tax scale. Which tax scale is better
The essence of the progressive tax is simple and understandable even to a child. Small monthly incomes are taxed at a low rate, and higher ones at a high rate. As a result, the budget receives the same amount of taxes in total, but at the same time, the poor feel more comfortable, and they have additional funds for their own savings.
The progressive tax rate is valid in most countries of the world - in many European countries, the USA, Canada and even in China. By the way, the Chinese decided to make a giant indulgence for the poor. If an employee earns less than $9,000 a year, he will pay no income tax at all, which should help the poorest citizens. In addition, the Chinese are shifting the bar for more affluent citizens. You can read about this reform.
And if in general, then countries with a flat taxation scale, as in Russia, are still worth looking for. These are the countries of the former Soviet camp, the Baltic countries, Hungary, Romania, Ukraine, Mongolia, as well as other, mainly developing countries.
In Russia, talks about the introduction of a progressive rate are often conducted, but to no avail. The bills were put forward by the Liberal Democratic Party, Just Russia, but they were not even taken into consideration. The project of the Communist Party of the Russian Federation came closest to the goal - at least it got under consideration. However, later the State Duma also rejected it.
Why is this happening? I see five reasons for this.
1. The first is banal and, as they say, lies on the surface. It's just that the deputies themselves, receiving a higher salary (about 400 thousand rubles a month), will in any case fall under a higher tax rate. This fact cannot be ruled out, because they are the ones who make the decision to accept a progressive bet.
2. The second reason is not so obvious, but much more serious - these are those who form our white legal sector of the economy, which pays most of the funds to the budget. The point is this. At the moment, the lion's share of those employed in the economy are civil servants, state employees, security forces, military and employees of state enterprises. There is no exact figure as to how many there are. In 2013, Komsomolskaya Pravda counted 33.6 million of them, of which 22.5 million are employees of state-owned enterprises like Russian Railways or the Russian Post. The overwhelming majority, and these are millions of people, are sitting on low salaries of 15-20 thousand rubles. The state is their main employer, which does not benefit from increasing their salaries, since these are its expenses. But the important thing is that these salaries are white, and deductions from them go in full. In the meantime, almost all the remaining commerce works in gray or black, and pension contributions and personal income tax there are either paid at a minimum or not paid at all.
Thus, if the state introduces a progressive tax, or, even more so, a progressive rate of insurance premiums, it will lose most of its revenue, which is precisely formed by payments from low-earning state employees.
3. In those countries where the progressive tax rate works, the main tax burden falls on the shoulders of the rich. However, in these states, as a rule, there is low corruption, and the authorities can quite effectively deal with the shadow sector and non-payers. In our case, the introduction of a progressive tax is fraught with the fact that the rich will easily evade paying higher taxes to the detriment of the budget.
4. Some territories will become poorer. More affluent citizens, so to speak, are unevenly distributed across the territory of Russia. Basically, they all live in Moscow. In the meantime, income tax is paid to the budgets of the regions. If the rate is progressive, payments in some particularly poor areas of the country will drop significantly.
5. A progressive tax is harder to administer. The progressive rate will require citizens to independently account for and calculate taxes on income from various sources, regularly fill out and submit a tax return.
Let's take a simple example. We work and get paid. The accountant automatically enters all the data into the system, and tax is paid from us. With a progressive scale of taxation, the accountant cannot be sure that the amount he pays for any additional earnings, lecture fee or article will not go to the next degree of the scale. Therefore, any inconsistencies will have to be verified at the end of the tax year using a declaration. In many countries, this process is automated, and citizens submit declarations themselves by sending them over the Internet. But we do not yet have such an opportunity, and this may paralyze the work of tax inspections.
To date, the interest of most entrepreneurs is riveted to a proportional, regressive and progressive taxation system. There is constant debate about what is better and under what conditions you can pay less taxes. There are many supporters and opponents of the progressive personal income tax scale, so let's try to understand all the pros and cons of this system in comparison with the proportional taxation system. What is better?
Proportional formation of personal income tax
This system implies a single tax base for all. This means that regardless of income, a private entrepreneur will pay a fixed contribution of 13%. Accordingly, whether he is the director of the largest retail chain, who receives about 1 million rubles a month, or a loader with a salary of 10 thousand, he must pay the same percentage.
Of course, this system seems unfair to most public figures, because in this case it turns out that a person with a lower income is forced to pay the same as millionaires. Therefore, today there are more and more supporters of a different, progressive personal income tax scale. Is such a system really beneficial? Let's consider it in more detail.

Progressive personal income tax scale
If the proportional system implies a single rate for all businessmen, regardless of their income, then this scale implies changes in the amount of taxation for residents, depending on how much the business actually brings to its owner. Accordingly, the more a person earns, the more he must pay taxes.
However, it should be said that the progressive scale for personal income tax in 2017 is not yet accepted and available to taxpayers. To date, bill No. 1148107 is only under consideration. And if it is adopted, it will enter into force only in 2018, since now the country is still in an economic crisis, which does not allow immediately moving to a new level of taxation.
If compared with other countries, then, for example, in Sweden, the owner of a private business is completely exempt from taxes if his income is minimal. Only excess income (above the average wage) is taxed.

The progressive personal income tax scale, which may soon appear in Russia, works according to the same system. This means that if a resident earned 180 thousand rubles in a year, then the tax on this amount will be 0%. If the amount is from 180 thousand to 2.4 million rubles, then annually 13% will need to be paid to the treasury. With income up to 100 million rubles, you will have to pay 30% and so on, depending on the level of profit. The largest percentage, equal to 70%, will be paid by business owners who receive more than 100 million rubles every year.
It is also worth mentioning that a bill on a progressive personal income tax scale has already been adopted earlier and was in effect until 2001. Later, the President of Russia decided to switch to a "flat" taxation system, which meant a single percentage for all (13%). Perhaps this decision may seem like a "step back", but only thanks to this it was possible to increase the collection of taxes, which led to a faster recovery of the country from the crisis.
However, the possibility of introducing a more "fair" system of taxation is still questionable due to many factors. Therefore, we will consider the pros and cons of the progressive personal income tax scale that can be expected.
What do opponents of the new taxation system think?
If we discard the moral aspect, which concerns what is more fair when a person with a higher income pays more taxes, and we turn to dry facts.

The fact is that the introduction of a progressive personal income tax scale, although it can help equalize the social status of citizens, but at the same time it can lead to a decrease in real incomes that will be distributed by the population. Based on this, in order for "the rich to pay more", it will be necessary to significantly increase taxes for the middle class. Accordingly, this system may even lead to a lowering of the poverty threshold, since economic growth will be reduced.
If you impose heavy taxes exclusively on those entrepreneurs who earn a lot, then it will not work to collect the necessary profit to the treasury. This is due to the fact that most wealthy citizens use optimized schemes and withdraw their finances through offshore companies. Thus, there will be no choice but to raise taxes for individuals and force them to declare their income.
Benefits of a progressive tax system
If a proportional personal income tax scale is left in the country, this will lead to the fact that the poor will always get poorer, and the standard of living of the rich population will only increase.
Therefore, a progressive taxation system is the only possible tool to smooth out the existing differentiation. This opinion cannot be ignored, so there is a high probability that this system will still be adopted, as in many other countries.

In this case, with a minimum income, the owner of a small business will be exempt from taxes, which will help him grow faster. Thus, more firms will appear in the country, which will receive large incomes in the future, and, accordingly, more and more money will flow into the state treasury.
Today, most start-up businessmen are afraid to open organizations only because of the fear of high tax rates. If at first they do not have to pay interest, then the number of new individual entrepreneurs or LLCs will constantly grow.
Past experience
The proportional taxation system is nothing new. Before the transition to the "flat" personal income tax scale, the number of tax collections was much higher (about 54), after 2001, when a general income tax of 13% was introduced, there were only 15 of them left. Thus, with "fair" taxation, people had to pay more additional contributions. This was supposed to help the country's economy. However, most of the taxpayers hid their income and the treasury did not receive anything.

Initially, the idea of proportional taxation was that if the percentage is less, then it makes no sense for citizens to hide income. However, based on practice - it turned out the opposite. And only the "flat" personal income tax scale contributed to the way out of the crisis.
regressive system
This type of taxation has not found support in Russia. The essence of this system lies in the fact that an increase in the income of an entrepreneur leads to a decrease in tax rates. This type of personal income tax can lead to even greater social inequality, so it has few supporters.
However, there are those who propose to introduce a progressive-regressive personal income tax scale in order to smooth out the possible spread in the social statuses of citizens. But today we are not even talking about the appearance of this system in our country.
Finally
Of course, the proportional system of taxation looks like a way to equalize the social status of citizens. However, we must not forget that the general level of the economy also depends on this. Therefore, it will not be possible to introduce this personal income tax scale quickly.
The authorities have repeatedly proposed to introduce a progressive personal income tax scale. However, not a single bill has passed through the State Duma. And so, on March 17, another similar document was submitted.
In February, the State Duma rejected a bill on a progressive scale of personal income tax. Recall that the document kept the rate of 13 percent for profits up to 5 million rubles. But for large amounts, a progressive scale was provided: from 18 to 28 percent. And now, just a month later, another bill on the same topic was submitted to the Parliament. It provides for three rates - 13, 30 and 50 percent.
Hold your pocket wider
The bill extends a 13 percent personal income tax rate for incomes up to 400,000 rubles per month. With excess of this amount of earnings, you will have to pay already 30 percent. And with a monthly income of more than 1 million rubles - 50 percent.
“The bill introduced on March 17, 2015, in general, can be called the next in a series of similar ones. Indeed, the progressive scale of personal income taxation looks more fair. But we must not forget about the realities of our life,” notes Maxim Gladkikh-Rodionov, General Director of the audit company "Confidence". He believes that the an excessive burden on the wage fund (contributions) in our country already leads to shadow employment and other consequences that are not very pleasant for society and the state. Of course, the authors of the bill suggest an increase in the rate only for those whose income exceeds 400,000 rubles a month. Nevertheless, as follows from the explanatory note, there are almost 26.5 million such citizens in Russia. This is a lot. “The desire of deputies to help fill the budget is understandable. But such a sharp increase in rates, as can be assumed, will cause attempts to divert part of the income "into the shadows," continues Mr. Gladkikh-Rodionov.
Most of the experts interviewed by "Calculation" named the return to "envelope" salaries as one of the main disadvantages of the transition to a progressive personal income tax scale. “If these changes in the Tax Code are nevertheless adopted, we will very quickly see a revival of “envelope” salaries, and as a result, the budget will receive significantly less than what it would have received under the previously existing personal income tax rates,” notes Ekaterina Boldinova, senior lawyer of the law firm "YUST".
If these changes in the Tax Code are nevertheless adopted, we will very quickly see a revival of “envelope” salaries, and as a result, the budget will receive significantly less than what it would have received under the previously existing personal income tax rates ...
I agree with this conclusion and Valeria Arsenyeva, Dean of the Faculty of Economics, Doctor of Economics, Professor of the Department of Taxation and Accounting of the South Russian Institute of Management of the Russian Academy of National Economy and Public Administration under the President of the Russian Federation. She is confident that the innovations will not lead to an increase in budget revenues. “With such tax rates, only budgetary institutions will actually pay salaries officially,” Ms. Arsenyeva notes. The most effective, in her opinion, from the position of replenishing state revenues: to reduce and simultaneously increase personal income tax; the amount of tax received by the budget should be partly directed to compensate for the losses of off-budget funds from the reduction in insurance premiums. “When planning changes in terms of increasing tax exemptions, one should always keep in mind the Laffer model, according to which the tax exemption threshold is effective up to the level of 35 percent. Then the effect decreases down to 0,” she sums up.
“Obviously, at such rates, there is a sharp increase in the amount of tax at the junction of wage categories. At certain amounts of income, employees with a higher salary will actually receive less,” notes Julia Kulakova, Head of the Customer Support Department of the company "First BIT". In her opinion, if the amendments are adopted, tax revenues to the budget will increase. However, firms may face one difficulty: “If the employer wants to keep the actual income of employees, then he will have to increase the amount of wages. The amount of additional expenses will most likely be attributed to the cost of products / services, which may ultimately affect the buyer,” Ms. Kulakova notes.
PR project
Ariadna Denisova, President of the Association of professionals in the field of personnel motivation and organizational development , notes that the proposed version of the progressive scale is more of a PR initiative than a tool to increase budget revenues. “According to the faction of the Communist Party of the Russian Federation, which proposed this bill for consideration, the rate increase will only affect those who receive more than 400 thousand rubles a month. A similar level of salary is typical for top managers of large federal-scale companies (both in the capital and in the regions), as well as for middle-level managers of these organizations in Moscow and St. Petersburg,” notes Ms. Denisova. She recalls that, according to Rosstat, the average monthly accrued wages in the country in February 2015 amounted to 30,620 rubles. “Thus, the introduction of a progressive scale will only affect large businesses, which will eventually have to compensate for the loss of part of the income of employees by increasing their wages,” she notes. According to the expert, this, in turn, will hurt the crisis budgets of companies that are already “lined up” for state assistance. As a result, the treasury will not receive additional income, and "the taste of displeasure among the population will remain."
According to Maxim Gladkikh-Rodionov, a fairly large part of the taxpayers who will be affected by the amendments are employees of companies with state participation, that is, they receive income from the budget in one way or another, and if such a law is adopted, their salaries will most likely be indexed, which will lead to additional expenses and will reduce the expected effect. “I am sure that the MPs themselves, the authors of the bill, understand this. Otherwise, it would have been more carefully worked out. So, in my opinion, the authors do not count on its adoption,” the expert sums up.
The idea of increasing the tax burden on those who earn more is supported by many segments of the population, not realizing that richer people, paying the same tax rate as less well-off citizens, pay much more in absolute terms...
I agree that there is no chance that the deputies will adopt this document and Inna Alekseeva, CEO of the PR Partner agency: “It seems to me that now a progressive tax scale will not be accepted, since the country is in crisis, unemployment is growing. And if they accept, then for the SMB sector (medium and small businesses. - Note. ed.) this will mean leaving for black and gray wages, mass transfer of employees to individual entrepreneurs, for large businesses - transfer of business to offshore companies. According to her, the state, with the help of a progressive scale, solves the problem of replenishing the budget at the expense of entrepreneurs, but it is not certain that this is possible right now.
As the authors of the amendments note, the flat scale that exists in Russia does not meet the needs of economic and social development. However, repeatedly rejecting bills on a progressive tax, the State Duma just referred to the fact that it is the existing procedure for levying a tax that contributes to an increase in its collection, and not to abuses of hiding it. If we recall recent history, it shows that the transition to a flat personal income tax scale in 2001 contributed to the fact that business began to “come out of the shadows”. This has been repeatedly reported by officials.
“Given that such a tax scheme existed until 2001 and was replaced by the establishment of a single rate of 13 percent, returning to it again is unlikely to change the situation for the better. For such fundamental changes, a certain base developed by the state is needed (in particular, changes in other branches of law),” notes Anastasia Morgunova, Product Director of My Business. According to her, today the realities of the economic downturn serve as an additional reason for considering such bills. According to Ms. Morgunova, behind the positive aspects of such initiatives in the form of achieving social justice, there are also a lot of negative trends. In addition to the growth of gray wages, the expert also cites the following argument: the uneven filling of territorial budgets, in other words, regions with a high level of income among the population will become even richer.
Poor versus rich
It should be noted that the progressive personal income tax scale operates in more than twenty countries of the world.
Ekaterina Boldinova argues: “The system of progressive taxation in the USA, Germany, France, and most European countries is regulated in great detail. In our country, a progressive tax existed for some time during the Soviet period. Since the early 2000s, the idea of such a system has periodically been discussed by legislators, but usually the proposed projects are more populist in nature.
Director of recruiting agency TEHNOLOGOS Evgeny Chesnokov notes: "As a person with experience in combating major tax crimes, I believe that taxation should certainly be differentiated." Small businesses and middle-income people, he said, should pay less, and owners of luxury real estate and large businesses that control huge financial flows should be socially responsible. "Otherwise, it is fraught with an increase in social tension in society." As an example, the expert names Belgium, where a similar tax reaches almost 54 percent, Austria (up to 50 percent), Germany and Israel (up to 47 percent), China, France and Switzerland (up to 45 percent). “Only everything will be in vain if the implementation of these norms is not controlled. And it is possible to control all this, I can say this as a specialist,” the expert says. According to him, now the state is doing a lot of work to counteract "cashing out", respectively, this already affects gray incomes, and in this vein there is hope that the personal income tax novel will help stabilize the situation in society. “Previously, many bills affecting the interests of the elites were not passed, since our state is just coming out of its formation period, becoming more independent, the influence of the business elites is balanced by a strong bureaucracy and security forces,” sums up Mr. Chesnokov.
Boris Fedosimov, CEO of the People of Dela Holding notes that the progressive scale is formally aimed at increasing the tax burden on those who earn more. “This idea is supported by many segments of the population, not realizing that richer people paying the same tax rate as less wealthy citizens in absolute terms pay much more,” the expert notes. According to him, with the introduction of a progressive scale, higher-paid citizens, being more qualified and educated, will find loopholes to start avoiding increased taxation - up to a complete refusal to receive income in the territory of the Russian Federation. “It would be appropriate to recall Gerard Depardieu, who changed his French citizenship to Russian in order not to pay high income tax rates,” the expert gives an example. Also, according to Mr. Fedosimov, the costs of fiscal administration will increase, as there will be additional motivators, schemes for avoiding payment of dues.
One of the arguments in favor of introducing a progressive personal income tax scale, the project developers saw in helping to reduce social tension. “It seems that most of the population will be perceived positively. It won't relieve tension, but it will divert attention,” concludes Mr. Fedosimov. In addition, it is worth recalling the presidential address to the Federal Assembly of December 4, 2014. In it, the head of state promised not to revise the existing tax rates in the near future. “Another blow will be dealt to the investment attractiveness of the Russian Federation,” the expert sums up.
And finally, we recall that on March 13, a project to increase the personal income tax rate to 16 percent was also submitted to the State Duma. At the same time, it became known almost immediately that the Ministry of Finance spoke out against increasing the tax. “They used to offer 15 percent of personal income tax, now it’s 16. The main thing is that in 2017 they don’t offer 17,” RBC reports the words of the head of the Department of Tax and Customs Tariff Policy of the Ministry of Finance Ilya Trunin.
Veronika Pozdnyakova
, for the magazine "Calculation"
Read about everything useful for the work of an accountant in the professional accounting press!
The concept of progressive taxation
At the present stage of taxation in Russia, there is a unified system of tax collection. At the moment, the rate is 13% and it is charged to all citizens of any income level. Modern countries today use progressive taxation, with the help of a gradation of income levels, and on the basis of this they charge personal income tax. In order to determine the essence of a progressive tax, it is necessary to define its concept.
Definition 1
Progressive taxation. Progressive Taxation is a system of taxation that is designed to shift the bulk of the tax burden to high income taxpayers.
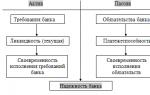
This taxation is used in almost all developed countries. However, the vast minority of countries still use fixed rates. The progressive tax scheme is shown in the figure below.
Figure 1. Scheme of a progressive tax. Author24 - online exchange of student papers
Remark 1
In Russia, at the present stage, a flat taxation scale is used. Residents of the country pay 13%, regardless of the level of income and the way it is received.
A single scale exists in the countries of Estonia, Georgia, Ukraine, etc. The progressive scale is used in European countries. One example is France, where there is an extremely progressive scale.
If a citizen has an income below 6,000 euros (which is a low income level), the tax is not charged at all. If the income exceeds 150 thousand or 1 million euros, a rate of 45% is charged. Above this amount, income is taxed at a rate of 75%. However, the authorities did not take into account that instead of covering the budget, these actions led to an outflow of capital from the country.
The rate also fluctuates in the UK from 14-45%. The highest rates were recorded in Sweden - 56.6%, Israel - 57 and the Netherlands - 52%. Developed countries boast low-income rates. For example, in the USA the rate is 10%, and in China 5%.
Pros and cons of progressive taxation
As mentioned above, in Russia they use a flat rate with a rate of 13%. For non-residents, a 35% rate is used. Nevertheless, the issue of introducing a progressive scale has been discussed more and more lately. The pluses include the following:
- replenishment of the budget deficit, however, individual examples with France suggest otherwise,
- stabilization of the regional budget. Recently, most of the taxes that were covered by the local budget began to be deducted to the state budget, which creates a deficit in the field. A progressive tax would fill this gap.
- social justice course. The single tax rate does not quite suit the population, which, on a level with millionaires, transfers 13% to the budget.
However, in addition to the pros, there are also disadvantages of progressive taxation:
- Large regional budgets will be enriched, while remote regions will become impoverished, since taxes are paid at the place of work.
- There will be a return to gray payroll schemes.
- Unemployment will rise against the backdrop of a lack of incentives to work.
- The need for citizens to independently report income with all administrative costs.
Progressive scale in Russia
Based on the possible pros and cons of the progressive scale, the deputies made a proposal:
- Set a rate of 13% for citizens whose income does not exceed 24 million for a period of 12 months.
- If income exceeds this mark, then a rate of 25% must be applied.
- If earnings amounted to 100-200 million per year, the rate should be 35%
- If the income exceeds the level of 200 million, then the rate will be 50%.
Until now, disputes over the introduction of a progressive tax do not stop. The deputies suggest that if this scale is introduced, all the profits of enterprises will be directed to development and modernization. On the other hand, it can lead to the development of a gray economy. In addition, wealthy citizens can register a company where taxation will not force them to give half and profits.
In order to understand whether Russia needs a progressive taxation system, it is necessary to build a scheme for the transition to this system, evaluate all the pros and cons. On the one hand, the positive aspects are obvious, on the other hand, they may simply not work in our country.
An analysis of various approaches has shown that today there is a need to develop a general methodology for assessing taxation, which would take into account all the necessary factors that affect the calculation of the level of taxation and the region's need for financial assistance from the higher budget for the implementation of activities aimed at socio-economic development .
At the present stage, the tax system is rapidly developing, there is an optimization of intergovernmental relations. The taxation system is a set of taxes and fees that are levied on taxpayers on the basis of the Tax Code. The necessity and importance of the tax system follows from the functional tasks of the state.
Remark 2
It should be noted that the effective implementation of the taxation system in the Russian Federation. This is rightfully considered the most important condition for the dynamic development of the Russian economy as a whole. Ensuring the consistent development of taxation contributes to the growth of the financial independence of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, which is a necessary condition for the subfederal authorities to fulfill their functions and tasks to provide the population with the necessary social, cultural, housing and communal services.
When introducing a progressive income tax, it is necessary to carefully calculate the gradation of interest and taxes, so that the middle class - small entrepreneurs and highly qualified specialists - does not suffer.