | free payment | the payer gets some right or service |
| Punishment for non-payment | administrative or criminal liability | adverse consequences in the form of revocation of licenses, permits, services |
Excise taxes are taxes because they have all the necessary characteristic features taxes, including compulsory and individual gratuitousness. That is, it is a mandatory gratuitous cash payment to the state budget, which is collected from the taxpayer in the manner and amount established by law.
Obligation means the legal obligation of the payer to the state. The excise tax is established by the state in unilaterally, in case of late payment or deviation from the amount of tax is collected by compulsion, administrative measures may be applied.
Types of excise taxes
There are several types of excise taxes, depending on the resignation of taxation:
- Ad valorem... Calculated as a percentage of the total cost of the product. It is used to tax the most expensive goods: natural gas, gasoline, gold and jewelry.
- Specific... A fixed amount of tax for 1 product unit. For example, for 1 liter of direct race gasoline - 11.1 rubles.
- Combined... Simultaneous application of specific and ad valorem rates to the same object of taxation.
For example, when selling cigarettes, a flat tax is levied on a unit of goods (cigarette), 8% of the estimated cost is added to this amount.
New and old excise taxes
Since April 2016, the cost of the excise stamp has increased in Russia: 1,700 rubles per 1,000 marks (previously it was 1,600 rubles). Has changed and appearance excise stamp. The new brand is characterized by:
- background in the form of guilloche non-rapport grids with 2 iris transitions;
- an aluminum hologram with a bas-relief pattern, demetallization and color-variable property;
- machine-readable anti-counterfeiting elements;
- phosphorescence.
The brand is made of self-adhesive paper that does not glow under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. This paper is chemically protected. On the reverse side, under the adhesive surface, there are visible patterns and colorless text that can luminesce when exposed to light.
Having citizenship of any state and being in constant interaction with various government agencies, we receive various benefits: education, medicine, we are protected, we solve any problems in administrative institutions, we receive various benefits, etc. Formation of the state budget for these purposes is possible when direct and indirect taxes are received from the regions in full.
Direct versus indirect taxes - what's the difference?
Taxes are mandatory, statutory payments that are withheld from citizens and legal entities(various types of enterprises) to the budgets of different levels in order to form their revenue side. There are various tax classifications, in this case, we will consider direct and indirect taxes.
Direct taxes are based on the income of all categories of taxpayers and are withheld when income is generated or otherwise material wealth... These include: income tax, property taxes, income tax and others.
Indirect taxes are usually included in the price of the goods we buy, and we pay them just by making a purchase. Customs duties, excise taxes, VAT are all varieties of indirect taxes.
Thus, the essential difference between direct and indirect taxes is that the former depend on income and are levied when it is generated, while the latter do not depend on income and are included in the cost of goods and services.
Simply put, direct taxes are taxes on income and property, and indirect taxes are on goods and services. Therefore, if you, for example, do not buy imported or excise goods, then you will not be a payer of these types of indirect taxes.
Let's take a closer look at what direct and indirect taxes are.
Direct taxes - from the taxpayer to the budget!
The most important direct taxes for citizens are personal income tax and property tax.
The name "property tax" speaks for itself - it is a tax imposed on the property of citizens: houses, apartments, land, vehicles, antiques. Property accepted as a gift or inherited is also subject to taxation.
Personal income tax, or income tax, is taken on all types of income available to citizens: from wages, from rented property, from interest on shares and other valuable papers etc. Even if a miracle happened and you won money in the lottery, you will have to pay income tax on this amount.
Pensions and various social benefits are not taxed.
The interest rate for income tax depends on the type of income, for example, 13% is withheld from wages, and dividends received from shares are taxed at a 15% rate.
For individual entrepreneurs and organizations carrying out certain types of activities, tax legislation RF provides for several special regimes that allow a single tax to replace several types at once tax payments.
Many enterprises and individual entrepreneurs choose for their activities such a type of income tax as UTII - single tax on imputed income.
The essence of UTII lies in the fact that this tax does not depend on the actual profit that an individual entrepreneur or organization receives, but on the estimated income established (or imputed) by the tax inspectorate.
Activities falling under UTII mode, are determined by law at the level of local authorities. Imputed income tax must be transferred quarterly. 
For small business good option is a simplified taxation system. It, like UTII, involves the replacement of several taxes with one. The objects of taxation under the simplified tax system are the income of the organization, and then the rate is 6%, or income minus expenses, in this case, a rate of 15% is applied. Individual entrepreneurs and organizations working under the simplified tax system have the right to choose themselves which indicator will be the object of taxation. To report on the simplified tax system, a declaration is submitted to the tax authorities once a year.
The main direct tax for legal entities is income tax. Here, the object of taxation is the balance sheet profit. The tax rate is 32%, and the tax on profits from intermediary services reaches 45%.
As property taxes, legal entities are obliged to pay corporate property tax based on its average annual book value, land tax, etc. Rates on property taxes are depending on the type of activity of the enterprise (but not for each specific enterprise).
Taxpayers independently calculate taxes in accordance with the established tax periods.
Indirect taxes - exploring the specifics!
So, we have already found out that the main types of indirect taxes are value added tax, various kinds of customs duties, excise taxes. The importance of indirect taxes is very high, since they bring almost half of the revenue to the state treasury.
What is the peculiarity of this type of taxes? It lies in the fact that formally their payers are producers of certain goods and services, but in fact - consumers of these very goods and services. 
For example, no matter how long the chain from the manufacturer to the final consumer, each person involved in it is a VAT payer at its stage, including the consumer himself. Thus, all business participants who create added value are subject to this type of taxation.
Currently, the VAT interest rate is 18%. For some licensed activities, tax incentives are provided by law.
Customs duties are levied on the import of goods from abroad, and their calculation depends on many factors, including political ones.
Excise taxes are levied only in the sphere of production; this type of tax does not apply to services. There is a list of excise goods, in particular, alcohol and tobacco products.
And yet, in order to avoid serious problems, we advise you to respect not only the criminal code, but also the tax code. As they say, pay your taxes and sleep well ...
The tax systems operating in our country are periodically reformed. Conditions, rates, coefficients, types of reporting forms are changing, therefore, for those for whom the topic of direct and indirect taxes is relevant, it is important to be aware of these changes.
Income tax 2015 rate: how much profit will the state take from business? Income tax rate 2015-2016: it is a pity that money cannot be invested in taxes!
Depending on the method of collecting taxes, they are divided into direct and indirect. This division is considered by some to be conditional, since, ultimately, indirect taxes are paid by the final consumers of the products.
Characteristics of taxes
Direct taxes are levied on either the taxpayer's income or property belonging to him. These include taxes on the income of individuals, on the profits of enterprises, on the property of citizens and organizations. Payers of direct taxes are specific citizens or organizations, the tax base software is relatively easy to define, so it's easy to administer and collect.Indirect taxes are called taxes, the amount of which is included directly in the cost of production. They are sometimes referred to as consumption taxes. Indirect ones include value added tax, customs duties, excise taxes, state fees and fees that are levied on the taxpayer for the implementation of a number of legally significant actions.
Features of indirect taxes
Indirect taxes are conventionally divided into:- individual - paid from certain groups of goods;
- universal - they are imposed on almost all goods.
Individual indirect taxes include excise taxes that are levied, for example, on alcohol, tobacco products, gasoline and other fuels, and are paid by consumers of these products. Other indirect customs duty, which is ultimately borne by all consumers imported goods.
Tax exemptions are provided for certain types of goods and services. For example, for children's goods and foodstuffs, the VAT rate is 10%, and for other goods - 18%. Some goods, such as medical products, are not subject to VAT.
The attractiveness of indirect taxes for the state is due to the fact that their collection does not directly depend on financial results activities of the enterprise. Even if the firm is unprofitable, these taxes must be assessed and paid. The fiscal effect of indirect taxes persists amid falling production and declining sales of goods.
At the same time, the administration of indirect taxes is unnecessarily complicated. Both company accountants and specialists tax authorities agree that the methodology for calculating VAT is replete with ambiguously interpreted provisions, and the procedure for refunding this tax is confusing. Therefore, most tax audits they reveal a lot of violations related to the calculation of VAT, and are accompanied by additional assessment of tax amounts, as well as the imposition of penalties and fines on taxpayers.
Tax classification- This is the distribution of taxes and fees for certain groups, due to the goals and objectives of systematization and comparisons. At the heart of each classification, and there are a sufficient number of them, there is a completely definite classifying feature: the method of collection, belonging to a certain level of management, the subject of taxation, the method or source of taxation, the nature of the rate applied, the purpose of tax payments, any other feature.
Taxes and fees are classified according to various criteria:
1. According to the method of withdrawal, two types of taxes are distinguished:
direct taxes are levied directly on income and property (income tax, property tax, income tax);
indirect taxes are set in the form of price or tariff surcharges. The ultimate payer of such taxes is the consumer (VAT, excise taxes, customs duties).
2. By impact, taxes are subdivided into:
proportional - these are taxes, the rates of which are set at a fixed percentage of income or property value;
progressive - these are taxes, the rates of which increase with the growth of the value of the object of taxation;
degressive or regressive - these are taxes, the rates of which decrease with the growth of the value of the object of taxation;
firm taxes are taxes, the rate of which is set in an absolute amount per unit of measure of the tax base.
3. Distinguish by purpose:
general taxes - funds from which are not assigned to certain areas of government spending (income tax, VAT, personal income tax);
marked (special) taxes - have a designated purpose ( land tax, insurance premiums).
4. For the subject of payment, there are:
taxes levied on individuals;
taxes levied on legal entities;
mixed taxes.
5. According to the object of taxation, the following are divided:
property taxes;
resource taxes (rental payments);
taxes levied on revenue or income;
consumption taxes.
6. According to the source of payment, there are:
taxes attributable to individual income;
taxes attributable to the costs of production and circulation;
taxes attributable to financial performance;
taxes levied on sales proceeds.
7. According to the completeness of the rights to use tax revenues, the following are distinguished:
own (assigned) taxes;
regulatory taxes (allocated between budgets.
8. By terms of payment:
periodic (they are also called regular or current) are taxes, the payment of which is systematically regular in statutory terms;
urgent (they are also called one-time) - these are taxes, the payment of which does not have a systematically regular nature, but is made by the due date upon the occurrence of a certain event or the commission of a certain action.
9. By belonging to the level of government:
federal;
regional;
There are three ways to collect taxes:
1. Cadastral (cadastres are used, ie registers containing the classification of typical objects according to their external characteristics). Applies to land, buildings, deposits.
2. At the source (collected before the income is received by the taxpayer).
Direct taxes
Direct taxes- These are taxes levied by the state specifically on income (salaries, profits, interest) or on the taxpayer's property (land, buildings, securities). When direct taxation the amount of tax is paid by the payer specifically to the treasury. The following system of main direct taxes operates in the Russian Federation: - Direct taxes withheld from legal entities, corporate income tax (corporation tax), corporate property tax; land tax from the enterprise.
Direct taxes levied on individuals (population) - personal income tax; property tax from the population; property tax transferred by inheritance and donation; tax on the owners of the vehicle. An important direct tax levied on legal entities is corporate income tax. Who is the payer of this tax? Its payers are enterprises and organizations that are legal entities under the legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as foreign companies specializing in entrepreneurial activity in Russia. The object of taxation is the gross profit of an enterprise, which is the sum of profit from the sale of products (works, services), fixed assets (fixed capital), other property and income from non-sale operations minus the amount of expenses on these operations.
Types of direct taxes
1. Personal income tax (personal income tax) is a deduction from the income of taxpayers - individuals, both with and without permanent residence in the Russian Federation, including foreigners and stateless persons. Payments are made throughout the year, but the final settlement is done at the end of it. The taxation norm is the tax rate - the amount of tax per unit of taxation. Small rate in Russia income tax is 12%, the largest is 45%. Not subject to taxation: municipal social insurance benefits; all types of pensions; income acquired from individuals by inheritance and donation; the price of gifts purchased from companies, institutions and organizations during the year in the form of things or services, not exceeding the amount of 12 times the statutory small monthly wage. 2. Corporate income tax is levied if they are recognized as legal entities. This tax constitutes the main part tax payments companies. Profit, unblemished income, is subject to tax. In Russia, the rate of this tax is close to that in advanced countries - up to 35%. Production associations, enterprises, as well as capital owners pay tax on the basis of the declarations they have submitted. A tax return is a statement by a taxpayer about the amount of his income. Certain types of profits received by legal entities are taxed separately. Thus, profits from dividends purchased on shares, bonds and other securities issued in the Russian Federation are taxed at a rate of 15%. This rate applies to profits from an equity role in other businesses established locally in the Russian Federation. 3. Social contributions encompass company contributions to social security and payroll and labor taxes. They represent payments that are made partly by the workers themselves and partly by their employers. They are heading to different extrabudgetary funds: unemployment, pension, etc. The government is also involved in financing these funds. Payroll taxes and labor taxes are paid only by employers. 4. Property taxes are taxes on property, land and other real estate, gifts and inheritance. The size of these taxes is determined by the task of redistributing wealth. 5. Taxes on products and services, customs duties and taxes first, excise taxes, sales tax and value added tax. Price added tax is identical to sales tax, in which the final consumer bears the full burden. Taxpayers who, in the process of work, add a price to the objects of labor received at their disposal, are taxed on this added price. But each taxpayer includes this amount in the cost of his own product, which moves along the chain right to the final consumer. The law defines a list of products (works, services) exempted from tax. This list is uniform throughout the territory of the Russian Federation. Services in the field of public education related to the educational and production process are exempted from VAT; care services for the unhealthy and elderly; funeral home funeral services; services of cultural and art institutions, religious associations; theater and entertainment, sports and other entertainment events. R&D activities carried out at the expense of VAT are exempt from VAT. municipal budget, and contractual work performed by institutions of public education.
Indirect taxes
Indirect taxes are taxes on products and services: value added tax; excise taxes (taxes directly included in the price of a product, tariff or service); for the legacy; on transactions with real estate and securities and others. They are partially or completely transferred to the cost of the product or service. The owner of the product or services, upon their implementation, receives tax amounts, which he transfers to the state. In this case, the link between the payer and the state is mediated through the taxable object. In the case of direct taxation, the tax amount is paid by the payer specifically to the treasury. In case of indirect taxation, the amount of tax acquired by the owner (trader) of products or services when they are sold from the buyer is transferred to the state. As it follows, formally, the indirect tax is paid by the owner (trader) of the product, in reality - by his client.
Types of indirect taxes
Indirect taxes on the objects of collection are divided into: excise taxes, fiscal monopoly, customs duties. In advanced countries, excise taxes prevail - indirect taxes on products and services that are carried out by personal enterprises. Excise taxes are installed on domestically produced products; in some countries, excise taxes are also imposed on the import of products (Our homeland). Excise taxes based on the collection method are divided into personal ones - set on certain types and product groups, and universal - levied on the price of the entire gross turnover (VAT). Universal excise taxes are more profitable from a fiscal point of view (with the expansion of the range of products, the receipt of the universal excise tax in the budget increases), they are levied on all products that are sold. Initially, the universal excise tax was levied at one stage (consumption) in the retail trade. After the 2nd World War, a cascading turnover tax was introduced (that is, it was levied at all stages of production). Nowadays it is characterized by a one-off taxation. A kind of universal excise tax is VAT, which, unlike turnover tax, is not levied on the entire price of a product, but only on that part of the price that is added at a certain stage of production. The added price includes: salaries, depreciation, interest on loans, expenses. The second type of indirect taxes - fiscal monopoly - the country's monopoly on the creation and (or) sale of certain products, it pursues a purely fiscal goal. Rates are not set, since the government is a monopolist in the production of certain types of products (for example, wine and vodka products) and sells the product at a very high cost, which includes the tax itself. Fiscal monopoly can be partial (either creation or implementation), or complete. The third type of indirect taxes is taxes on foreign trade: customs duties. They are divided: 1. by types - for export, imported from other countries, transit; 2. on the construction of rates - on special (installed in a fixed amount), ad valorem (as a percentage of the price) and complex (a combination of specific and ad valorem rates); 3. in terms of economic role - to fiscal, protectionist (to protect domestic market from products imported from other countries), anti-dumping (excessive duties on products imported at dumping prices), preferential (preference system - preferential duties on one imported product, or on all imports).