Net assets: formula. Net assets: formula Indicative asset for financiers 8 letters
Let's consider the concept, calculation formula and economic meaning of the company's net assets.
Net assets
Net assets (EnglishNetAssets) – reflect the real value of the enterprise’s property. Net assets are calculated by joint stock companies, limited liability companies, state-owned enterprises and supervisory authorities. The change in net assets allows you to assess the financial condition of the enterprise, solvency and level of bankruptcy risk. The methodology for assessing net assets is regulated by legislation and serves as a tool for diagnosing the risk of bankruptcy of companies.
What is net asset value? Calculation formula
The assets include non-current and current assets, with the exception of the debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital and redemption costs own shares. Liabilities include short-term and long-term liabilities excluding deferred income. The calculation formula is as follows:
NA – the value of the enterprise’s net assets;
A1 – non-current assets of the enterprise;
A2 – current assets;
ZU – debts of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital;
ZBA – costs of repurchase of own shares;
P2 – long-term liabilities
P3 – short-term liabilities;
DBP – deferred income.
Example of calculating the net asset value of a business in Excel
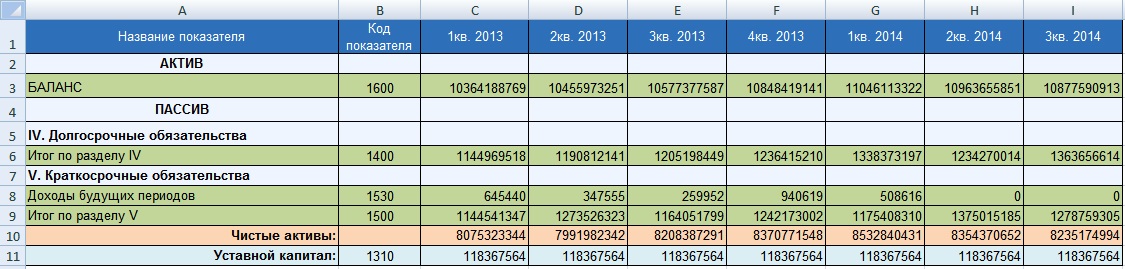
Let's consider an example of calculating the value of net assets for the organization OJSC Gazprom. To estimate the value of net assets, it is necessary to obtain financial statements from the official website of the company. The figure below highlights the balance sheet lines necessary to estimate the value of net assets; the data is presented for the period from the 1st quarter of 2013 to the 3rd quarter of 2014 (as a rule, the assessment of net assets is carried out annually). The formula for calculating net assets in Excel is as follows:
Net assets=C3-(C6+C9-C8) 
Video lesson: “Calculation of net assets”
Net asset analysis is carried out in the following tasks:
- Assessment of the financial condition and solvency of the company (see → “ “).
- Comparison of net assets with authorized capital.
Solvency assessment
Solvency is the ability of an enterprise to pay for its obligations on time and in full. To assess solvency, firstly, a comparison of the amount of net assets with the size authorized capital and secondly, assessing the trend of change. The figure below shows the dynamics of changes in net assets by quarter.

Analysis of the dynamics of changes in net assets
Solvency and creditworthiness should be distinguished, since creditworthiness shows the ability of an enterprise to pay off its obligations using the most liquid types of assets (see →). Whereas solvency reflects the ability to repay debts both with the help of the most liquid assets and those that are slowly sold: machines, equipment, buildings, etc. As a result, this may affect the sustainability of the long-term development of the entire enterprise as a whole.
Based on the analysis of the nature of changes in net assets, the level of financial condition is assessed. The table below shows the relationship between the trend in net assets and the level of financial health.
Comparison of net assets with authorized capital
In addition to the dynamic assessment, the amount of net assets for an OJSC is compared with the size of the authorized capital. This allows you to assess the risk of bankruptcy of the enterprise (see →). This comparison criterion is defined in the law of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation ( clause 4 art. 99 Civil Code of the Russian Federation; clause 4 art. 35 of the Law on joint stock companies ). Failure to comply with this ratio will result in liquidation judicial procedure of this enterprise. The figure below shows the ratio of net assets and authorized capital. The net assets of OJSC Gazprom exceed the authorized capital, which eliminates the risk of bankruptcy of the enterprise in court.
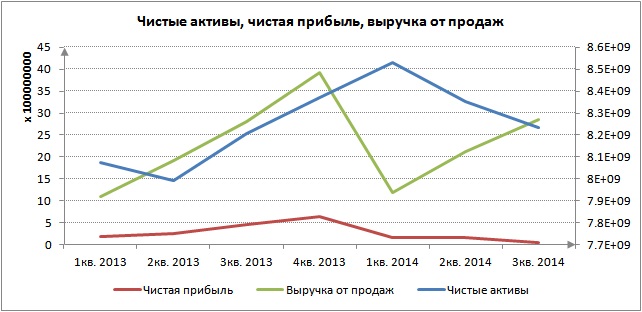
Net assets and net profit
Net assets are also analyzed with other economic and financial indicators of the organization. So the dynamics of growth of net assets is compared with the dynamics of changes in sales revenue and. Sales revenue is an indicator reflecting the efficiency of an enterprise's sales and production systems. Net profit is the most important indicator of the profitability of a business; it is through it that the assets of the enterprise are primarily financed. As can be seen from the figure below, net profit decreased in 2014, which in turn affected the value of net assets and financial condition.
Analysis of net asset growth rate and international credit rating
In the scientific work of Zhdanov I.Yu. shows the presence of a close connection between the rate of change in the net assets of the enterprise and the value of international credit rating agencies such as Moody's, S&P and Fitch. A decrease in the economic growth rate of net assets leads to a decrease in the credit rating. This in turn leads to a decrease investment attractiveness enterprises for strategic investors.

Summary
Net asset value is an important indicator of the amount of real property of an enterprise. Analysis of the dynamics of changes in this indicator allows us to assess the financial condition and solvency. The amount of net assets is used in regulated regulatory documents And legislative acts to diagnose the risk of bankruptcy of companies. A decrease in the growth rate of an enterprise’s net assets leads to a decrease not only financial stability, but also the level of investment attractiveness. Subscribe to the express mailing list financial analysis enterprises.
The calculation of net assets on the balance sheet is carried out in accordance with the requirements of Order No. 84n dated August 28, 2014. The procedure must be applied by JSCs, LLCs, municipal/state unitary enterprises, cooperatives (industrial and housing) and business partnerships. Let us consider in detail what the term net assets means, what significance this indicator has for assessing the financial condition of a company and what algorithm is used to calculate it.
What determines the size of net assets on the balance sheet
Net assets (NA) include those funds that will remain in the ownership of the enterprise after the repayment of all current liabilities. Defined as the difference between the value of assets (inventory, intangible assets, cash and investments, etc.) and debts (to contractors, personnel, budget and off-budget funds, banks, etc.) with the necessary adjustments.
The calculation of the value of net assets on the balance sheet is carried out based on the results of the reporting period (calendar year) in order to obtain reliable information about the financial condition of the company, analyze and plan further operating principles, pay dividends received or actually evaluate the business in connection with a partial/full sale.
When determination of net assets is required:
- When filling out annual reports.
- When a participant leaves the company.
- At the request of interested parties - creditors, investors, owners.
- In case of increasing the amount of the authorized capital due to property contributions.
- When issuing dividends.
Conclusion - NAV is the net assets of the company formed due to equity and not burdened with any obligations.
Net assets - formula
To determine the indicator, the calculation includes assets, except for the receivables of the participants/founders of the organization, and liabilities from the liabilities section, with the exception of those deferred income that arose due to the receipt of government assistance or donated property.
General calculation formula:
NA = ( Fixed assets + Current assets– Debt of the founders – Debt of shareholders in connection with the repurchase of shares) – (Long-term liabilities + Short-term liabilities – Income attributable to future periods)
NA = (line 1600 – ZU) – (line 1400 + line 1500 – DBP)
Note! The value of net assets (the formula for the balance sheet is given above) requires, when calculating, to exclude objects accepted for off-balance sheet accounting in the secondary storage accounts, BSO, reserve funds and etc.
Net assets - calculation formula for the 2016 balance sheet
The calculation must be drawn up in an understandable form using a self-developed form, which is approved by the manager. It is allowed to use the previously valid document for determining the NA (Order No. 10n of the Ministry of Finance). This form contains all required lines to be filled out.
How to calculate net assets on a balance sheet - shortened formula
The value of net assets on the balance sheet - the 2016 formula can be determined by another, new method, which is contained in Order No. 84n:
NA = Capital/reserves (line 1300) + DBP (line 1530) – Debts of the founders
Analysis and control
The size of Net Assets (NA) is one of the main economic and investment indicators of the performance of any enterprise. The success, stability and reliability of a business is characterized by positive values. A negative value shows the unprofitability of the company, possible insolvency in the near future, and probable risks of bankruptcy.
Based on the results of settlement actions, the value of net assets is estimated over time, which should not be less than the amount of the authorized capital (AC) of the company. If the reduction does occur, according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, the enterprise is obliged to reduce its capital and officially register the changes made in Unified register(Law No. 14-FZ, Article 20, paragraph 3). The exception is newly created organizations operating for the first year. If the size of net assets is less than the size of the capital, the enterprise may be forcibly liquidated by decision of the Federal Tax Service.
Additionally, there is a relationship between the value of the NAV and the payment of required dividends to participants/shareholders. If, after accrual of income/dividends, the value of net assets decreases to a critical level, it is necessary to reduce the amount of accruals to the founders or completely cancel the operation until the normatively designated ratios are achieved. You can increase the NAV by revaluing the property resources of the enterprise (PBU 6/01), receiving property assistance from the founders of the company, taking an inventory of obligations in terms of terms limitation period and other practical methods.
Net asset value on balance sheet – line
The organization's financial statements contain all the indicators required for mathematical calculations, expressed in monetary equivalent. In this case, data is taken at the end of the reporting period. When it is necessary to determine the value for another date, interim reports should be prepared at the end of the quarter/month or half-year.
Attention! The amount of net assets is also displayed on page 3600 of Form 3 (Statement of Changes in Capital). If a negative value is obtained, the indicator is enclosed in parentheses.
A). The standard establishes a maximum ratio between short-term assets (short-term receivables for loans provided by the cooperative) repaid within twelve months after current date and the amount of obligations of the cooperative (for the personal savings of shareholders transferred to the cooperative, their loans attracted from shareholders and persons who are not shareholders of the cooperative), the due date of which falls on the next twelve months.
The standard is calculated using the formula:
FN8 = SDT/SDO * 100%
- MDT – the amount of monetary claims of a credit cooperative, the payment period for which occurs within 12 months after the reporting date.
- SDO – amount monetary obligations credit cooperative, the repayment period for which occurs within 12 months after the reporting date.
B). The minimum acceptable value of the FN8 standard for credit cooperatives whose period of activity is 180 days or more from the date of their creation is set at:
- 30 percent – until June 30, 2016 inclusive;
- 40 percent – from July 1, 2016;
- 60 percent – from January 1, 2017;
- 75 percent – from January 1, 2018.
For credit cooperatives whose period of activity is less than 180 days from the date of their establishment, the minimum acceptable value of the financial standard FN8 is set at 50%.
5.2.2. Economic meaning of the standard
In its economic meaning, the financial standard FN8 is similar to the general liquidity indicator, which regulates the risk of loss of liquidity over the next twelve months. The standard characterizes the cooperative's ability to cover its short-term obligations using current assets. The current assets of a credit cooperative are represented by accounts receivable for loans provided to shareholders and second-level cooperatives, and the bulk of liabilities are formed from personal savings transferred by shareholders and loans raised from shareholders - legal entities and persons who are not shareholders of the cooperative. Therefore, the standard actually regulates the relationship between funds receivable and obligations due within the next twelve months.
The financial standard is being implemented over two years with a consistent tightening of the share of short-term assets in liabilities. If in the first half of 2016 it is assumed that only 30% of the obligations on funds attracted by the cooperative, the repayment period of which falls in the next year, will be fulfilled through loans repaid by shareholders, then by January 1, 2018 this share should already be 75%. In this way, the level of liquidity of the cooperative will be consistently increased in relation to obligations on raised funds. This does not mean that the structure of receivables and liabilities for borrowed funds will shift to the short-term segment. Along with short- and medium-term lending, the cooperative can also develop the practice of long-term lending, while motivating shareholders to transfer savings and loans for a long term.
5.2.3. Initial data and procedure for calculating the FN8 standard.
The amount of receivables for loans provided by the cooperative, repayable within 12 months after the reporting date, available to the cooperative Money determined by account indicators:
The amount of liabilities for borrowed funds repaid within 12 months after the reporting date is determined according to the account indicators:
- 66.1 “Short-term loans”;
- 66.3 “Short-term loans”.
Not all assets can be repaid on time; some of them are formed from problem debts, the repayment of which was delayed. In accordance with the Directive of the Bank of Russia dated July 14, 2014 N 3322-U, the cooperative forms a reserve for such debt for possible losses on loans. In order to adequately assess the liquidity resources of the Cooperative, it is advisable to take into account, along with obligations maturing within the next 12 months, the amount of the reserve formed by the cooperative for possible loan losses in successively increasing shares, as provided for in clause 9 of Directive No. 3322-U.
The amount of the reserve formed by the cooperative for possible losses on loans is reflected in account 59 “Provisions for the depreciation of financial investments.”
The ratio between the amount of monetary claims and obligations of a credit cooperative due within the next 12 months is calculated using the following formula:
FN8 = ∑(account.58.3;account.58.2)/∑(account.66.1;account.66.2;account.63(account.59)) * 100% ≥30%;40%;60%;75%;50%
To assess the FN8 standard in the system of accounts accounting in the NFO introduced from January 1, 2018, along with the previously described accounts, the following accounts can be used:
- Account 48501 “Loans issued legal entities»;
- Account 48510 “Provisions for impairment of loans issued to legal entities”;
- Account 48601 “Loans issued to legal entities”;
- Account 48610 “Provisions for impairment of loans issued to legal entities”;
- Account 48701 “Microloans (including targeted microloans) issued to legal entities”;
- Account 48710 “Provisions for impairment of loans issued to legal entities”;
- Account 48801 “Microloans (including targeted microloans) issued to individuals”;
- Account 48810 “Provisions for impairment of loans issued to individuals”;
- Account 49301 “Loans issued to individual entrepreneurs”;
- Account 49310 “Provisions for impairment of loans issued to individual entrepreneurs”;
- Account 49401 “Microloans (including targeted microloans) issued to individual entrepreneurs”;
- Account 49410 “Provisions for impairment of microloans (including targeted microloans) issued to individual entrepreneurs”;
- Account 49501 “Loans issued to a second-level credit consumer cooperative”;
- Account 49510 “Provisions for impairment of loans issued to a second-level credit consumer cooperative”;
- Account 42316 “Raised funds individuals»;
- Account 43708 “Raised funds from non-state financial organizations”;
- Account 43808 “Raised funds from non-state commercial organizations”;
- Account 43908 “Raised funds from non-governmental non-profit organizations”;
- Account 50104 “Debt securities Russian Federation»;
- Account 50105 “Debt securities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local governments.”
5.2.4. Reporting indicators in the format established by Bank of Russia guidelines No. 3357-U, which monitor compliance with the FN8 standard, which regulates the relationship between short-term claims and short-term liabilities
To assess compliance with the FN8 standard, the following reporting indicators are used:
From the summary form “Activity Report”:
- Page 1.1.1 " Accounts receivable for loans provided to shareholders to individuals (the repayment period of which is expected within one year after the reporting date).”
- Page 1.1.2. “Accounts receivable for loans provided to shareholders to legal entities (the repayment period of which is expected within one year after the reporting date).”
- Page 1.1.3. “Receivables for loans granted to second-tier credit cooperatives (expected to mature within one year after the reporting date).”
- Page 3.1.1.1. “Raised funds from shareholders - individuals for a period of up to one year.”
- Page 3.1.2.1. “Raised funds from shareholders - individuals for a period of up to one year.”
- Page 3.1.3. “Raised funds from persons who are not shareholders of the cooperative.”
The standard is calculated from the following ratio of indicators of the consolidated reporting form “Activity Report”:
FN8 = ∑ reporting activity line 1.1.1; line 1.1.2; line 1.1.3/∑ reporting activity line 3.1.1.1; line 3.1.2.2; line 3.1.3 * 100%
When generating reports, the cooperative can independently check compliance with the standard on the “Standards” sheet. If the FN8 standard is not met in the parameters set for the corresponding date of the transition period, an “error” code will be displayed in the “Checking compliance with the FN8 standard” column. If the ratio of short-term assets and liabilities is maintained at a normal level, the “norm” code is displayed.