Formula for net assets by balance sheet lines. Net assets on balance sheet
What are net assets? Net assets A business is the difference between the adjusted amount of a business's assets and its liabilities; in short, it is the value of the business itself minus its debts.
The value of the net assets of an enterprise is calculated on the basis of Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 10-dated January 29, 2003 “On approval of the procedure for assessing the value of net assets of joint-stock companies.” For limited liability companies, when calculating net assets, the same calculation procedure is used (except for trustees investment funds, organizers of gambling) (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia N 03-03-06/1/39 dated January 26, 2007).
The calculation of the value of net assets of organizations (with the exception of credit organizations) is made on the basis accounting, the order of which is established federal body executive power.
When calculating the net asset value in credit organization takes into account the amount of equity (capital) determined Central Bank Russian Federation according to established order.
When is net asset value assessed? Net assets are assessed by the company quarterly, as well as at the end of the year at the reporting date. This assessment is reflected in the financial statements, quarterly and annually, respectively.
If at the end of the second and each subsequent reporting year the value of the net assets turns out to be less than the authorized capital of the company, it must announce a reduction in its authorized capital to the resulting value of the net asset value, and register such a decrease in the prescribed manner (clause 4 of Article 35 federal law dated December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ, clause 3 of Art. 20 of the Federal Law of 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ).
If new size the authorized capital is less than the minimum established by law, such an enterprise is subject to liquidation (clause 5, article 35 of the federal law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ, clause 3 of article 20 of the federal law of 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ, article 90 of the Civil Code RF, Article 99 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
To calculate the assets accepted for calculation, we take:
1.Outside current assets. They are reflected in the first section balance sheet and include: intangible assets (intangible assets), fixed assets (fixed assets), construction in progress (CW), profitable investments into material assets, long-term financial investments, others fixed assets;
2.Current assets. They are reflected in the second section of the balance sheet and include: inventories, value added tax on acquired assets, accounts receivable, short-term financial investments, cash, Other current assets. The value of current assets does not take into account the cost of the actual costs of repurchasing its own shares, which are purchased by the joint-stock company from shareholders for their subsequent resale or cancellation, and the debt of the participants (founders) for contributions to the authorized capital.
To calculate liabilities taken into account when calculating the value of net assets, the following are included:
1. long-term liabilities for loans and credits and other long-term liabilities;
2. short-term liabilities for loans and credits;
3. accounts payable;
4. debt to participants (founders) for payment of income;
5. reserves for future expenses;
6. other short-term liabilities.
That is, the following balance sheet indicators are involved in calculating the net assets of an enterprise.


An example of calculating the net assets of enterprises (for any form of ownership)
Balance sheet of Stroymaterialy LLC as of 10/01/2012:
| Balance indicators | Balance data |
| Balance sheet asset | |
| 1. Non-current assets (section I): | |
| - residual value fixed assets | RUB 2,300,000 |
| - capital investments in unfinished construction | RUB 1,600,000 |
| - long-term financial investments | 700,000 rub. |
| 2. Current assets (section II): | |
| - stocks | 200,000 rub. |
| - accounts receivable, | 800,000 rub. |
| including the debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital | 50,000 rub. |
| - cash- | 1200 000 rub. |
| Liability balance | |
| 3. Capital and reserves (section III): | |
| - authorized capital- | 200,000 rub. |
| - retained earnings | RUB 1,500,000 |
| 4. Long-term liabilities (section IV): | |
| - long-term loans | 1,000,000 rub. |
| 5. Short-term liabilities (Section V): | |
| - short-term loans | 400,000 rub. |
| - debt to the budget | 200,000 rub. |
| - other short-term liabilities | RUB 1,900,000 |
When calculating the amount of assets, the calculation does not include such an indicator as the debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital (50,000 rubles). The amount of assets in our example will be 6,750,000 rubles. (2,300,000 + 1,600,000 + 700,000 + 200,000 + 800,000 – 50,000 + 1,200,000).
When calculating liabilities, data on the section are not included in the calculation III accounting balance (RUB 1,500,000). Then the amount of liabilities in our example will be equal to 3,500,000 rubles. (1,000,000 + 400,000 + 200,000 + 1,900,000).
Total net asset value as of October 1, 2012 will be 3,250,000 rubles. (6,750,000 – 3,500,000).
The “net assets” indicator is necessary for analyzing activities, as well as for... It must be positive and exceed the size of the authorized capital. If there is an increase in net assets, then the profit of the enterprise is increasing. Those. the enterprise not only increased the funds that were initially invested in it, but also multiplied them. Of course, it is possible that this indicator will decrease, and it may be less than the authorized capital at the very first difficult year start of activity. But during normal operation of the enterprise, the situation evens out. If, nevertheless, the situation has not improved, then the company must either reduce its authorized capital or liquidate it in accordance with the law.
Free book
Go on vacation soon!

To receive a free book, enter your information in the form below and click the "Get Book" button.
New page 1
In conditions of significant independence of economic entities in carrying out their production and financial activities, assessment of the financial condition, investment attractiveness of enterprises, and the reliability of their partners becomes especially important. In such situations, analysis becomes practically significant financial stability and solvency of the organization. To evaluate them, modern theory and practice economic analysis have developed numerous criteria, among which a special place is given to the net asset indicator.
Widely known in world practice net asset ratio began to be used to assess the financial condition of Russian enterprises relatively recently. The obligatory nature of its calculation was introduced by Part 1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), which came into force in 1995, and by a number of other regulations. In the Civil Code of the Russian Federation this indicator is indicated in Art. 90 and 99, devoted to the disclosure of provisions on the procedure for forming and changing the size of the authorized capital of a limited liability company and a joint stock company, respectively. These articles define the requirements for comparing the net asset indicator with the registered amount of the authorized capital when making various decisions. However, the definition of the essence of net assets is reflected in other regulations. In particular, in the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 10n, FCSM of the Russian Federation No. 03-6/pz dated January 29, 2003 “On the procedure for assessing the value of net assets of joint-stock companies”, net assets are understood as “the value determined by subtracting from the amount of assets of the joint-stock company accepted for settlement, the amount of his obligations accepted for settlement.” And in Methodical recommendations to conduct an examination of the presence (absence) of signs of fictitious or deliberate bankruptcy, approved by order of the FSDN of the Russian Federation No. 33-r dated October 8, 1999 (hereinafter referred to as the Methodological Recommendations), it was indicated that the value of net assets characterizes the presence of assets not encumbered with liabilities. Thus, net assets show how much an organization's assets exceed its liabilities (both short-term and long-term), that is, they allow one to assess the level of solvency of the enterprise. At its core, net assets can be identified with the amount equity, since they reflect the level of security of the funds invested by the owners with the assets of the organization.
Today in regulatory documents and special economic literature, there is no unambiguous approach to calculating net assets (NA), and there is no comprehensive methodology for their analysis. Since 1995, this indicator began to be reflected in the financial statements, in particular, in Form No. 3 “Report on changes in capital” (p. 150). The methodology for the formation of net assets is currently defined in Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 10n, FCSM of the Russian Federation No. 03-6/pz dated January 29, 2003 “On the procedure for assessing the value of net assets of joint-stock companies” and provides for the following calculation based on balance sheet data:
HA=A – P,
where A, P are assets and liabilities, respectively, taken to calculate net assets.
The value of assets (A) is determined as the sum of non-current assets (p. 190) and current assets (p. 290) minus the articles “Debt of participants (founders) for contributions to the authorized capital” and “Own shares purchased from shareholders.” In connection with changes to the content of financial statements in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 22, 2003 No. 67n “On forms of financial statements of organizations” in the balance sheet, the line “Own shares purchased from shareholders” was moved from an asset to a liability - to the section III “Capital and reserves” - as a line regulating the authorized capital. Therefore, the amount of assets taken into account for calculating net assets no longer needs to be adjusted to the balance sheet line mentioned above.
The amount of liabilities (P) is calculated as the sum of the items “Long-term liabilities” (p. 590) and “Short-term liabilities” (p. 690) minus the item “Deferred income” (p. 640). Before the release of this order, the liabilities included the article “ Targeted funding and receipts” (p. 450), which was illegal, since it contains amounts equated to one’s own.
At the same time, in other regulations and economic literature there is a slightly different scheme for calculating the NAV. In particular, the Methodological Recommendations established that the amount of assets involved in their calculation should also be reduced by the amount of the item “VAT on acquired assets” (p. 220). This can be explained by the fact that, according to existing tax legislation(Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) this amount can be taken to reduce the amount of VAT paid by the organization on goods, products, works, services sold only if a sufficiently large number of conditions are met (posting and payment of valuables, issuing an invoice, etc.), then There are serious doubts regarding the actual write-off of the amount of VAT on purchased assets to repay the “output” VAT. However, in the same way, one can doubt that other assets will actually become sources of covering the enterprise’s liabilities, since they may include “stale” inventories, overdue receivables, obsolete fixed assets, investments in illiquid securities, and the organization’s balance sheet will not discloses information about such facts. Therefore, in our opinion, it was unlawful to reduce the amount of net assets by the amount of VAT on acquired assets. It should be noted that this norm, also provided for by the previously in force order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 71, FCSM of the Russian Federation No. 149 of August 5, 1996 “On the procedure for assessing the value of net assets of joint-stock companies,” has now been canceled by the new order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 10n, FCSM of the Russian Federation No. 03-6/pz dated January 29, 2003
At the same time, the Methodological Recommendations stipulated that the organization’s liabilities reflected in Section V of the balance sheet and accepted for calculating net assets do not include the item “Reserves for future expenses” together with the item “Deferred income” (p. 650). In our opinion, there is every reason for this, since, according to many specialists in the field of economic analysis (O.V. Efimova, L.T. Gilyarovskaya, etc.), this article relates to a greater extent to one’s own funds (formed at the expense of one’s own funds) and not to the organization's obligations. All this indicates that a unified methodology for calculating net assets is needed, excluding different interpretations of this indicator.
No less problematic is the development of a harmonious methodology for analyzing net assets. In our opinion, its main directions are:
· analysis of net asset dynamics . To do this, it is necessary to calculate their value at the beginning and end of the year, compare the obtained values, and identify the reasons for changes in this indicator;
· assessment of the reality of net asset dynamics , since their significant increase at the end of the year may not be significant compared to the growth of total assets. To do this, it is necessary to calculate the ratio of net and total assets at the beginning and end of the year;
· assessment of the ratio of net assets and authorized capital . Such a study allows us to identify the degree of proximity of an organization to bankruptcy. This is evidenced by the situation when net assets in value are less than or equal to the authorized capital. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes that if the value of the company’s net assets becomes less than specified by law minimum size authorized capital, then the company is subject to liquidation;
· assessment of the efficiency of use of net assets . To do this, the indicators “net asset turnover” and “return on net assets” are calculated and analyzed over time, and their factor study is carried out.
Let's consider how these areas of analysis of net assets are implemented using the example of the reporting data of OJSC Confectioner. As noted earlier, the study of this indicator should begin with an analysis of the dynamics of net assets.
Data indicate that at the end of the reporting year, the value of net assets decreased by 13,250 thousand rubles, or 9%, and amounted to 133,222 thousand rubles. Such a significant reduction in this indicator occurred against the background of a decrease in both assets taken into account in calculating net assets and liabilities. At the same time, the value of assets decreased to a greater extent - by 17% (RUB 17,159 thousand) compared to liabilities (their decrease amounted to 7%, or RUB 3,909 thousand). It is important to note that a significant reduction in the organization’s assets was caused mainly by a reduction in their mobile part: inventories (by 23.5%, or 16,927 thousand rubles), accounts receivable (by 43.9%, or 8,152 thousand rubles .) and the amount of VAT on purchased values (almost 2 times). At the same time, there was an increase in non-current assets: fixed assets (by 4.1%, or 1,796 thousand rubles), construction in progress (by 10.2%, or 6,000 thousand rubles), intangible assets (almost 2 times). This means that in the reporting year the company made capital investments, diverting significant amounts from economic turnover, which ultimately led to a significant reduction of 17%. In addition, the asset management policy pursued by the enterprise has other negative consequences - an increase in property tax, growth fixed costs in the form of depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets, which leads, in turn, to an increase in the profitability threshold of the organization.
At the same time, the reduction in liabilities by 7% was caused by a significant (by 13,344 thousand rubles, or 34.5%) decrease in accounts payable, while a simultaneous increase in loans and borrowings by 3,060 thousand rubles, or 20.5%, that is the enterprise in the structure of borrowed sources of financing its activities increased the share of the most expensive financial resources. In addition, it follows from the organization’s balance sheet that all loans and borrowings received are short-term in nature. Considering the previously noted fact of an increase in non-current assets, which are long-term, it is not difficult to notice the irrational placement of sources of financing in the assets of the enterprise. Thus, the analysis of the factors that caused the decrease in net assets made it possible to see a number of other problems that negatively affect the solvency and financial stability of Confectioner OJSC.
At the next stages, you should compare the value of net assets with the total assets and authorized capital of the organization (Table 2).
Table 2. Analysis of the ratio of net assets to total assets and authorized capital of the organization, thousand rubles.
|
Index |
Code lines balance |
On Start of the year |
On end of the year |
Deviation («+», «–») |
|
1. Net asset value |
146 472 |
133 222 |
–13 250 |
|
|
2. Value of total assets |
202 366 |
185 207 |
–17 159 |
|
|
3. Ratio of net assets to total assets, coefficient. |
0,724 |
0,719 |
–0,005 |
|
|
4. Authorized capital |
410 – 411 |
4004 |
4004 |
|
|
5. Ratio of net assets to authorized capital, coefficient. |
36,6 |
33,3 |
–3,3 |
From the data in table. 2 shows that the ratio of net assets to total assets at the end of the reporting year is decreasing. In particular, if at the beginning of the analyzed period the share of net assets in total assets was 72.4%, then at the end it was already 71.9%. This means that the real decrease in net assets was even more significant compared to their absolute decrease. At the same time, the calculation of the second ratio showed that net assets significantly (33.3 times at the end of the year) exceeded the authorized capital. This circumstance indicates that despite the emerging problems associated with the deterioration of the financial stability of Confectioner OJSC, this organization does not show signs of bankruptcy.
At the end of the analysis, it is necessary to evaluate the efficiency of using net assets (Table 3). Since the value of net assets must be compared with volumetric (generated during the year) indicators of sales revenue and net profit, then in the calculation it is more correct to use not a fixed value of net assets for a specific date (for example, at the end of the year), but their average annual value, which is the most in a simple way can be calculated as the arithmetic mean (one-half of the sum of the values at the beginning and end of the year). In particular, in the reporting year the average annual value of net assets is 139,847 thousand rubles. ((146,472 + 133,222) / 2). Information for the previous year was obtained in a similar way.
Table 3
Analysis of the efficiency of using net assets
|
Index |
Code lines form No. 2 |
Reporting year |
Deviation (+, -) |
Pace growth, |
|
|
1. Average annual cost net assets, thousand rubles |
145 826 |
139 847 |
–13 250 |
91,0 |
|
|
2. Revenue from sales of goods, products, works, services, thousand rubles. |
409 463 |
313 719 |
–95744 |
76,6 |
|
|
3. Net profit (loss), thousand rubles. |
2896 |
2797 |
–99 |
96,6 |
|
|
4. Net asset turnover, turnover (clause 2 / clause 1) |
2,808 |
2,243 |
–0,441 |
84,2 |
|
|
5. Duration of net asset turnover, days (360 / clause 4) |
150,0 |
||||
|
6. Return on net assets, % (item 3 / item 1) |
1,99 |
2,00 |
0,12 |
106,1 |
Table data 3 allow us to see that in the reporting year there is a slowdown in net asset turnover by 32 days, which is caused by a more significant reduction in revenue from product sales (by 23.4%) compared to the reduction in the average annual value of net assets (by 9%). Return on net assets remained virtually unchanged. However, noteworthy is the extremely low value of this indicator - 2% in the reporting year. This means that for every ruble of its own funds the enterprise received only 2 kopecks. net profit. Summarizing all these facts, we can talk about insufficiently efficient use of the organization’s own capital.
To summarize, it should be noted that the article examines a rather narrow issue, devoted to the analysis of just one, although very important for assessing the financial condition of an organization, indicator. However, such a study revealed a number of problems that require more in-depth study.
In general, conducting an in-depth analysis of net assets allows us to identify ways to increase them (improving the structure of assets; choosing and using optimal methods for valuing inventories, calculating depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets; sale or liquidation of property not used in the activities of the enterprise; increasing sales volumes by improving product quality, searching for new markets for its sales, and optimizing pricing policy; implementation of effective control over the status of inventories, accounts receivable and payable, other assets and liabilities of the organization). Based on this, there are opportunities to increase the financial stability and solvency of an economic entity, its investment attractiveness.
T.A. Pozhidaeva, Ph.D. econ. Sciences, Associate Professor Department of Economic Analysis and Audit, Voronezh State University
The financial condition of the company is assessed, among other things, by the amount of net assets. Since this is the value of all property minus creditor obligations. The article contains a formula for calculating net assets in 2018 based on the 2017 balance sheet with examples.
Net assets in 2018: general provisions
Every day the company uses objects in its ownership for circulation. For example, buildings, offices, land, money, etc. These are the assets of the organization. But this is only a small part of the financial component, because companies often have obligations: credits, borrowings, debts to partners. Therefore, it is important to know what the company’s NAV value is.
Net assets (NA) - This own funds, which will remain with the company after settlements with all creditors. Therefore, this indicator is often used to fully assess the financial well-being of an organization. Also, the value of net assets may be needed in other cases.
Scheme. When is it necessary to calculate a company's net assets?
Formula and procedure for calculating net assets in 2018
The value of the company's NAV is determined based on the balance sheet indicators. This procedure was officially approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated August 28, 2014 No. 84n, according to which the following must be included in the calculation of net assets in 2018:
– non-current assets: fixed assets, intangible assets, work in progress, etc.;
– current assets: inventories, VAT on acquired assets, money;
– short-term obligations on loans and borrowings;
– long-term obligations on loans and borrowings;
- accounts payable;
– other assets from sections IV and V of the balance sheet form.
The calculation of the NAV for LLC and JSC is the same; use the formula for this:
NA = KR – DZ + DBP,
where NA is net assets,
KR – Capital and reserves (line 1300 of the balance sheet),
DZ – receivables from participants for deposits and authorized capital (on page 1230 of the balance sheet only the amount of debt of participants (founders) to the authorized capital is the debit balance of account 75 “Settlements with founders”, subaccount “Settlements for contributions to the authorized capital”),
DBP – deferred income (line 1530 – credit balance account 98 “Deferred income”).
An example of calculating net assets on a balance sheet
The chief accountant of Alliance LLC uses balance sheet indicators to calculate net assets. At the end of 2017 balance total amount assets is equal to:
– long-term liabilities – 35 million rubles;
– short-term liabilities – 15 million rubles;
– future income – 500 thousand rubles.
The value of the LLC's net assets will be 15,500,000 rubles (35,000,000 – 15,000,000 – 5,000,000 + 500,000).
Valuation and ways to increase net assets
The financial well-being of a company directly depends on investments, as well as the correct expenditure of assets to pay off liabilities. Therefore, it is necessary to assess its solvency. To do this, compare the NA indicators with the volume of status capital. Then, based on the final data, analyze the identified changes.
The main thing in the assessment is to understand how much is the difference between the solvency and creditworthiness of the organization. Moreover, the second indicator is the company’s ability to meet all its obligations. For example, pay taxes and fees, loans, as well as amounts of debt for the supply of goods.
Tax inspectors also assess the company's NA. They can put it on the “black list” if the net assets are less than the main ones material assets. Since the meager amount of net assets is a consequence of large financial losses. This means that tax authorities will be interested in what the losses are associated with and may call the director to a commission for explanatory measures. Their goal is for the company to increase its net assets, otherwise it will go bankrupt or be liquidated. The results of the assessment may be as follows.
Net assets are equal to the authorized capital. The company is at risk if the assessment results turn out to be so. After all, if a participant leaves the organization, then all debt to him will be written off by reducing the authorized capital. This means that the share of remaining participants will not increase.
Net assets are less than authorized capital. If the assessment shows such a result, then urgently take measures to increase the NAV or reduce the authorized capital. There are different methods, you can find them below in the article.
Let's look at an example when the NAV is less than the authorized capital. Our set value is 600 thousand rubles, this is the value of the NAV at the end of 2017. Therefore, measures should be taken to reduce the authorized capital. Previously it was 800 thousand rubles, now lower the bar to 600 thousand rubles. For this:
– make changes to the charter of the enterprise. In this case, the share of each of the resigning participants will decrease. Therefore, amendments to the charter will protect against claims.
– reduce the amount of the authorized capital by the amount of payment of the withdrawing participant, having previously carried out a calculation. For example, there are 6 participants, the payment per exit is 120 thousand rubles. As a result, the capital will be equal to 680,000 rubles (800,000 - 120,000).
Net assets are greater than the authorized capital. In this case, the company has nothing to fear. The only thing is that when a participant leaves, he needs to be given a payment based on the difference between the cost of the private equity and the authorized capital.
Let's look at an example. The LLC has 5 participants, authorized capital – 500 thousand rubles, net assets – 650 thousand rubles. Let's determine the size of the share of each exiting participant: 130,000 rubles. (650,000 / 5 people). Then we calculate the difference between the NAV and the authorized capital: 150,000 rubles. (650,000 - 500,000). The share of each participant is 130 thousand rubles, which is less than the difference in assets – 150 thousand rubles. Then, if one of the participants leaves, the share of the remaining participants will increase from 100 thousand rubles to 125 thousand rubles (500,000 /5 people and 500,000 /4 people).
Ways to increase net assets in 2018
Companies themselves choose how to increase the value of their NA. But on the list legal ways, the following are listed:
– revaluation of fixed assets;
– free receipt of property from founders or shareholders;
– contributions to property from shareholders;
– capitalization of surpluses based on inventory results in accounting.
How to create and check a balance sheet
Let us tell you the algorithm of actions using the example of BukhSoft Online.
1. We generate transactions for all operations: Operations log, “Fill” button. We fill out the transaction log for the entire period of work.
2. Then you need to close the accounts sequentially for each month (determine financial results). Next, year-end closing transactions are generated. Click “Fill” in the Operation Log. After this, you need to check the correctness of the reflection of data in the accounting register: Journal of Operations/Reports/By Analytics - The debit and credit balances should be the same, accounts 90, 91, 99 should not have a balance at the end of the year. If one of the points is not fulfilled, you need to check the correctness of record keeping.
3. In the “Reporting Preparation” module, select the desired year. Then, in the “Balance” section, select reporting.

Select the desired period and click "Fill". The program will fill out reports based on Accounting data. The file itself can be viewed, saved or printed in the Ready reports tab.


Let's consider the concept, calculation formula and economic meaning of the company's net assets.
Net assets
Net assets (EnglishNetAssets) – reflect the real value of the enterprise’s property. Net assets are calculated by joint stock companies, limited liability companies, state-owned enterprises and supervisory authorities. The change in net assets allows us to estimate financial condition enterprises, solvency and level of bankruptcy risk. The methodology for assessing net assets is regulated by legislation and serves as a tool for diagnosing the risk of bankruptcy of companies.
What is net asset value? Calculation formula
The assets include non-current and current assets with the exception of the debt of the founders for contributions to authorized capital and costs of repurchasing own shares. Liabilities include short-term and long-term liabilities excluding deferred income. The calculation formula is as follows:
NA – the value of the enterprise’s net assets;
A1 – non-current assets of the enterprise;
A2 – current assets;
ZU – debts of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital;
ZBA – costs of repurchase of own shares;
P2 – long-term liabilities
P3 – short-term liabilities;
DBP – deferred income.
Example of calculating the net asset value of a business in Excel
Let's consider an example of calculating the value of net assets for the organization OJSC Gazprom. To estimate the net asset value it is necessary to obtain financial statements from the company's official website. The figure below highlights the balance sheet lines necessary to estimate the value of net assets; the data is presented for the period from the 1st quarter of 2013 to the 3rd quarter of 2014 (as a rule, the assessment of net assets is carried out annually). The formula for calculating net assets in Excel is as follows:
Net assets=C3-(C6+C9-C8) 
Video lesson: “Calculation of net assets”
Net asset analysis is carried out in the following tasks:
- Assessment of the financial condition and solvency of the company (see → “ “).
- Comparison of net assets with authorized capital.
Solvency assessment
Solvency is the ability of an enterprise to pay for its obligations on time and in full. To assess solvency, firstly, a comparison is made of the amount of net assets with the size of the authorized capital and, secondly, an assessment of the trend of change. The figure below shows the dynamics of changes in net assets by quarter.

Analysis of the dynamics of changes in net assets
Solvency and creditworthiness should be distinguished, since creditworthiness shows the ability of an enterprise to pay off its obligations using the most liquid types of assets (see →). Whereas solvency reflects the ability to repay debts both with the help of the most liquid assets and those that are slowly sold: machines, equipment, buildings, etc. As a result, this may affect the sustainability of the long-term development of the entire enterprise as a whole.
Based on an analysis of the nature of changes in net assets, the level of financial condition is assessed. The table below shows the relationship between the trend in net assets and the level of financial health.
Comparison of net assets with authorized capital
In addition to the dynamic assessment, the amount of net assets for an OJSC is compared with the size of the authorized capital. This allows you to assess the risk of bankruptcy of the enterprise (see →). This comparison criterion is defined in the law of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation ( clause 4 art. 99 Civil Code of the Russian Federation; clause 4 art. 35 of the Law on joint stock companies ). Failure to comply with this ratio will result in liquidation judicial procedure of this enterprise. The figure below shows the ratio of net assets and authorized capital. The net assets of OJSC Gazprom exceed the authorized capital, which eliminates the risk of bankruptcy of the enterprise in court.
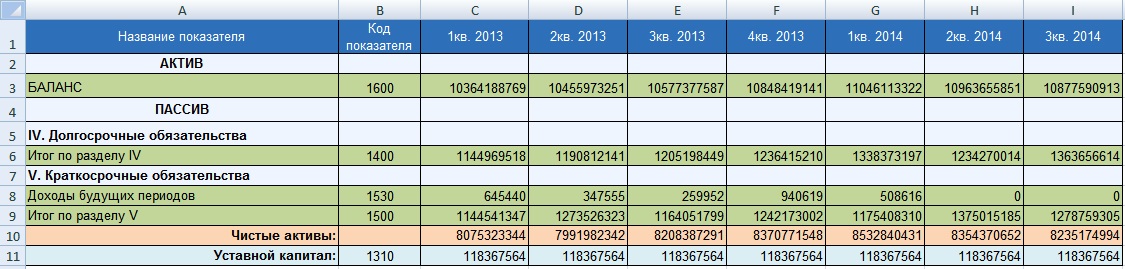
Net assets and net profit
Net assets are also analyzed with other economic and financial indicators of the organization. So the dynamics of growth of net assets is compared with the dynamics of changes in sales revenue and. Sales revenue is an indicator reflecting the efficiency of an enterprise's sales and production systems. Net profit is the most important indicator of the profitability of a business; it is through it that the assets of the enterprise are primarily financed. As can be seen from the figure below, net profit decreased in 2014, which in turn affected the value of net assets and financial condition.

Analysis of net asset growth rate and international credit rating
In the scientific work of Zhdanov I.Yu. shows the presence of a close connection between the rate of change in the net assets of the enterprise and the value of international credit rating agencies such as Moody's, S&P and Fitch. A decrease in the economic growth rate of net assets leads to a decrease in the credit rating. This in turn leads to a decrease in the investment attractiveness of enterprises for strategic investors.

Summary
Net asset value is an important indicator of the amount of real property of an enterprise. Analysis of the dynamics of changes in this indicator allows us to assess the financial condition and solvency. The value of net assets is used in regulated regulatory documents and legislative acts to diagnose the risk of bankruptcy of companies. A decrease in the growth rate of an enterprise's net assets leads to a decrease not only in financial stability, but also in the level of investment attractiveness. Subscribe to the express mailing list financial analysis enterprises.
In the article we will determine what property, material and monetary values an economic entity can be classified as a net asset. We will provide a calculation formula and tell you how to analyze and improve the indicators.
General concepts
Successful business is impossible without detailed analysis financial and economic indicators of economic activity of an economic entity. To evaluate property and financial position organization and make the right management decisions in a timely manner, it is necessary to determine important solvency and profitability ratios. One of the key calculation indicators is the calculation of the value of net assets on the balance sheet.
The organization's net assets (NA) are the amount of funds of an economic entity, determined by calculation, which will remain at the disposal of the company after full repayment debt obligations. In other words, the value of net assets is calculated as the arithmetic difference between the total indicators of the company’s property, material and financial assets and assumed liabilities.
Note that calculating the value of net assets on the balance sheet is mandatory for organizations. The indicator is calculated once a year based on accounting data. Indicators are reflected in the third section of the report on changes (movements) of capital; net assets are (in the balance sheet) line 360 of this reporting form.
Formula for calculating net assets
The key procedure for calculating the value of net assets on the balance sheet is determined by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and is presented in a separate order No. 84n dated August 28, 2014. Please note that previously a different procedure was in effect, but it is not currently used.
This formula for net assets on the balance sheet is applicable to the following range of economic entities:
- public or non-public joint stock companies;
- state or municipal unitary enterprises;
- limited liability companies;
- production cooperatives or housing cooperatives;
- business partnerships.
Net assets formula:
NA = (JSC - DU - ZA) - (OB - DBP),
- JSC - the sum of non-current and working capital economic entity as of the reporting date;
- DE - debt of the founder incurred to the enterprise for the formation of the authorized capital;
- FOR - debt on own shares, formed during release;
- OB - the sum of the company's short-term and long-term liabilities;
- DBP - deferred income in the form of government financial support or gratuitous transfer property values.
NA = (line 1600 - DU) - (line 1400 + line 1500 - DBP).
Calculating the amount of net assets in the balance sheet (the lines indicated above) using a pencil calculator is not enough. This calculation must be documented. However, a unified form for reflecting calculated data is not provided for in Order No. 84n. Organizations are required to independently develop a form and regulate it in their accounting policies.
Note that before the approval of Order No. 84n, the old form was in force ( Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 10 and the Federal Commission for the Securities Market of Russia dated January 29, 2003 No. 03-6/pz). In the new instructions, the Russian Ministry of Finance has not prohibited the use of this form, therefore, firms can use it to prepare calculations of net assets in the balance sheet (the document lines contain all the necessary information).
How to calculate net assets on a balance sheet, example
Vesna LLC prepared annual financial statements, including a balance sheet in the OKUD form 0710001.


Based on the balance sheet data, the following calculations were made:
NA = (13,800 +19,283 - 0) - (12,930 - 0) = 20,153 rubles.
Analysis of indicators
Having completed the arithmetic calculations, we move on to analyzing the result obtained. With a positive amount of net assets in the balance sheet, we can conclude that the company is profitable and has high solvency. And, accordingly, the higher the indicator, the more profitable the enterprise.
Negative net assets are an indicator of the low solvency of an enterprise. In other words, a company with a negative NAV will most likely go bankrupt soon; the company will simply have nothing to pay off its debts. However, in such a situation, exceptional circumstances must be taken into account. For example, a company has just been formed and has not yet covered its costs, or the company has received big loan for expansion.
An increase in net assets can be achieved by increasing the authorized, reserve or additional capital or by reducing the founder’s debts to the enterprise.