Lending principles briefly. Basic principles of credit
Principles of credit represent requirements for the organization credit process. IN modern conditions Bank lending is carried out in strict compliance with the principles of lending, therefore, in order to receive a loan, you should clearly understand its basic principles.
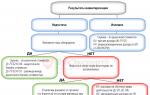
Basic principles of credit:
- 1) repayment and maturity of the loan;
- 2) loan differentiation;
- 3) loan security;
- 4) payment of the loan;
- 5) targeted nature of the loan.
Let's take a closer look at each of the principles that, in essence, form the basis of lending.
The principle of repayment and urgency of the loan.
Repayment is the feature that distinguishes credit as an economic category from other economic categories of commodity-money relations. This principle of credit means that without repayment, a loan cannot exist, therefore repayment is an integral part of the loan, its attribute.
Principle repayment and urgency loan is due to the fact that banks mobilize temporarily free funds of enterprises, institutions and the population for lending. These funds do not belong to banks, and, ultimately, they come to the bank from various market segments and go to them. main feature such funds is that they are subject to return to the owners who invested them in the bank on the terms time deposits. Magnitude and timing financial requirements the bank must correspond to the size and timing of its obligations.
Urgency of lending is a necessary form of achieving loan repayment. Urgent loan must be returned strictly certain period. Urgency is the temporary certainty of loan repayment. The loan term is the maximum time the loaned funds will remain in the borrower’s household and is the measure beyond which quantitative changes over time turn into qualitative ones. If the loan term is violated, the essence of the loan is distorted and it loses its true purpose.
Violation fundamental principle loan leads to bank bankruptcy.
The principle of credit differentiation.
The principle of differentiation lending determines a differentiated approach on the part of the credit institution to various categories of potential borrowers.
Differentiation means a different approach to lending different categories borrowers. That is, commercial banks should not take an unambiguous approach to the issue of issuing a loan to their clients applying for it. For example, a loan can only be provided to those who are able to repay it on time, so differentiation of lending must be carried out based on an analysis of creditworthiness.
The practical implementation of this principle of credit may depend both on the individual interests of a particular bank, and on the centralized policy pursued by the state to support certain industries or areas of activity (for example, small businesses, etc.).
The principle of credit also determines an individual approach to individual borrowers within one bank. Those. Today, the principle of credit differentiation is being further developed in the consumer lending segment.
The principle of loan security.
The principle of loan security closes one of the main credit risks- risk of non-repayment of the loan. If this principle were not taken into account, then banking would turn into a speculative activity, where the high risk of conducting transactions would lead to sharp growth interest rates.
Security loan reflects the need to ensure the protection of the lender’s property interests in the event that the borrower violates its obligations. That is, through the implementation of this principle, one of the main credit risks is “closed” - the risk of non-repayment of the loan. The loan can be secured by collateral, guarantee, surety, insurance policy, etc. If this principle were not taken into account, bank lending could turn into a speculative activity, the high risks of which could lead to a sharp rise in interest rates.
The size and types of collateral depend on financial situation borrower, loan terms, relationship with the borrower.
Considerable attention is paid to this principle of credit.
Current legislation provides that one of the ways to ensure bank loans is collateral. By virtue of the pledge, the creditor (bank) has the right, in the event of failure of the debtor to fulfill the obligation secured by the pledge, to receive satisfaction from the value of the pledged property, preferentially before other creditors. Satisfaction of the demands of a commercial bank from the value of the pledged property is carried out by decision of the court or arbitration (commercial court).
The creation of a deposit insurance system in Russia has not yet led to an increase in growth rates bank deposits. Nevertheless, this increased the reliability of banks.
Institute credit bureaus not yet fully developed. However, without such a tool credit risks for consumer loans will be extremely high. Without knowledge about credit history borrowers, banks issue loans almost blindly, guided only by scoring procedures that work on information provided by the borrower himself and not confirmed by an independent source.
According to the principle of loan security, banks can accept any property of the borrower as collateral, including buildings, material values, securities, foreign currency etc.
Only property free from collateral that is owned by the borrower or belongs to him with full right is accepted as collateral. economic management. Goods accepted by the bank as collateral must be insured at the expense of the borrower.
The principle of loan repayment.
The principle of payment for a loan means that loan recipients pay a certain fee for the temporary use of funds for their needs, which is practically carried out through the mechanism of bank interest. The bank interest rate is, in essence, the “price” of the loan.
The principle of repayment of the loan ensures that the bank covers its costs associated with the payment of interest on other people's funds attracted into deposits, the costs of maintaining its apparatus, and also ensures the receipt of profit to increase the lending resource funds and use them for its own needs.
The principle of targeted use of credit.
This principle of credit applies to the vast majority of credit transactions. This principle of credit expresses the need for the targeted use of funds received on credit.
Thus, the borrower must use the loan for specific purposes - this is a strict condition.
For example, a loan received to buy a car should not be used to pay off rent debt.
The bank's credit department monitors compliance with this principle by conducting subsequent checks targeted spending funds.
introduction 3
1. Basic principles of lending 4
2.Main forms of credit 8
2.1 Commercial loan 8
2.2 Bank loan 9
2.3 Consumer credit 10
2.4 State credit 11
2.5 International credit 11
Conclusion 13
References 14
INTRODUCTION
Credit(Latin сreditum - loan) - an economic transaction in which one partner provides the other with funds or property on the terms of urgency, repayment and payment.
Nowadays, credit is of great importance. It solves problems facing the entire economic system. Thus, with the help of a loan, it is possible to overcome the difficulties associated with the fact that temporarily free funds are released in one area, while the need for them arises in others. With the help of a loan, inventory items, various types of machines, mechanisms are purchased, and goods are purchased by the population on an installment plan.
This topic is relevant because credit relations in modern conditions have reached their greatest development. Currently, there is an expansion of the subjects of credit relations, as well as an increase in the variety of operations themselves. The relevance of lending for credit institutions today is obvious. Every year it becomes more and more developed and widespread. It is no coincidence that a bank is called a credit institution. From year to year credit organizations develop and implement new credit programs.
Undoubtedly, these events can be called turning points for Russian market banking services and the banking system as a whole.
The purpose of this work is to consider the basic principles and forms of lending.
1. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF LENDING
Credit relations in the economy are based on a certain methodological basis, one of the elements of which is the principles that are strictly observed in the practical organization of any operation on the market loan capital. These principles spontaneously emerged at the first stage of credit development, and were later directly reflected in national and international credit legislation:
The basic principles of lending include:
Loan repayment
Urgency of lending;
Differentiation of lending;
Loan security;
Repayment of bank loans.
Let's look at each of the principles.
1. Repayment is the feature that distinguishes credit as an economic category from other economic categories of commodity-money relations. Without repayment, a loan cannot exist, therefore repayment is an integral part of the loan, its attribute.
The repayment and urgency of lending is due to the fact that banks mobilize temporarily free funds of enterprises, institutions and the population for lending. These funds do not belong to banks, and, ultimately, they, having come to the bank from various market segments, go to them (consumer, commercial lending, etc.). The main feature of such funds is that they are subject to return to the owners who invested them in the bank on the terms of time deposits. The main basic banking rule states: “the size and timing of the bank’s financial requirements must correspond to the size and timing of its obligations.” Violation of this fundamental principle leads to bank bankruptcy.
2. Urgency of lending - is a necessary form of achieving loan repayment. The principle of urgency means that the loan must be repaid within a strictly defined period. And, therefore, urgency is the temporary certainty of the repayment of the loan. The loan term is the maximum time for the loaned funds to remain in the borrower's household; in case of violation of this condition, it is a sufficient basis for the lender to apply economic sanctions to the borrower in the form of an increase in the interest charged, and in the event of a further postponement of the presentation of financial claims in court. A partial exception to this rule are so-called on-call loans. (Call loans are loans subject to repayment within a fixed period after receipt of official notification from the lender. Currently, they are practically not used not only in Russia, but also in most other countries, since they require relatively stable conditions in the loan capital market and in the economy as a whole).
3. Differentiation of lending means that commercial banks should not have a clear approach to the issue of issuing a loan to their clients applying for it. The loan should be provided only to those entities that are able to repay it in a timely manner. Therefore, differentiation of lending should be carried out on the basis of lending indicators, which mean the financial condition of the enterprise, which gives confidence in the ability and willingness of the borrower to repay the loan within the period stipulated by the contract. These qualities of potential borrowers are assessed by analyzing their balance sheet for liquidity and economic security own sources, level of profitability at the moment and in the future.
The degree of creditworthiness (or level of creditworthiness) of a client is an indicator of the individual or private credit risk for the bank associated with a specific client, a specific loan issued to the client.
4. Loan security covers one of the main credit risks - the risk of non-repayment of the loan. If this principle were not taken into account, banking would turn into a speculative activity, where the high risk of transactions would lead to a sharp rise in interest rates.
It should be noted that the solution to the problem of loan security depends on the type of lending and on the subject of the loan. If speak about big company, which has been successfully operating for decades, has a good and long credit history, occupies a leading position in the market, headed by well-known professionals, then resolving the issue of securing loans requires one approach.
If we consider the issue of issuing a loan for a small enterprise that has just registered and is starting its entrepreneurial activity from scratch, then it is impossible to issue a loan without resolving the issue of collateral.
5. Payment of bank loans is the payment by loan recipients of a certain fee for the temporary use of funds for their needs. The implementation of this principle in practice is carried out through the mechanism of bank interest. The bank interest rate is a kind of “price” of the loan. The repayment of the loan is intended to have a stimulating effect on the commercial settlement of enterprises, encouraging them to increase own resources and economical use of raised funds. For the bank, the repayment of the loan ensures that it covers its costs associated with the payment of interest on other people’s funds attracted into deposits, the costs of maintaining its apparatus, the costs of covering inflation, and also ensures the receipt of profit to increase the lending resource funds (reserve, authorized) and use them for its own and other needs.
When considering the size of the loan fee, banks take into account the following factors:
refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
average interest rate (the rate of attraction of interbank loans or the rate paid by the bank on deposits various types);
structure of credit resources (the higher the share of borrowed funds, the more expensive the loan should be);
demand for credit from potential borrowers (the lower the demand, the cheaper the loan);
the period for which the loan is requested, the type of loan, or rather the degree of its risk for the bank, depending on the collateral;
stability of monetary circulation in the country (the higher the inflation rate, the more expensive the loan fee should be, since the bank has an increased risk of losing its resources due to the depreciation of money).
The combined application of all principles in practice bank lending allows to observe both macroeconomic interests and interests at the micro level of both subjects credit transaction- bank and borrower.
2. BASIC FORMS OF CREDIT
Loans are classified according to various basic characteristics. Depending on the composition of the participants, the object of the loan, the interest rate and the scope of operation, five independent forms of credit are distinguished.
2.1 Commercial loan
A commercial loan is a loan provided by operating business entities to each other when selling goods on an installment plan. This is one of the earliest forms of credit relations. It is based on the delay by the seller company of payment for the goods and the provision by the buyer company of a bill as its debt obligation to pay the purchase price after a certain period. The two most common types of bills are: simple, containing the borrower's obligation to pay a certain amount directly to the lender, and translated(draft) - a written order from the lender to the borrower to pay a specified amount to a third party or to the bearer of the bill. A commercial loan is the basis of the credit system; it directly serves the movement of capital in the sphere of production. This credit is possible only between firms directly connected by economic relations (only those enterprises that create means of production and those firms that consume them).
A commercial loan has certain disadvantages:
size limitation reserve capital loan.
Sale by installments is possible if the lender has surplus capital;
dependence on the conditions of its return inflow. When production declines, loans are not repaid and the chain of credit connections is disrupted and its size is reduced;
a strictly defined direction, i.e. provided by one enterprise to another associated with the first technological chain (for example, a leather production plant provides a commercial loan to a shoe factory).:
In practice, the following varieties are used
with a return after the actual sale of goods received on credit;
By open account when a secondary supply of goods on the terms of a commercial loan is carried out to repay the debt on the previous delivery.
2.2. Bank loan
Bank credit is credit provided by banks and other monetary entities to borrowers in the form of cash advances. In the modern economy, this is the most common form of credit relations. It is banks that most often provide loans to business entities that temporarily need financial assistance.
Bank loans are classified according to different criteria.
By maturity:
short-term – usually up to 6 months to compensate for a temporary shortage of own working capital;
medium-term – for a period from six months to one year;
long-term – over a year (in some countries – over three to five years)
By repayment method:
a loan repaid by the borrower in a lump sum payment;
a loan repayable in installments over the entire term of the loan agreement.
By security:
trust loans, the only form of security for which is a loan agreement;
secured loans that are protected by the borrower’s property (real estate, securities);
a loan secured by a financial guarantee from third parties.
agricultural loans for agricultural production, usually seasonal in nature;
commercial loans to operating entities in the field of trade and services;
mortgage loans secured by real estate;
interbank loans that are provided by credit institutions to each other.
2.3. Consumer loan
Consumer loans are issued to individuals when purchasing, primarily consumer durable goods. Consumer credit is used for targeted lending to individuals in commodity or monetary forms. It is implemented either in the form of the sale of goods with deferred payment through retail stores, or in the form of a bank loan for consumer purposes. As a rule, high interest rates are charged for using a consumer loan.
Abroad, this form of credit has become very widespread and is used by all segments of the population through the system credit cards points. In Russia consumer loan began to develop in the form of lending to citizens secured by real estate or selling some goods in installments (for example, apartments).
2.4. State loan
State credit is a system of credit relations in which the state acts as a borrower, and the population and private business act as lenders. Money.
Distinctive feature state loan– participation in credit relations of the state represented by its authorities at various levels as a lender or borrower. As a creditor, the state, through the central bank or treasury system, provides lending:
1) priority industries, regional or local bodies in need of financial resources when budget financing from commercial banks is impossible due to market factors;
2) commercial banks and other credit institutions in the process of direct or auction sale of credit resources on the interbank loan market. As a borrower, the government places government loans through banks or on the government short-term securities market. The reason for the growth of such credit is the budget deficit, associated mainly with unproductive military and administrative expenses. This is the main form of government credit. In world practice, government loans are used not only to attract financial resources, but also as an effective tool for centralized credit regulation.
2.5. International loan
International credit is the movement of loan capital in the sphere of international economic relations. International credit is the latest form of development, when economic relations went beyond national boundaries. The loan operates on international level, its participants can be individual legal entities, state governments, as well as international financial and credit institutions (International Monetary Fund, World Bank, European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, etc.). This loan is classified according to several basic criteria:
by type - on commodity provided by exporters upon deferment for goods or services, and foreign exchange in cash;
by appointment - commercial related to foreign trade, financial– direct investment, repayment of external debt, foreign exchange interventions;
by loan currency - in the currency of the debtor country, creditor country, third country and in the international monetary unit.
in terms of security - protected (trade documents, real estate, securities etc.) and blank– against the obligations of the debtor (solo bill with one signature).
In the country's economy, international credit plays a dual role: positive - stimulating the acceleration of the development of production forces, expansion of the production process, foreign economic activity, and negative - exacerbating the contradictions of the market economy, forcing the overproduction of goods, increasing imbalances in social reproduction and competition for markets, areas of capital investment and sources of raw materials.
CONCLUSION
Credit can have an active impact on the volume and structure of the money supply, payment turnover, and the speed of circulation of money. By bringing to life various forms of credit money, it can ensure, during Russia’s transition to a market, the creation of a basis for the accelerated development of non-cash payments and the introduction of new methods. All this will help save distribution costs and increase the efficiency of social reproduction in general.
Thanks to credit, there is a faster process of capitalization of profits, and, consequently, concentration of production.
By regulating borrowers' access to the loan capital market, providing government guarantees, etc. benefits, the state directs banks to provide preferential lending to those enterprises and industries whose activities correspond to the objectives of implementing national socio-economic development programs. The state can use the loan to stimulate capital investment, housing construction, export of goods, and development of backward regions.
The importance of credit is manifested in the performance of its functions, principles, as well as in the implementation of all forms (commercial, banking, consumer, international, government).
LIST OF REFERENCES USED
"Banking". Edited by O.I. Lavrushin. – M.: Finance and Statistics, 2003.
"Money. Credit. Banks."
Edited by O.I. Lavrushin. - M.: Finance and Statistics, 2003.
“Money, credit, banks” E. F. Zhukov. – M.: UNITY, 1999. "Well economic theory
" Tutorial. / Ed. prof. Chepurina M.N., prof.
Kiseleva E.A. – Kirov: Publishing house “ASA”, 2001.
5. Credit / Russian Banking Encyclopedia / Moscow, Lavrushin O. I. 1996. 6. “International monetary, credit and financial relations” L. N. Krasavina, 2000. 7. “Finance.
Money turnover
Refund means that the funds must be returned. Economic basis repayment is the circulation of funds and their mandatory availability by the loan repayment deadline. Actually, a loan is like economic category This is what makes it different from other categories of commodity-money relations, in that here the movement of money occurs on the terms of repayment. Repayment is a necessary feature of a loan.
The principle of urgency of lending means that the loan must not only be repaid, but returned within a strictly defined period. The urgency of lending is the necessary standard for achieving loan repayment. Fixed time lending is the maximum time the borrowed funds will remain with the borrower. If the term of use of the loan is violated, then the essence of the loan is distorted and it loses its true purpose. The practice of long-term violation of the principle of urgency in lending to enterprises and individual industries has a negative impact on the state of money circulation in the country.
It must be emphasized that in market conditions In management, the principle of urgency acquires special significance. The normal provision of social reproduction with money depends on its observance. Its compliance is necessary to ensure the liquidity of commercial banks themselves. The principle of organizing their work mainly on borrowed resources does not allow them to invest these attracted credit resources into irrevocable investments. In addition, compliance with the principle of repaying the loan on time allows the borrower to obtain new loans from the bank and not pay increased interest for overdue loans. The terms of the loan are set by the bank taking into account the turnover time of the material assets being financed and the recoupment of costs.
Differentiation of lending means that commercial banks should not have the same approach to resolving the issue of issuing money to clients applying for a loan. Banks strive to provide loans only to those clients who are able to repay them on time. For these purposes, the bank, based on creditworthiness indicators, determines the financial condition of the enterprise in order to be confident in the borrower’s ability to repay the loan within the period stipulated by the agreement. The bank evaluates the enterprise's balance sheet for liquidity, the enterprise's availability of its own sources, its level of profitability and development prospects. By carrying out such preliminary work, the bank insures itself against the risks of untimely repayment of the loan.
Security as a lending principle means that the borrower's property, valuables or real estate allow the lender to be confident that the loan will be repaid on time. This principle presupposes the actual collateral of loans provided to the borrower by various types of property or obligations of the parties. To ensure timely repayment of the loan, creditors under the agreement assign a pledge, surety or guarantee, as well as obligations in other forms accepted in practice.
When giving a loan against collateral, the lender checks to what extent the pledged property meets the requirements, in particular, whether its liquidity is ensured. The liquidity of such assets refers to the ability of assets to quickly turn into money.
As for the size of loans based on property, it is set as a percentage of market value collateral at the time of concluding the loan agreement. As a rule, the price of the collateral slightly exceeds the loan amount, which is necessary to compensate for the risk of loss, damage, changes in property prices, etc. If the borrower turns out to be insolvent, the lender has the right to sell the collateral to compensate for internal funds borrower's debt and sales costs. In this case, the remaining proceeds are returned to the borrower.
Methods for repaying loans are important. The most common type of loan is a loan against inventories, since they are the most reliable collateral for a loan. The loan can be secured by goods and material assets, travel documents indicating the imminent delivery of certain goods, movable and immovable property, precious metals and etc.
When issuing large loans, real estate is accepted as collateral. Secured loans real estate are called mortgage loans. As collateral for mortgage loans for enterprises of various forms of ownership are land and agricultural buildings and premises. For individual borrowers, residential buildings and apartments can serve as collateral for mortgage loans. The loan size is usually 50-90% of the value of the property. As for movable property, the collateral can be equipment, inventory, machinery, vehicles, and for individuals- durable items, including cars.
The principle of payment for a loan means that the borrower must pay the bank a certain fee for temporarily borrowing money from him. In practice, this principle is implemented through the mechanism of bank interest.
Bank interest represents the fee received by the lender from the borrower for the use of borrowed funds. It is determined by the size of the loan, its term and the level of the interest rate. Payment of interest in terms of market economy is nothing more than the transfer of profit received by the borrower to his lender. The natural requirement of the creditor for payment for borrowed funds is determined by the fact that he transfers part of his capital to the debtor, thus losing the opportunity to receive during the validity of the credit transaction own profit. A loan at its final stage is a return of value, and interest is an increment to the loan. Loan interest, therefore, is a kind of loan price that guarantees the rational use of the loaned value and the preservation of the mass of credit resources. At the same time, the repayment of the loan should have a stimulating effect on the economic calculations of enterprises, encouraging them to increase their own resources and spend economically own funds.
Magnitude loan interest depends on the demand for credit from business owners. The lower the demand, the cheaper the loan. If the value is also determined base rate interest on loans provided commercial banks Central Bank, as well as the average interest rate on an interbank loan, i.e. for resources purchased from other commercial banks for their active operations.
The amount of loan interest depends on the average interest rate paid by the bank to its clients on deposit accounts of various types, on the structure of the bank’s credit resources (the higher the share of borrowed funds, the more expensive the loan).
The loan interest rate, as a rule, is higher, the longer the loan term. This is explained by the fact that an increase in the loan term is associated with an increase in the risk of non-repayment due to changes in economic conditions or financial condition borrower.
Loans that are not sufficiently secured by property or the obligations of a guarantor (third party) are also more expensive than secured loans. Loans issued to borrowers to eliminate financial difficulties have an increased risk, and therefore the lender takes these circumstances into account when conducting interest rate policy.
When determining the price of their product - credit, lenders naturally take into account such factors as the stability of money circulation in the country, primarily the rate of inflation growth. Inflation increases the lender's risk. Therefore, the higher the inflation rate, the more expensive the loan fee should be, since the bank has an increased risk of losing its resources due to the depreciation of money.
The real value of the loan interest is established in practice taking into account the totality of all these factors and makes it possible to comply with both the national interests and the interests of both subjects of the credit transaction - the bank and the borrower.
More on the topic of Lending Principles:
- Principles of lending: repayment, urgency, payment, security, targeted and differentiated nature
- Functions and role of credit in economic development. Principles of lending.
- 34. Principles of lending and their implementation in the activities of credit institutions.
- Copyright - Advocacy - Administrative law - Administrative process - Antimonopoly and competition law - Arbitration (economic) process - Audit - Banking system - Banking law - Business - Accounting - Property law - State law and administration - Civil law and process - Monetary law circulation, finance and credit - Money - Diplomatic and consular law - Contract law - Housing law - Land law - Electoral law - Investment law - Information law - Enforcement proceedings - History of state and law -
The lending process is carried out according to certain principles. The following are distinguished: lending principles: repayment, urgency, payment, material security of the loan, as well as the principle of a targeted nature.
Repayment principle implies that financial resources received from the creditor are subject to repayment in full. When applying for a loan, the borrower becomes responsible to the lender regarding the completeness of the loan repayment. This principle of lending is expressed in practice by operations aimed at transferring a certain amount of financial resources to the account of the bank that provided them. The stable financial position of a business firm and its classification as a reliable borrower is a guarantee of loan repayment.
The principle of urgency implies the need to return loan funds exactly specified period, and not at any time that is convenient for the borrower. This means that the loan is provided for a certain period. The period for using credit funds depends on the duration of the need for them. The loan repayment period is stipulated in the loan agreement, but the payment terms can be either specific or conditional - determined during the lending process.
If there are financial capabilities and if the borrower wishes, the loan can be repaid earlier than the deadline stipulated in the agreement. Violation of the specified deadlines is a good reason for the lender to apply to the borrower loan penalties. A long delay in repaying a loan debt may serve as grounds for declaring the borrower as an insolvent client. At the same time, by agreement between the lender and the borrower, credit institutions may provide a deferment in loan repayment and extension of the loan transaction.
The principle of payment implies that a loan is issued to the borrower with the condition of returning it with interest, which is the profit of the credit institution. Therefore this lending principle expresses the need for the borrower not only to return the loan funds received from the bank, but also to pay a fee for their use. The interest rate is set in the form of annual rates or norms, while interest rates can be fixed or floating. Interest may be accrued monthly or quarterly. In the calculation process, either simple or compound interest is used. The amount and type of interest are determined in the agreement between the bank and the borrower. The amount of interest is influenced by a number of micro and macroeconomic factors.
The principle of material security of a loan implies the need to ensure the protection of the property interests of creditors in the event of a possible violation by the borrower of accepted obligations and in practice is used in such forms of lending as loans against financial guarantees or on bail. This principle of lending means that, in accordance with the terms of the loan, the borrower must guarantee the lender the return credit funds, and if this requirement is refused, the lender must have something on the basis of which he can remove illegally used funds from the borrower’s circulation. The loan may not have material collateral if the lender is fully confident in the commitment and solvency of the borrower.
The principle of the targeted nature of the loan concerns many credit operations and is expressed in the mandatory targeted use of financial resources that the borrower received from the lender. In practice, this principle of lending is expressed in the corresponding section loan agreement, which establishes the specific purpose of the loan provided. Violation of the obligation regarding the intended use of loan funds may be grounds for the introduction of increased loan interest or early revocation of the loan.
10. Forms of credit and their characteristics.
The basis of any credit relationship is methodological basis principles. It is the principles of credit that determine banking entity and product formation scheme. In this article we will talk about the basic principles of credit, their formation and functions.
The origin of the term “credit” has not yet been fully established. Some people are inclined to think that this word is derived from the Latin, meaning “he believes.” Others believe that it also comes from the Latin word "creditum", which means "loan, debt." In modern understanding, credit is the process of movement of loan funds. This term also refers to a loan that can be obtained both in the form of cash and certain goods. The principles of credit are fundamental provisions that determine its essence, functions, structure and form of implementation of relations. Understanding the scheme and principles of lending allows the consumer to understand the essence of this banking service.
To understand it, it is worth considering such aspects of credit as functions and principles. It is also important to understand how these provisions are implemented in practice. At its core, a loan is a certain type economic relations, which have two sides. This is the lender and the borrower.

Subjects can be both legal entities and individuals. Lenders are those people or organizations that transfer funds for temporary use at a certain percentage. Borrowers, receiving sum of money, undertake to return it on time, as well as pay off the interest established by the agreement.
More about the subjects
Today, lenders most often are banks and microfinance organizations. Of course, such relationships can also arise between individuals. The object in relation to which they interact is value in commodity or monetary form. It is they who are transferred to the borrower with subsequent repayment.

Not only monetary units, but also certain goods can act as credit funds. It is important that it is not perishable and has a certain value.
Main functions
There are three functions of loans:
- emission (substitution);
- distribution;
- control.
The substitution function comes first. Based on the loan, they are formed means of payment, the use of which allows you to achieve savings in handling costs monetary units. This feature arose due to the predominance non-cash form settlements between business entities, as well as between them and individuals who are not entrepreneurs.

When a person chooses to keep money in a bank, he enters into a credit relationship with this organization. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to carry out credit transactions using such a specific form as bank records. It is the latter that have become more efficient compared to the use of cash.
Peculiarities
Credit relations arise under certain conditions. The first is that the interests of the lender and the borrower must be the same. The second states that these persons must be independent subjects, endowed with all necessary rights and responsibilities.

That is, an incapacitated individual or a bankrupt company cannot receive a loan.
In order to receive a bank loan, the borrower is required to provide a package of documents, which consists of:
- loan applications;
- originals and copies of identity documents (for individuals) or constituent papers (for legal entities);
- documents confirming the borrower's permanent income;
- if there is security for the contract, also - papers that confirm its existence (for example, a contract for the sale and purchase of an apartment or a private house).
Credit relations do not develop in isolation. This is facilitated certain principles. Among them are:


Of course, there are other principles of credit. Among them, we can, for example, highlight the differentiated nature of these relationships. It implies that credit institutions use different approaches depending on the category to which the borrower belongs.
Loan agreement as a tool for implementing the principles
Regardless of where you take it borrowed funds(in a bank, microfinance organization or private person), in mandatory a contract is drawn up. It is this document that guarantees that both parties will fulfill their obligations.

A loan agreement is a written agreement between a borrower and a lender. It must include the following aspects:
- the size of the loan provided for temporary use;
- interest rate;
- terms and conditions of loan repayment;
- presence or absence collateral property, its characteristics;
- guarantees of the borrower's solvency.
As you can see, it is in these instruments that the lending principles described above are implemented.
Types of loans
Modern market banking services replete with offers.
Everyone can find a product that suits their needs. The most popular options are:
- consumer loans;
- credit cards;
- car loans;
- mortgage.
| Consumer loans | Credit cards | Car loans | Mortgage loans | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | From 15 thousand to 3 million rubles. | From 10 to 700 thousand rubles. | From 1 to 5 million rubles. | From 100 thousand to 15 million rubles. |
| Repayment terms | From 5 to 20 years depending on the loan size and other conditions | Up to 3 years | Up to 5 years | From 15 to 30 years |
| Advantages | A small amount of documents is required, the procedure is quick, and you can receive money in cash. | Eat Grace period, and there is no need to provide property as security. The application procedure is simple. A minimum package of documents is required for registration. | Loan interest rates are low. The amount here is significantly higher when compared with consumer loan. The application is reviewed in a short time. | Thanks to this tool you can get a significant amount of money long term at a small percentage. Some banks also provide the opportunity to attract co-borrowers. |
| Flaws | Interest rates are quite high and size limit small loan. Since such loans are issued for short period of time, monthly payment quite significant. The maximum borrower age is the lowest. | Interest rates are quite high, as well as late fees. There is a fee for withdrawing funds from an ATM. Also present annual fee for card servicing. | A significant package of documents is required for registration. The loan term is short, so the amount of monthly payments increases. | In order to receive such a loan, you need to provide a voluminous package of documents. Applications for such loans usually take a very long time to be processed. The security guarantee is always the property you are going to purchase with a mortgage. |
Thus, each type of bank lending has both advantages and disadvantages. To understand which type is right for you, you should decide on the purposes for which you are going to spend the borrowed funds. When studying loan terms, pay attention to interest rates, terms and repayment terms, as well as whether the loan is targeted.
Features of microloans
If you need small amount funds for a short period of time, you should pay attention to the services of microfinance organizations. It is worth immediately noting that only those organizations that have received a license in established by law ok. This service can be used by people who:
- are citizens of the Russian Federation;
- have reached the age of majority and are not over 65 years of age;
- have a permanent income.
This loan can be obtained online.

To do this, just go to the website of a certain microfinance organization, fill out an application and wait for a company representative to contact you. After this, you will need to provide scanned copies of your identification documents. The money will be credited to your card within a few hours.
When choosing between loans and microloans, you should start from the amount of money you need and for how long. If you need a little money just to survive until payday or to make a small purchase, then you should resort to microcredit.
If there is a need for a more significant amount, pay attention to target, as well as consumer bank loans. This is how you can get a large amount funds for a long term.
The popularity of lending services today is due to many factors. In particular, borrowers are attracted by the simplicity of the application procedure, which is typical, for example, for credit cards and microloans. Also, if necessary, make large purchase and if you do not have the required amount of funds for this, you can resort to bank lending.
Video. Lending principles