Modern banking system presentation. Banks and their functions The banking system of Russia Banks and their functions The banking system of Russia Teacher of Economics and Informatics - Irina Vladimirovna Derbeneva, - presentation
-
Slide 9
Trends typical for the Bank of Russia.
Small and medium-sized banks prevail. According to the form of ownership, banks are divided into share, joint-stock and mixed. Most of the banks are still concentrated in the Central Region. The number of branches and representative offices is increasing, both in Russia and abroad. The Russian Federation is characterized by universal banks, there is practically no developed network of specialized banks, for example, such as mortgage banks. The main purpose of the banking system is lending to the economy in the person of three economic agents - the population, entrepreneurs and the state. In this regard, the domestic banking system lags far behind the western one. Lending to the population is practically only Savings bank... Lending to enterprises occupies a relatively small place in the operations of commercial banks. In structure passive operations the main share is occupied by ruble deposits of the population and legal entities. 9
Slide 10
Factors influencing the development of the banking system
The maturity of the commodity monetary relations; public and economic order, its purpose and social orientation; legislative framework and acts; general idea of the essence and role of the bank in the economy. 10
Slide 11
Conclusion
Banks in Russia are part of a two-tier system, the upper tier of which is represented by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, and the lower tier is represented by commercial banks. Gradually improving, the banking system of the Russian Federation is increasingly beginning to become a developed system, and not only externally, but also in essence of the operations carried out. The network of branches, representative offices both within the country and abroad is expanding, the network of non-bank credit institutions is expanding. eleven
Lesson questions. Both you and your parents probably wondered one of the
questions: where to get a loan? Where to place
available funds? How to transfer money
relatives?
How
save
money from inflation? Should I use credit
card? All these questions are somehow related to
the functioning of the banking system, because it is
banks
render
similar
services to their clients. In this lesson we
let's figure out what a bank is, what is a banking
system and what services are provided by commercial
banks.Banks. Banking system
Financial literacy.
Friendship with finances.Origin of banks
Word
"bank"
happens
from
Italian "banco" and means "table",
"bench". The predecessors of banks were
medieval money changers - representatives
monetary and trade
capital;
they
took cash from merchants and
specialized in money exchange
different cities and countries. With time
money changers began to use these deposits, and
also own funds for
granting loans and receiving interest, which
meant turning money changers into bankers.
In England, capitalist banking
the system originated in the 16th century, and the bankers
came out of the environment or gold affairs
masters or merchants. But barely in the vaults of ancient banks
treasure bags appeared, as in their
side
gaze turned
local
entrepreneurs / merchants
and
artisans. They had quite
a reasonable question: is it possible for a while
take advantage of other people's savings
for
enlargement
scale
their
operations? Naturally, for a fee!
So
crossed
interests
two
the most important participants in the economy -
savings owner and merchant,
needy
in
capital
for
expanding its activities. Exactly
this is what banks owe their birth to. Bank is financial institution, the main function
which is the receipt of monetary resources from those
people from whom they are temporarily released, and
introduce them to those who need them now. The banking system is a set of operating in
country of banks, credit institutions and individual
economic organizations performing banking
operations central bank
bank
Central
Banks
Non-bank credit
organization I stage of banking reform
system refers to 19881990. (preparatory).
Vneshtorgbank
The main result of the first stage is the creation
two-tier banking
systems
Central Bank of the Russian Federation - Bank
Of Russia
Sberbank
Commercial banks
The second stage of the banking system reform began in 1991.central bank
bank)
-
main bank countries,
who has the exclusive right to
emission of national
currency and controls the activities of other banks
(central
Bank of Russia, Moscow
9Central Bank functions
emission national currency, quantity regulation
money in the country;
maintaining the stability of the national currency;
general supervision over the activities of credit and financial
institutions of the country and the execution of financial
legislation;
lending to commercial banks;
issue and redemption of government securities;
management of government accounts, execution of foreign
financial transactions. Commercial Bank
bank) - a company that attracts savings from households and other firms for
deposits and lending.
(commercialBank operations
Active operations
Passive operations
Granting loans
Mobilizing cash
income and savings and their
accumulation
Banking services
Exercise cash and
cashless payments, issue and
custody of securities, trust
(trust) operations Financial Institutions - Commercial Institutions
carrying out financial transactions FINANCE - cash
funds, securities and other
monetary obligations
states, enterprises, families
FINANCE - aggregate
monetary relations,
organized by the state, in
process which is
formation, use
national funds,
funds for
implementation of economic,
social and political challenges Financial organization,
carrying out activities on:
accepting deposits;
Granting loans;
Settlement organizations;
Purchase and sale of securities
Insurance company
services providing
life, health insurance,
property, liability Created by private and
state-owned companies,
enterprises fund to pay
pensions and benefits for contributors
pension contributions to this fund
Financial- credit organisation.
Acts as an intermediary
between the borrower and the private
investor, expressing interests
the last An organized market in which
deals with valuable
securities and other financial
documents World Bank
international
monetary fund
Institute dealing
financing and lending
different countries promoting world
trade, assisting in
stabilization financial system
developing countries
European bank
reconstruction and development main destination financial institutions
- organization of mediation, i.e. effective
transfer of funds from savers to
borrowersQuestions
Why do we need a banking system?
How do banks help us in our lives?
How the banking system affects development
economy?
Which
bank
preferable
–
with
state
participation
or
without
state
participation
in
statutory
capital.Private educational institution of higher education "Siberian Academy of Finance and Banking" Executed by A.S. Ivanova Cand. econom. Sciences, Associate Professor S.Yu. Sidorenko Novosibirsk 2016
MODERN BANKING SYSTEM OF RUSSIA
Illustration material
to the final qualifying work
Table 1 - Purpose, objectives, object, subject and research methods of FQP
Table 2 - Variants of the concept of "banking system"Item name
Characteristic
Research of the modern banking system of Russia and selection of recommendations for its development
1. Consider theoretical aspects banking models.
2. Perform an assessment state of the art the banking system of Russia.
3. Describe the problems of the Russian banking system.
Banking system
Development of the Russian banking system
Observation object
Central Bank and commercial banks of Russia
Research methods
Monographic method, logical approach to assessing economic phenomena, method of analysis and synthesis, as well as a systematic approach
Definition
O. M. Bogdanova
the banking system has its own internal structure, its own structure (levels of the system) and from an organizational point of view, it can be defined as a set of banks operating in the country of two levels (central and commercial), as well as auxiliary organizations, without which banks could not function normally
G.G. Korobova
it is a set of credit institutions within the country with internal relationships between them
A.M. Tavasiev
it's included in economic system countries, a single and integral set of credit institutions, each of which performs its own special function (functions), maintains its own list of monetary transactions / transactions, as a result of which the entire volume of society's needs for banking products (services) is fully satisfied and with the widest possible degree of efficiency
EAT. Konstantinova
it is an ordered system of elements (credit institutions, central bank), conditioned by the level of development of monetary relations, linked by common goals of functioning, which maintains stable ties between themselves and the external environment
Figure 1 - Features of the banking system that distinguish it from other systems
An artificial system is the result of human activity
Large system - includes many elements
Complex system - a huge number of connections and interactions
Controlled system
A dynamic system with the property of self-development
Hierarchical system
Purposeful system
An open system by the way of interaction with the external environment
Figure 2 - Possible models of banking systems
American
European
Centralized
Decentralized
Islamic
Universal
Specialized
Figure 4 - Volumetric histogram of the number of credit institutions in the Russian Federation for the period from 01/01/2014 to 05/01/2016, units
Table 6 - Total assets of the banking system of the Russian Federation for the period from 01.01.2011 to 01.01.2016 according to the data of the Bank of Russia from the documents “Review banking sector Russian Federation "(Internet version)"Index
Index
Total assets of the banking sector (RUB bln)
Http://www.cbr.ru/analytics/bank_system/obs_1601.pdf
Http://www.cbr.ru/analytics/bank_system/obs_1606.pdf
Table 8 - Growth rates of indicators of the banking system of the Russian Federation (% for the period from 01.01.2014 to 01.01.2016)Loans to non-financial organizations
Loans to individuals
Involved funds
Neo-specific
2,1*
1,3
0,7
1,9
1,6
4,3
0,4
9,1
0,8
5,3
0,1
1,1
2,6
8,7
1,7
1,0
1,7
0,4
0,7
2,6
2,1
1,0
0,1
0,2
0,1
0,7
0,4
3,2
5,0
3,0
0,1
8,0
2,2
* In the numerator - for the month; in the denominator - for 12 months preceding the reporting date.
Table 9 - Indicators of financial and economic activity of the banking system of the Russian Federation, billion rubles.
* Loans also includes other allocated funds
Table 13 - Concentration of assets of TOP-5 banks by federal districts RF,%
Federal district
Central Federal District
including Moscow and Moscow region
Northwestern Federal District
Southern Federal District
North Caucasian Federal District
Volga Federal District
Ural federal district
Siberian Federal District
Far Eastern Federal District
Crimean Federal District
the Russian Federation
Figure 4. Volumes of profit and loss of credit institutions in the Russian Federation, million rubles.
Figure 5. The number of profitable and unprofitable credit institutions, units.
Table 16 - Problems of the modern banking system of the Russian Federation
Thank you for your attention.Restructuring the entire banking system in order to increase bank capital, improve the quality base of customer service
Recapitalization of banks and a fundamental turn in their relationship with the sphere material production will create a solid economic environment for development banking business on a healthy basis
Discourage bad behavior of participants financial market... Increased attention of banks to limiting risks and improving the quality of asset management
Ensuring consumer protection financial services and raising financial literacy population of the Russian Federation. Restoring confidence in the banking system of all segments of the population
Lesson topic:
"Banks and banking system"
Compiled by: teacher of economics
the city of Verkhnyaya Salda

Lesson plan
- Introduction
- Banking system
- Financial institutions
- Conclusion

Introduction
Finance - aggregate economic relations in the process of using funds

Origin of banks
Banks are a very ancient economic invention. The first banks appeared in the Ancient East in the 7th-6th centuries. BC. Then Ancient Greece took up the baton. Here, the most revered temples began to accept money for safekeeping during the wars, since the belligerent countries considered it unacceptable to plunder the sanctuaries.
Word "bank" comes from Italian "Banco" and means "table", "bench"
In England, the capitalist banking system emerged in the 16th century, with bankers emerging from either goldsmiths or merchants.

But as soon as bags with treasures appeared in the vaults of ancient banks, the gaze of local entrepreneurs - merchants and artisans - turned towards them. They had a very reasonable question: is it possible to temporarily use other people's savings to expand the scale of their operations? Naturally, for a fee!
This is how the interests of the two most important participants in the economy crossed - the owner of savings and the merchant who needed capital to expand their activities. This is what banks owe their birth to.

Economic interests that led to the emergence of banks
Savings owner
It has:
- saving
Needs to:
- savings income
Ready:
Refrain from consuming your savings and allow them to be used for a fee
Businessman
It has:
Profitable use of funds project Needs to:
Cash capital
Ready:

In 1809, in the town of Slobodskoy, Vyatka province, the merchant K.A. Anfilatov established the "First City Public Anfilatov Bank" which is quite modern in its principles
In 1863, with the support of the Minister of Finance Mikhail Reitern and on the initiative of the Governor of the State Bank of Russia Yevgeny Lamansky,
Petersburg Society of Mutual Credit
Mikhail Reitern

Today the circle banking services extremely diverse, but almost all of them can be classified into one of four main categories:
- Collection of citizens' savings for the organization profitable investment these savings into commercial activities.
- Submission of savings of citizens for temporary paid use commercial organizations.
- Assistance to commercial organizations and citizens in organizing payments for goods and services.
- Creation of new forms of money to speed up and facilitate payments for goods and services.

BANK is a financial intermediary that carries out activities on:
- accepting deposits;
- presentation of loans;
- organization of settlements;
- buying and selling securities

Loan price structure
Profit
banker
Bank costs for
business management
Interest income
per savings holder

Lending principles:
- urgency;
- chargeable;
- return;
- warranty

Deposits - all types of funds transferred by their owners for temporary storage to the bank with the granting of the right to use this money for lending
Demand deposits
these are the contributions from which
depositor can
withdraw money at any
Time deposits
these are the contributions from which the owner
undertakes not to take money
before the expiration of a certain


Banking system
Banking system -
a set of banks and other credit institutions and organizations operating in the country
CENTRAL BANK
Commercial banks
Other financial and credit
institutions

Banking system
Main functions
- Implementation of the state monetary policy
- Lending to commercial banks
- Ensuring the stable operation of the banking and financial systems
- Maintaining the stability of the national currency
- Keeping stocks of cash and gold

Banking system
Types of commercial banks:
- Branch banks(serve certain sectors of the economy)
- Cross-sectoral(serve all sectors of the economy)
- Regional banks(serve certain regions of the country)

Types of commercial banks
Commercial
Universal
Specialized
Investment
Implementing
specialized
Innovative
Mortgage
Savings

Banking system
Operations commercial bank:
Passive- operations to mobilize monetary resources: accepting deposits (deposits); obtaining loans from other banks and the central bank; issue of own securities
Active- operations for the placement of funds: the provision of loans of various terms and sizes

The structure of modern national banks
Issuing banks
The control
citizens and
Saving
citizens and firms
Cash

Financial institutions
Financial and credit institutions accumulate free funds and provide them to those who need additional capital or financial assistance
Pension fund - a fund created by private and state-owned companies, enterprises for the payment of pensions and benefits to persons who make pension contributions to this fund
Investment companies - a financial and credit institution that collects funds from private investors through the sale of their own securities

Financial institutions
Insurance companies are organizations that provide insurance services, are intended to compensate for damage, loss by accidents
Stock exchanges specialize in the sale and purchase of securities
Interstate financial and credit institutions:
(World Bank, International Monetary Fund, European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, etc.). They finance and lend to various countries, facilitate world trade, and help stabilize the financial system.

Conclusion
Finance plays a huge role in structure market relations and their mechanism state regulation... Any country must maintain and strictly control its banking system and money turnover in order to prevent the development of barter, on the one hand, and the growth of inflation, on the other.

Workshop
Objective 1. Marina Georgievna invested 12,500 rubles in SBERBANK. at 11% per annum. The bank lent the same amount to the Iceberg Organization at 17% per annum. What profit will Sberbank receive?
Objective 2. How much money will Svetikova S.A. have? after 3 years, if she invested 120,000 rubles in the bank. at 11% per annum?

Workshop
Solution to problem number 1:
1) 17-11 = 6% bank profit in%
2) 12500 * 6: 100 = 750 (P) bank profit in rubles
Solution to problem number 2(120,000 * 11: 100) * 3 + 120,000 = 159600 (P) after 3 years

Class: 10
Lesson presentation
Back forward
Attention! Slide previews are for informational purposes only and may not represent all the presentation options. If you are interested in this work, please download the full version.
Lesson objectives:
Lesson Objectives:
- features of a two-tier banking system;
- the main functions of the Central and commercial banks, and their role in the economy;
- classification of commercial banks, types banking operations and types of deposits;
- basic principles of lending;
- purpose of creation and types bank reserves;
- to give an idea of the issue of credit and the banking multiplier;
develop:
- the ability to work with additional literature, search for the necessary information on the Internet;
- ability to solve problems;
- selection skills more profitable bank for cooperation.
Basic concepts of the lesson: bank, banking system, Central bank, assets, bank liabilities, credit, issue, deposits, collateral, margin.
Lesson type: combined.
Equipment: projector, interactive board, presentation for the lesson "Banking system".
Lesson objectives:
- consider the types of banks and their main functions in modern economy, the role of the Central Bank in regulating the monetary system;
- find out the essence of the credit issue.
During the classes
I. Organizational moment: familiarization with the structure and objectives of the lesson.
II. Control test of knowledge:
Test. Test task "Money"
1. Name the functions of money.
A) world money;
B) a means of circulation;
C) means of payment;
2. The equation of I. Fisher determines that the money supply depends on:
A) the speed of circulation of money;
B) the price level;
C) the volume of transactions;
D) gold and foreign exchange reserves.
3. The emission of cash in the Russian Federation is monopolized by:
A) Ministry of Finance and Economic Development;
B) Federal Treasury;
C) Central Bank;
D) Federal Reserve System.
4. If the Central Bank intends to increase the money supply, then it can:
A) carry out an operation to buy securities on the open market;
B) reduce the discount rate;
C) there is no correct answer.
5. The purchasing power of money under inflation:
A) does not change;
B) can both increase and decrease;
C) is directly proportional to the rate of inflation;
D) decreases.
6. The money supply increases due to:
A) issue of government bonds;
B) emission coverage of the state budget deficit;
C) increasing the state's gold reserves;
D) sales of foreign currency.
7.the amount of money in circulation has increased within a few days if:
A) someone borrowed a certain amount from their friends;
B) the vacation season has begun;
C) the company has delayed the payment of wages.
8. Value modern money is determined by:
A) the gold reserves of the country;
B) the price level;
C) absolute liquidity.
D) the amount of money in circulation.
9. Fisher's equation shows that:
A) the value of securities is directly proportional to their number;
B) the measure of the value of money does not depend on their quantity in circulation;
C) the amount of money in circulation is in direct proportion to the available commodity mass;
D) the sum of commodity prices is in direct proportion to the circulating money supply.
10.the money supply will increase if:
A) the businessman took large sum cash at 5% monthly;
B) the Central Bank presented a loan to a commercial bank;
C) The Central Bank sold short-term government bonds on the open securities market.
Key:
- A B C,
- A B C,
III. Learning new material.
- The reasons for the emergence of banks. (Slide No.)
- Types and functions of banks. (Slide No.)
- Lending principles. (Slide No.)
1. Reasons for the emergence of banks.
Banks are a very ancient economic invention. It is believed that the bank first appeared in the Ancient East in the 7th-6th centuries. BC, when the level of well-being of people allowed them to save while maintaining an acceptable level of current consumption. Then Ancient Greece took up the baton. Here, the most revered temples began to accept money or storage for the duration of the wars, since the warring parties considered it unacceptable to plunder the sanctuaries.
But as soon as bags with treasures appeared in the vaults of ancient banks, the gaze of local entrepreneurs - merchants and artisans - turned towards them. They had a very reasonable question: is it possible to temporarily use other people's savings to expand the scale of their operations? Naturally, for a fee!
This is how the interests of the two most important participants in the economy crossed - the owner of savings and the merchant who needed capital to expand their activities. This is what banks owe their birth to.
2. Types and functions of banks.
A bank is a financial organization, the main function of which is to receive monetary resources from those people from whom they are temporarily released, and present them to those who need them now.
The central bank is the main bank of the country, which acts as the banker of the state and the whole credit system.
In almost all countries, the banking system is organized according to the same principle of two levels of banks - consider the scheme:
1st level
central bank- the main bank of the country, which has the exclusive right to issue the national currency and controls the activities of other banks.
Main functions of the Central Bank:
- exercises the monopoly right to issue credit money (banknotes);
- regulate the circulation of the money supply in the country and the exchange rate of the national currency;
- keep a centralized and gold reserve;
- be the chief banker and financial advisor to the government;
- assist the government in budget management;
- provide a variety of services to others credit institutions and monitor the work of other banks;
- conduct monetary policy.
2nd level
Level 2 of the credit system is represented by commercial banks that directly work with clients: individuals or legal entities.
Commercial Bank- a firm that attracts savings from households and other firms for deposits and lending.
Functions of commercial banks -
- opening and maintaining cash accounts.
- providing loans for the needs of citizens and the activities of firms.
- currency exchange.
- purchase and sale of securities.
- implementation cashless payments and etc.
Types of commercial banks (group work - 2 students) - the children are given the task to correlate the name of the commercial bank and the functions performed (indicate with arrows in the table):
Name Savings Issue loans for the introduction of scientific and technical inventions and innovations into production Investment Give out long-term loans enterprises for various projects, i.e. makes cash investments in production and construction for a long time Innovative Provide their customers with the opportunity for a fee to store any valuables belonging to them (money, things, etc.) Mortgage Granting loans for purchase real estate. Safe bank These are large banks in the region: “Zoloto-Platina Bank, Ural Bank reconstruction and development, Inkombank, etc. Pawnshop Banks that issue loans in foreign currency to different countries: the World Bank, or International Bank reconstruction and development. Its governing bodies are located in Washington, DC, USA.
Regional banks A kind of bank (credit institution). You can pledge property (valuables) in a pawnshop in order to get cash for them. In this case, the loan amount is only a part of the real value of the pledged thing. The thing is pledged for a certain period.
International banks keep depositors' money, paying a certain amount for it; lend money;
perform various settlement transactions with the population;
buying and selling currency, securities, precious metals.
3. Principles of lending.
The term "credit" comes from the Latin "creditum" - a loan, debt. The loan is of a monetary nature. The bank, as an intermediary, accumulates temporarily free funds, forming loan capital, and provides it at a temporary disposal to those persons who need to attract additional financial resources on certain conditions. Credit is a form of movement of loan capital.
Lending is the provision of funds for temporary use and for a fee.
Deposits - all types of funds committed by their owners for the time being kept by the bank with the granting of the right to use this money for lending.
A loan agreement is an agreement between banks and the one who borrows money from him (the borrower), which defines the obligations and rights of each of the parties, and, above all, the term for the loan, the payment for using it and the guarantee of the money back to the bank.
Creditworthiness - the borrower's willingness and ability to fulfill their obligations on time credit agreement, that is, to return the principal amount of the loan and pay interest on it.
The pledge is the property of the borrower, which he transfers under the control or at the disposal of the bank, allowing it to be sold if he himself cannot repay the debt.
Credit issue - an increase by the bank of the country's money supply by creating new deposits for those customers who received loans from it.
Credit classification
By providing: - Unsecured (blank)
- Collateral
- Guaranteed
- Insured
By loan terms: - Poste restante
- Short-term (up to 1 year)
- Medium-term (from 1 y. To 3 y.)
- Long-term (over 3 years)
By repayment methods: - By installments (in parts, shares)
- With one-time repayment (on a specific date)
By types of loan accounts - Simple s / s. (regular)
- Special
- Contract accounts
- Overdraft
By main groups borrowers - Individuals
- Legal entities
- Industry focus
- Organizational legal form
Loan security forms:
- Bank guarantee.
- Pledge (movable property, immovable property, property rights).
- Guarantee (legal entities, individuals).
- Forfeit (interest, fine).
Principles modern system lending in Russia:
The price of a loan (interest rate) is determined by the ratio of demand for credit resources and supply; naturally, taking into account the monetary policy of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
Lending is carried out on a contractual basis, the obligations of the lender and the borrower have real legal force;
Transition from lending to a state-owned enterprise to lending to an entity credit relations- the borrower;
Demonopolization of a single loan fund, credit resources are formed by each bank independently;
The Bank of Russia may have an indirect impact on the size of resources by establishing prudential standards instead of lending limits.
IV. Consolidation of the studied material.
Solving problems.
Problem number 1.
The borrower takes a loan from the bank in the amount of 10 thousand rubles at 100% annual term for 2 years. What amount he will pay to the bank after this period as payment for the loan. (Answer: 30 thousand rubles)
Problem number 2.
Calculate interest on a loan issued for 2 years and seven months at 12% per annum. Follow the rules of normal banking practice. (Answer: 34.22%)
V. Summing up the lesson.
Vi. Homework.
Textbook I.V. Lipsitsa chapter 6. 1-3 tasks.
Slide 1
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION FEDERAL STATE BUDGET EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION OF HIGHER PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION "St. Petersburg National Research University of Information Technologies, Mechanics and Optics" economic theory and business Banking system RF and its improvement. Student of group No. 2652 Nazarova Marina Vladimirovna Checked by: Manko Victoria Vyacheslavovna St. Petersburg 2012
Slide 2
Goals and objectives of the study ……………………….… .3 What is the banking system of Russia? ........................... ............. …… ..... ………….… .4 The Central Bank of Russia its goals and objectives. …………………………………………… ……. …… .5 Commercial banks. ………………………………… .6 Largest banks of Russia …………………………… 8 Trends characteristic of the Bank of Russia ………… ..9 Factors influencing the development of the banking system …………………………………………… .10 Conclusion …………………… .. …………… ..... …… 11 2
Slide 3
Goals and objectives of the research
The purpose of this work is to find out what the banking system of the Russian Federation is and the prospects for its development. This goal required the following tasks to be solved: The structure of the banking system of the Russian Federation What tasks are performed by the banking system of the Russian Federation. Prospects for the development of the banking system in Russia. 3
Slide 4
What is the Russian banking system?
BANKING SYSTEM OF RUSSIA - a set of national banks and other credit institutions operating within the framework of a single financial and credit mechanism. Includes two levels: central bank Russian Federation(Bank of Russia) and credit institutions. 4
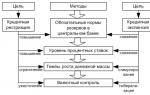
Slide 5
The Central Bank of Russia its goals and objectives.
The main objectives of the Bank of Russia are: to protect and ensure the stability of the ruble, including its purchasing power and exchange rate against foreign currencies; development and strengthening of the banking system of the Russian Federation; ensuring stability and development of the national payment system. The main tasks of the Bank of Russia are: regulation of money circulation; holding a single monetary credit policy; protection of interests of depositors, banks; supervision over the activities of commercial banks and other credit institutions; carrying out operations in foreign economic activity. five
Slide 6
Commercial banks.
Commercial Bank is a non-state credit institution that carries out universal banking operations for legal entities and individuals (settlement, payment transactions, attracting deposits, providing loans, as well as market operations valuable papers and intermediary operations). 6
Slide 7
Services provided by commercial banks.
lending to legal entities and individuals; deposit operations; currency transactions (only authorized banks); operations with precious metals; exit to stock market and Forex; conducting settlement accounts business economic entities; exchange of spoiled money (torn, burnt, washed bills) signs for unspoiled ones; mortgage; car loans; etc. 7
Slide 8